OBJECTIVES
1. A meal consisting of yam and a lot of vegetables is not balanced because it does not contain
A. minerals
B. proteins.
C. vitamins.
D. carbohydrates.
2. In a Biuret test, some protein was mixed with sodium hydroxide solution. Which of the following chemicals should be added to the mixture for a positive result?
A. Mercurous nitrate
B. Copper sulphate.
C. Sodium carbonate.
D, Silver nitrate.
3. The purpose of proteins in the diet of a mammal is to
A. promote growth and repair cells.
B. break down molecules
C. regulate the flow of chymie.
D. serve as co- factors for enzyme.
4. The appropriate food to be given to the child in the picture below is
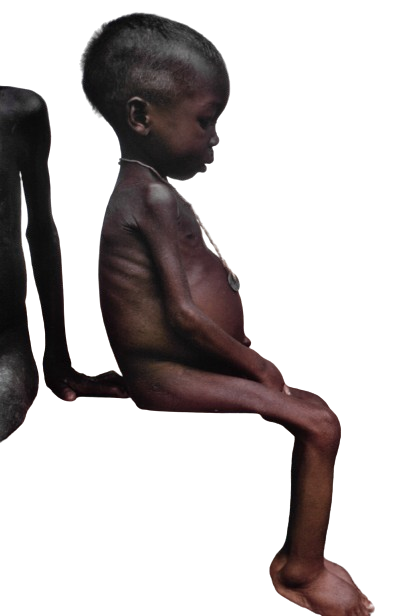
A. beans.
B. garri.
C. bread.
D. avocado pear.
5. Which of the following food substances will have little or no calorific value?
A. Proteins
B. Carbohydrates
C. Lipids.
D. Water.
Use this information to answer questions 6-8
A student used the following steps in testing for a non- reducing sugar: I. added Benedict’s solution to the sugar solution: II. added dilute hydrochloric acid to the sugar solution and boiled it; III. added sodium hydroxide solution to the solution in it and boiled: IV. added Benedict’s solution to the cooled solution in III.
6. Why did the student add the dilute hydrochloric acid to the sugar solution in step II? To
A. oxidize the sugar solution.
B. hydrolyze the sugar solution.
C. dry the sugar solution.
D. increase the volume of the sugar solution.
7. What is the importance of step II in the testing process? To
A. neutralize the sugar solution.
B. soften the sugar solution.
C. change the colour of the sugar solution.
D. increase the acid content of the sugar solution.
8. The colour change to be observed in step IV is
A. blue-black.
B. brick red.
C. purple.
D. violet.
9. Which of the following food substances gives the least amount of calories?
A. Rice
B. Groundnuts.
C. Cabbage.
D. Egg yolk.
10. The correct arrangement of food classes of the same quantity in the order of magnitude of energy value in animals in descending order is
A. Carbohydrates, fats and oils, water, protein.
B. Fats and oils, carbohydrates, protein, water,
C. Water, fats and oils, carbohydrates, protein.
D. Protein, fats and oils, water and carbohydrates.
11. Which of the following substances is not complex carbohydrate?
A. Glycogen.
B. Cellulose.
C. Starch.
D. Glucose.
12. Yeast is added to the dough during the preparation bread because it produces
A. ethanol.
B. heal.
C. carbodioxide.
D. carbohydrate.
13. Biuret’s test is carried out on a food substance to indicate the presence of
A. vitamins.
B. fats.
C. prote.
D. starch.
14. In a test for non-reducing sugars like sucrose, what is the significance of adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the original sugar solution? to
A. hydrolyze the non reducing sugar.
B. accelerate the rate of the reaction
C. stabilize the medium.
D. sterilize the solution
15. The colour that is associated with a positive lodine is
A. brown.
B. red.
C. blue-black.
D. yellow.
16. A man suffering from obesity must avoid meals containing
A. margarine and butter.
B. rice and bean
C. carrots and oranges
D. beef and fish.
17. In testing for starch in a leaf, the leaf is first boiled in water for about a minute so that the
A. cell walls are hardened.
B. cells are killed.
C. chlorophyll is dissolved out.
D. iodine will penetrate.
18. Use the following equations to answer this question
I. Boiled saliva + starch=>X II. Fresh saliva + starch=>Y.
What substances do X and Y represent?
A. X – Maltose and Y Sugar.
B. X – Starch and Y Maltose
C. X – Sugar and Y Starch.
D. X – Maltose and Y Starch
19. Which of the following groups of substances are notsix carbon compounds?
A. Glucose and laetpse
B. Lactose and cellulose.
C. Glucose, Lactose and Pyruvate
D. Pyruvate and cellulose
20. A purple colour was obtained when sodium hydroxide solution and a drop of copper sulphate solution were added to a food substance. The food substance is likely to be
A. carbohydrate.
B. fat.
C. protein.
D. sugar.
21. Excess carbohydrates can be stored in the muscles in the form of
A. cellulose,
B. glycogen.
C. chitin.
D. lip
22. The bones of the legs of a six years old boy are observed to be weak and crooked. Which of the
following elements were deficient in his mother’s diet at pregnancy?
A. Sodium and iron.
B. Iron and manganese.
C. Calcium and phosphorus.
D. Magnesium and sulphur.
23. In which of the following organic compounds is the hydrogen-oxygen ratio equal to 2:1?
A. Proteins
B. Carbohydrates.
C. Lipids.
D. Vitamins.
24. The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up to test the action of yeast. What test would be used to confirm the nature of the gas given off?

A. Insert a glowing splint.
B. Pass the gas through lime water
C. Insert a piece of litmus paper.
D. Smell the gas
25. A few drops of fehling’s solution was added to juice extracted from fresh maize grain and boiled. A red precipitate was formed, indicating the presence of
A. alcohol,
B. protein.
C. non-reducing sugar.
D. starch.
26. Which of the following mineral salts is a trace element?
A. Zinc.
B. Carbon.
C. Hydrogen.
D. Potassium,
27. Which of the following reagents is used for the test for starch?
A. Millon’s reagent.
B. Iodide
C. Sudan III.
D. Iodine solution.
28. Water in the human body is derived from the following sources except through
A. drinking water.
B. food substances.
C. cytoplasm of worn out cells.
D. absorption by the skin
29. The deficiency disease that results from the lack of vitamin B due to frequent eating of rice, is
A. rickets.
B. night blindness.
C. scurvy,
D. beri-beri.
30. When a food substance gives a purple colour on the addition of sodium hydroxide and a drop of copper sulphate, then the food substance is likely to contain
A. carbohydrates.
B. fat.
C. protein.
D. sugar.
31. Which of the following groups consists of only micro- nutrients?
A. Molybdenum, sulphur and copper.
B. Boron, Zinc and Calcium.
C. Manganese molybdenum and zinc.
D. Magnesium, phosphorus and manganese.
32. Using iodine solution, Biuret test, Benedict reagents and ethanol, respectively in testing for reducing
sugars, which of the following trends of colour changes would be observed?
A. Blue → black → blue → brown → clear.
B. Brown → blue → brick red → clear.
C. Brown → violet → blue → clear.
D. Brown → blue → violet → milky.
33. A very poor growth in plants and discolouration of leaves signifies the deficiency of
A. calcium.
B. magnesium.
C. potassium.
D. manganese
34. Vitamin C which is water soluble is
A. cabalamine.
B. pyridoxine.
C. ascorbic acid,
D. riboflavine.
35. Vitamin C deficiency results is
A. ricket.
B. beri-beri.
C. scurvy.
D. pellagra.
36. Members of the vitamin B complex are
A. water – soluble.
B. fat-soluble.
C. water insoluble.
D. generally insoluble.
37. Pellagra can be prevented by taking food rich in
A. vitamin A.
B. vitamin B.
C. vitamin D.
D. calcium.
38. Which of the following statements about phosphorous is not correct?
A. Helps to regulate the acid-base balance of the body.
B. regulates the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
C. Required in many chemical reactions occurring in the blood.
D. Phosphorous is a major constituent of bones and teeth.
39. In testing for a reducing sugar, the food substance is usually warmed with
A. Sulphuric acid.
B. Millon’s reagent.
C. Sudan III.
D. Benedicts’ solution.
40. Which of the following elements is required in large amounts by plants
A. Molybdenum
B. Boron
C. Copper.
D. Phosphorus
41. Vitamin E is concerned with
A. bone formation
B. reproduction
C. normal growth.
D. formation of red blood cells
42. Which of the following substances has the highest amount of energy in joules per unit weight
A. Carbohydrates.
B. Proteins.
C. Fats
D. Vitamins
43. A balanced meal for an adult person may consist of
A. two pieces of chicken, four balls of bean cake, two eggs and two cups of tea with milk.
B. four slices of bread, one bowl of pap, two oranges and two bananas.
C. four slices of yam and stew, two pieces of beef, one cup of tea with milk and two oranges.
D. a plate of beans, two pieces of meat, two eggs, one cup of tea with milk and two oranges.
44. Which of the following food substances turns bright red when warmed with Sudan Ill solution?
A. Starch.
B. Reducing sugar.
C. Proteins.
D. Fat.
45. Which of the following is not regarded as a micro- nutrient or trace element for plant growth?
A. Phosphorus.
B. Zinc.
C. Boron
D. Silicon.
46. Which of the following is a product of brewing when yeast is used as a fermenting agent?
A. Nitrogen
B. Oxygen.
C. Malt.
D. Ethanol.
47. In a water culturè experiment a plant showed poor growth and yellowing of the leaves. These symptoms were probably due to the absence of
A. calcium.
B. phosphorus.
C. iron.
D. zinc.
48. Mammals require a relatively high amount of carbohydrates because
A. they maintain the weight of the body.
B. they are required for growth.
C. they initiate enzyme production.
D. they yield energy for activities.
49. In which of these forms is carbohydrate stored in yam?
A. Glucose.
B. Maltose.
C. Starch.
D. Glycogen.
50. Excessive bleeding from an injury may be due to lack of vitamin
A. A.
B. B.
C. D.
D. K.
Use the diagram below to answer this questions 51-53.
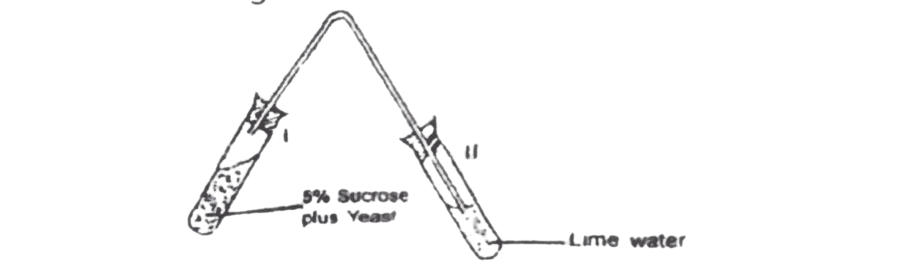
51. The set-up above is used to demonstrate
A. plasmolysis.
B. osmosis.
C. suction pressure.
D. fermentation
52. What will be the colour of the solution in the test tube labelled II at the end of the experiment?
A. Pink:
B. Yellow.
C. Milky.
D. Reddish white.
53. Which gas will pass into the test tube labelled II from I?
A. Carbon monoxide.
B. Carbon dioxide.
C. Oxygen.
D. Ammonia
54. In palm-wine, yeast acts as a
A. carrier.
B. culturing agent.
C. preservative.
D. catalyst.
55. When a mixture of a food substance and Benedict’s solution is warmed, the solution changes colour from blue to a brick-red precipitate. This test indicates the presence of
A. reducing sugars.
B. fatty acid.
C. sucrose.
D. amino acid.
56. Which of the following groups contains only macro- nutrients?
A. phosphorus, nitrogen and molybdenum.
B. manganese, copper and zinc.
C. boron, sulphur and iron
D. calcium, magnesium potassium
57. A solution which contains all the required elements in their correct proportions is known as a
A. culture nutrient.
B. growth medium
C. complete culture solution.
D. nutrient solution.
58. The deficiency of manganese in plants results in
A. death of shoot
B. leaves turning yellow
C. stunted growth.
D. poor root development.
59. The deficiency of vitamin D and calcium ions in the diet of a human causes
A. anaemia
B. night-blindness
C. kwashokor
D. rickets
60. Which of the following conditions is responsible for the presence of sugar in the blood of diabetic patients
A. High intake of carbohydrates.
B. Low production of insulin,
C. Low intake of carbohydrates.
D. High production of insulin
61. Which of the following is not a product of fermentation of glucose?
A. Energy.
B. Alcohol,
C. Lactic acid.
D. Carbon dioxide
Study the following list of deficiency symptoms in animals, use it to answer questions 62 to 64
I. Loss of appetite and weight. II. Delayed healing of wounds, III. Rickets, IV. Sterility in animals V. Failure of blood to clot: VI. Night blindness
62. Which of the following deficiencies is caused by lack of vitamin A?
A, I.
B. III.
C. V.
D. VI.
63 Which of the following vitamins would correct the deficiency numbered V?
A. Vitamin K.
B. Vitamin A.
C. Vitamin C.
D. Vitamin B
64. Which of the following combination of food substances would correct the deficiency numbered II?
A. Tomatoes, oranges and mangoes.
B. Yeast, liver and rice.
C. Red palm oil, carrot and egg yolk.
D. Green vegetables, butter and meat
65. The deficiency of calcium in a plant may result in
A. stunted growth and poor root development.
B. poor growth, leaves become orange or brown.
C. stunted growth, slender stem and yellowing of leaves.
D. very small leaves and yellowing of leaves.
66. Which of the following food substances would próduce a translucent mark when rubbed on a white paper
A. Potato.
B. Beans.
C. Mango.
D. Groundnut.
67. In testing for starch in a leaf the function of alcohol is to
A. kill the cells of the leaf.
B. soften the veins of the leaf.
C. aid iodine to penetrate the cells.
D, extract the chlorophyll from the leaf,
68. Which of the following contains a reducing sugar?
A. Milk
B. Cassava.
C. Grapefruit.
D. Beans.
69. Magnesium is needed by plants for
A. protein synthesis
B. formation of cell membrane
C. activation of enzymes
D. formation of chlorophyll
70. Which of the following is not a micronutrient
A. Manganese
B. Copper
C. Polapum.
D. Zine
71. In the test for starch, the leaf is first placed into water to
A. remove the chlorophyll
B. dissolve the waxy cuticle
C. kill and make the leave permeable
D. turn it blue-black
72. Which of the following statements about water in humans is not correct? It
A. plays an important role in temperature regulation
B. acts as solvents for substances conveyed around the body.
C plays a role in the formation of vitamin D.
D. is needed for many life processes.
73. Good quality food will perform the following functions in humans except
A. supplying energy
B. providing resistance against malaria.
C. sustaining growth.
D. maintaining health
74. Fresh milk is often kept in refrigerated vehicles, for distribution to customers in order to
A. ensure proper share of fresh milk to all customers.
B. ensure delivery of milk to customers in good time.
C. improve the quality of the milk.
D. ensure that the milk is preserved for a longer period
75. In water culture experiments, the culture solution are protected from sunlight in order to
A. control temperature of the culture solution.
B. prevent algae from growing in the solution.
C. prevent the minerals in the solution from being destroyed.
D. allow the minerals to be used up at room temperature.
76. The importance of a balanced diet is to
A. Maintain constant size of an animal.
B. provide good taste in the food.
C. increase the effectiveness of digestion
D. provide good health for an individual.
77. A urine sample of a patient, tested with Benedict/Fehling solution, gave an orange coloured precipitate, indicating the presence of
A. glucose.
B. sucrose,
C. lactose.
D. maltose.
78. Which of the following essential substances is contained in vegetables
A. Chlorophyll.
B. Glucose
C. Mineral salts.
D. Carbon dioxide.
79. Clotting of blood is a function of
A. vitamin C
B. vitamin K.
C. vitamin B.
D. vitamin E.
80. The major sources of vitamin A are
A. egg yolk, carrot and palm oil.
B. mango, pawpaw and eggs.
C. sorgum, soya bean and liver.
D. rice bran, green vegetables a milk.
81. The food substance that would produce the highest amount of energy is
A glucose.
B. fat
C. amino acid
D. protein.
THEORY
1. (a) Explain why an athlete in a race would be given a glucose drink rather than a piece of bread. (b) Outline the need for starch in a given food substance. (c) State five reasons why water is important in human diet.
2. State the deficiency symptoms of the following vitamins: (a) vitamin A (b) vitamin C (c) vitamin K
3. (a) Name one mineral element each needed for the proper functioning of (i) bones (ii) red blood cells (i) thyroid gland. (b) State three reasons why proteins are important to humans.
4. Outline the procedure used for testing for starch in a leaf.
5. (a) What is a balanced diet? (b) Name the classes of food stating the importance of any two to the human diet.
6. Describe how to test for protein in a food sample.
7. Define the term balanced diet
8. (a) List five classes of food other than carbohydrates (b) Explain why glucose is taken by an athlete ready for a race rather than corn meal (c) Describe the test for starch
9. What is the importance of water to living organisms?
10. (a) What is a balanced diet? (b) Name four classes of food other than protein (i) Giver one example of food substance for each class named (c) State three functions of proteins in humans (i) Describe the appearance of a child with protein deficiency.
11. The table below shows the percentage composition of fat and protein in six different meat types. Study it and answer questions (a) to (d)
| Meat Type | Fat(%) | Protein(%) |
| A | 07.2 | 21.3 |
| B | 25.3 | 10.6 |
| C | 20.0 | 22.5 |
| D | 03.1 | 28.2 |
| E | 12.6 | 17.3 |
| F | 13.2 | 14.3 |
(a) (1) Which two of the meat types may be recommended for an obese patient? (ii) State one reason for the answer in (a)(i). (b) (i) Which two of the meat types would provide the most energy? (i) State two reasons for the answer in (b)(i). (c) (i) Which three of the meat types could be recommended for a child suffering from kwashiorkor? (i) State one reason for the answer in (c)). (d) Which of the meat types would most likely be suitable for: (i) an active teenager; (ii) a 70-year old human? (e) Which other class of food provides energy? (f) State three uses of fat in the human body. (g) Describe briefly the procedure for testing for fat in a meat sample using a piece of white paper.
12. (a) (i) What is a deficiency disease? (i) Complete the table below by naming five nutrient deficiency diseases in humans and stating one remedy each for the diseases.
| Nutrient | Deficiency | Disease | Remedy |
(b) Outline a chemical test for: (i) starch in a tuber of yam; (ii) glucose in orange fruit.
13. (a) Complete the table below
| Element | Function in plants | Effects of deficiencies in plants |
| Iron | ||
| Molybdenum | ||
| Potassium | ||
| Copper | ||
| Nitrogen |
(b) Name three classes of organic foods which are essential constituents in the diet of a mammal.




I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme.
Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do
it for you? Plz reply ass I’m looking to construct my own blog andd would
like to find out where u got this from. aopreciate it https://evolution.org.ua
Опытные вебмастера используют раскрутка сайта хрумером, чтобы повысить видимость проекта.
Pro cenově dostupné řešení doporučujeme betonova stresni krytina roofer.cz, která představuje efektivní a estetickou volbu pro váš dům. Vhodná je především tam, kde je prioritou rychlá instalace.