OBJECTIVES
Study the diagram below and use it to answer questions 1&2
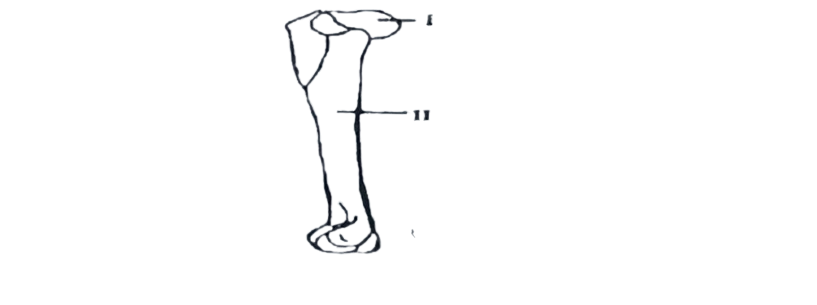
1. To form a ball and socket joint, the structure labelled I fits into another structure in the scapula called the
A. blade.
B. glenoid cavity.
C. olecranon fossa.
D. patella.
2. The structure labelled II is called
A. deltoid ridge.
B. trochanter.
C. shaft.
D. trochlea.
The diagram below illustrates a part of the mammalian skeleton. Use it to answer questions 3 & 4.

3. The part of the mammalian skeleton illustrated in the diagram is the
A. atlas vertebrae.
B. axis vertebrae.
C. cervical vertebrae.
D. thoracic vertebrae.
4. The function of the part labelled I is to
A. provide support to the spinal cord.
B. provide surface for attachment of the muscle.
C. carry the spinal cord.
D. articulate with adjacent vertebrae.
5. Which of the following parts of the skeleton does not have a protective function?
A. Ribs.
B. Carpals.
C. Skull.
D. Pelvis.
6. The longest bone in the body is the
A. humerus.
B. femur.
C. scapula.
D. tibia.
7. Which of the following structures is not a skeletal material?
A. Chitin.
B. Cartilage.
C. Bone.
D. Muscle.
8. The axial skeleton is composed of the
A. skull and vertebral column.
B. limbs and girdles.
C. atlas and axis.
D. radius and ulna.
9. The inorganic components of bone consist of
A. magnesium, sodium and calcium.
B. magnesium, phosphorus and calcium.
C. sodium, phosphorus and calcium.
D. potassium, magnesium and calcium.
The diagram below illustrates a part of the human skeleton. Study it and answer questions 10 to 12

10.The diagram represents the bones of the
A. upper arm.
B. lower arm.
C. upper leg.
D. lower leg.
11. Which of the labelled parts articulates with the head of the trochlea to form a hinge joint
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
12. The labelled part that provides surface for the attachment of the triceps is
A. 1.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
13. Muscles are attached to bones by means of
A. tendons.
B. ligaments.
C. cartilage.
D. nerves.
14. A vestigial structure in humans is
A. earlobe.
B. toe bone.
C. tail bone.
D. spleen.
15. The odontoid process is found on the
A. axis vertebra.
B. atlas vertebra.
C. thoracic vertebra.
D. sacral vertebra.
16. Which of the following sequences is the correct arrangement of tissues in the anatomy of a young dicotyledonous stem from the inside to the outside?
A. Pith, phloem, cambium, xylem, parenchyma, collenchyma and epidermis.
B. Xylem, phloem, cambium, cortex, endodermis, collenchyma and epidermis.
C. Pith, xylem, cambium, phloem, collenchyma, parenchyma and epidermis.
D. Phloem, xylem, cambium, cortex, endodermis, collenchyma and epidermis.
17. Lateral meristem in flowering plants is found in the
A. cortex.
B. pericycle.
C. cambium.
D. pith.
The diagram below is an illustration of a mammalian bone. Use it to answer questions 18 & 19
18.The bone illustrated above is the
A. femur.
B. humerus.
C. radius.
D. ulna.
19. The function of the part labelled I is to
A. fit into the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
B. fit into the acetabulum of the pelvic girdle.
C. support the lower arm.
D. prevent the arm from bending backwards.
20. Which of the following is not a skeletal tissue?
A. Plasma.
B. Chitin.
C. Cartilage.
D. Bone.
21. Muscles act in opposite directions in order to
A. cause a bone to move.
B. prevent dislocation at joints.
C. prevent muscle fatigue.
D. regulate bodily activities.
22. The thoracic vertebra differs from all the other vertebrae, by the possession of
A. long neural spine.
B. odontoid process.
C. vertebraterial canal.
D. Large centrum.
Study the list below and use. it to answer questions 23-25
The vertebral column of mammals consists of the following: I. Lumbar vertebrae II. Thoracic vertebrae
III. Caudal vertebrae IV. Cervical, vertebrae V. Sacral vertebrae.
23. Which of the following are found immediately next to the skull?
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
24. Which of the following articulates with the ribs?
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
25. Which of the following articulates with the pelvic girdle?
A. V.
B. IV.
C, III.
D. II.
26. Which of the following is not a function of the mammalian skeleton?
A. gives the body its shape.
B. provides a framework on which internal organs are suspended.
C. protects soft and delicate parts of the body.
D. contracts and relaxes to bring-about olmovement.
Use the digram below to answer questions 27 & 28

27. What type of vertebra is represented in the diagram
A. Atlas.
B. Axis.
C. Cervical vertebra.
D. Lumbar vertebra.
28. The structure labelled A represents the
A. transverse process.
B. neural spine.
C. neural canel.
D. centrum.
29. Which of, the following statements is not correct about the functions of each group of mammalian
vertebrae?
A. Cervical vertebrae support the neck.
B. Thoracic vertebrae articulate with the ribs.
C. Lumbar vertebrae provide attachment for abdominal muscles.
D. Sacral vertebrae support the skull and allow nodding and rotating movements.
30. The stems of young herbaceous plants are kept upright mainly by
A. osmotic pressure.
B. turgor pressure.
C. transpiration pull.
D. suction pressure.
31. Different tissues in plants contribute to the support of the parts as a result of the following characteristics except
A. malleability.
B. rigidity.
C. flexibility.
D. resilience.
32. Water vapour is lost in plants during transpiration through
A. stomata and lenticels.
B. xylem and stomata.
C. sclerenchyma and stomata.
D. parenchyma and lenticels.
33. Which of the following will ease the friction between the ends of bones in a movable joint?
A. Serum.
B. Tissue.
C. Blood plasma.
D. Synovial fluid.
34. The following are the functions of supporting tissues in plant except
A. rigidity.
B. flexibility.
C. strengthening.
D. secretory
35. Which of the following plant parts does not perform supportive function?
A. Parenchyma, xylem and collenchyma.
B. Epidermis, sclerenchyma and xylem.
C. Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
D. Sclerenchyma, xylem and collenchyma.
36. Which of the following structures is not present in the vascular bundles of a dicot stem?
A. Xylem.
B. Phloem.
C. intra-fascicular cambium.
D. inter-fascicular cambium.
37. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by a sheet of muscle called
A. pleural membrane.
B. intercostal muscle.
C. diaphragm.
D. pericardium.
38. Which of the following statements is true about movement of the forearm? In
A. bending the arm, the biceps relax and the triceps contract.
B. bending the arm, the biceps contract and the triceps relax.
C. straightening the arm the biceps contract and the triceps relax.
D. straightening the arm, both biceps and triceps contract.
39. Which of the following statements about the modifications of pentadactyl fore-limb is not correct?
A. Wings are modified for flying in birds.
B. Flippers are modified for grasping in sharks.
C. Legs are modified for walking and running in antelopes.
D. Arms are adapted for grasping and holding in human beings.
40. Which of the following hind limb bones is equivalent to the humerus of the forelimb?
A. Patella.
B. Tarsal.
C. Tibia.
D. Femur.
The diagram below represents a section of the stem of a plant. Use it to answer questions 41 and 42.

41. Which of the labelled-parts is made up of dead cells?
A. Ill and IV.
B. I, II and IV.
C. IV and V.
D. II and III.
42. The part labelled I in the diagram is called
A. stoma.
B. epidermis.
C. lenticel.
D. cortex.
43. Which of the following groups of vertebrae have two branches at the end of their transverse processes
A. sacral,
B. thoracic.
C. cervical.
D. lumbar.
44. The axial skeleton is made up of the following
A. skull, vertebral column, rib cage and sternum.
B. limbs and limb girdles.
C. lumbar and thoracic vertebrae.
D. vertebral column and lumbar vertebrae.
45. The xylem elements perform the function of transport but they also help to support plants because
they
A. are internally located.
B. are tubular.
C. have rigid thick walls.
D. constantly absorb water.
46. Which of the following structures occupies the neural canal of the vertebral column?
A. cerebellum.
B. hypothalamus.
C. medulla oblongata.
D. spinal cord.
47. Support in young herbaceous plants is provided by
A. translocation.
B. guttation.
C. turgidity.
D. osmosis.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 48-50.
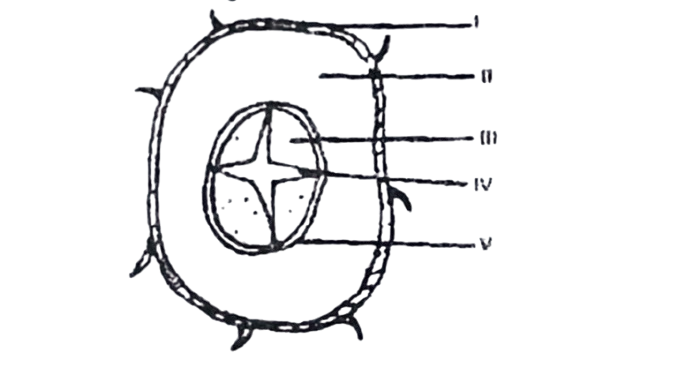
48. The above diagram represents a
A. longitudinal section of a stem.
B. longitudinal section of a root.
C. cross section of a root.
D. transverse section of stem.
49. The part labelled II in the diagram is the
A. epidermis.
B. cortex.
C. phloem.
D. xylem.
50. The part labelled IV in the diagram is the
A. phloem.
B. pericycle.
C. cortex.
D. xylem.
51. Which of the following groups contains a non- supporting structure in animals?
A. Cartilage, bone and pseudopodia.
B. Pellicle, chitin and bone.
C. Humerus, ribs and cartilage.
D. Femur, pellicle and chitin.
52. Which of the following vertebrae provide articulating surfaces for the ribs
A. Thoracic.
B. Lumbar.
C. Cervical.
D. Sacral.
53. Which of these is not part of the appendicular skeleton?
A. Clavicle.
B. Vertebral column.
C. Scapula.
D. Femur.
54. Which of the following is not a component of the appendicular skeleton
A. Ulna.
B. Atlas.
C. Femur.
D. Pelvic girdle.
55. Which of the following constitutes the main internal tissue of a leaf?
A. Cuticle.
B. Mesophyll.
C. Vascular tissue.
D. Lower epidermis.
56. The following are functions of the skeleton except
A. providing support for the body.
B. protection of delicate internal organs.
C. maintenance of the shape of the body.
D. controlling growth rate in animals.
57. Excessive loss of water from the leaf is prevented by the
A. vascular bundle.
B. cuticle.
C. midrib.
D. parenchyma.
58. Which of the following tissues does not offer support in plants?
A. Meristem.
B. Sclerenchyma.
C. Collenchyma.
D. Xylem.
59. In animals the main protective covering is found in the
A. adipose tissues.
B. epithelial tissues.
C. bonetissues.
D. connective tissues.
60. Which of the following structures does not function as support in animals?
A. Cuticle in arthropods.
B. Scales in birds.
C. Cartilage in mammals.
D. Body fluid in earthworms.
61. The upward movement of the sap in the xylem vessel is brought about by
A. transpiration stream.
B. guttation.
C. capillarity.
D. osmosis.
62. Which of the following groups carry out similar functions in living things?
A. Vertebral column, chitin, and guard cells.
B. Sclerenchyma, cartilage and chitin.
C. Tendon, chitin and neuron.
D. Collenchyma, intercellular spaces and blood vessels.
63. Which of the following statements is correct? The
A. biceps muscles has its origin on the head of the humerus.
B. biceps muscle is inserted at the ulna.
C. triceps muscle originated at the scapula and head of the humerus.
D. ulna is pulled up when the biceps is relaxed.
64. Which of the following pairs of tissues is responsible for strengthening the plant?
A. Phloem and Epidermis.
B. Parenchyma and Cambium.
C. Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma.
D. Collenchyma and Cambium.
65. Which of the following is not a tissue found in plants?
A. Epidermis.
B. Phloem.
C. Xylem.
D. Dermis.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 66-68
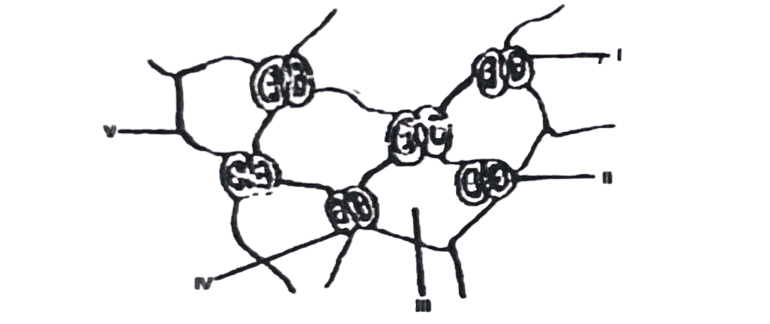
66. The function of the part labelled I is
A. controlling water loss.
B. trapping solar energy.
C. absorbing water.
D. storing sugar.
67. The part labelled II is the
A. stoma.
B. palisade cell.
C. spongy cell.
D. guard cell.
68. The structure that will be stained blue-black by iodine is labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
Study the diagram below and use it to answer question 69-71
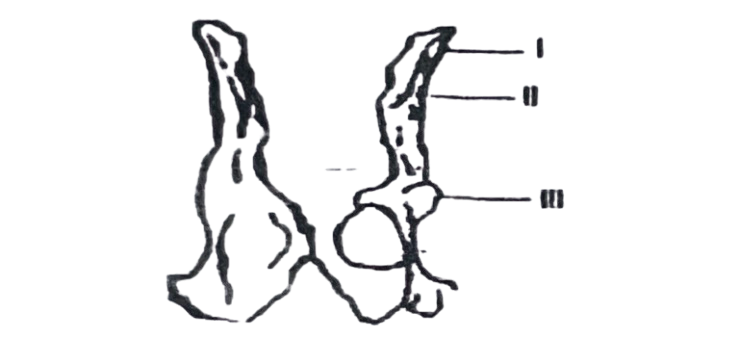
69. The piece of bone represented in the diagram is found in the
A. pelvic region.
B. pectoral girdle.
C. vertebral column.
D. skull.
70. The part labelled I is the
A. lumbar.
B. sacrum.
C. ilium.
D. pubis.
71. The bone that articulates with the part labelled III is the
A. humerus.
B. Fermur.
C. tibia.
D. sacrum.
72. The large intercellular air spaces which penetrate the tissues of most hyrophytes provide a pathway through which
A. carbon dioxide absorbed by leaves can diffuse to the roots.
B. oxygen produced in the leaves can diffuse to the submerged parts,
C. salts absorbed by roots can reach other parts of the plant.
D. plant hormones are transported to various parts.
Study the diagram below. Use it to answer questions 73.-75

73. Which of the following bones is illustrated in the diagram?
A. Tibia.
B. Humerus.
C. Patella.
D. Scapula.
74. The part labelled I in the diagram is for the attachment of
A. ribs.
B. biceps.
C. shoulder muscles.
D. the vertebral column.
75. Which of the following bones forms a joint at the point labelled II in the diagram?
A. Humerus.
B. Sternum.
C. Radius.
D. Femur.
76. The major mineral present in the shell of Molluscs is
A. copper.
B. sodium.
C. iron.
D. calcium.
77. Which of the following tissues does not provide support in flowering plants?
A. Collenchyma
B. Parenchyma
C. Xylem
D. Phloem
78. Radius and ulna are bones of the
A. pectoral girdle.
B. upper arm.
C. pelvic girdle.
D. lower arm.
79. The total number of caudal vertebrae in animals X and Y is 4 and 27 respectively. The animals are likely to be
A. fish and human.
B. toad and rat.
C. toad and fish.
D. humans and rat.
The diagram below is an illustration of a structure in the skeletal system of humans. Study it and answer questions 80 and 81.

80. The illustrated structure is a part of the
A. cervical vertebrae.
B. axial skeleton.
C. axis vertebrae.
D. appendicular skeleton.
81. An individual was involved in a car accident and the illustrated structure was badly injured. Which of the following structures would most likely be affected?
A. Lumbar, eye and teeth.
B. Bar, brain and hinge joint.
C. Lye, cerebellum and ear.
D. Clavicle, tongue and pelvis.
THEORY
1. (a) Explain the following terms dislocation (b) State three signs of dislocation
2. (a) What is a joint? (b) List three types of movable pints and mention one location in the mammalian body of each type (c) Make a labelled diagram, 8-10 cm long, of a typical movable joint (d) Explain how the structure of the joint adapts it to its function
3. (a) List four functions of the mammalian skeleton and name a particular part of the skeleton which performs each of these functions (b) Briefly describe how muscles and bones bring about movement at the elbow (c) How is support provided for in each of the following plants (i) Herbaceous plants (ii) Woody plants (d) Name one vitamin and one mineral element necessary for healthy development of bones
4. (a) Name three types of skeletons found in animals and in each case name one animal which possesses it (b) State four functions of the mammalian skeleton (c) Name four types of joints found in the mammalian skeleton. (d) Describe three features of a typical vertebra



