OBJECTIVES
1. Which of the following statements about the transfer of energy in an ecosystem is correct?
A. Energy increases at higher trophic levels. B. More organisms can be supported at higher levels. C. There are fewer organisms at lower trophic level. D. Energy is lost at each trophic level.
2. An organism at the start of a food chain which provides the total input of energy into an ecosystem is the
A. sun B. producer. C. consumer. D. decomposer.
3. The producers in a food chain in an aquatic environment are
A. birds. B. phytoplankton. C. zooplankton. D. fishes.
Study the diagram below and use it to answer this questions 4 & 5
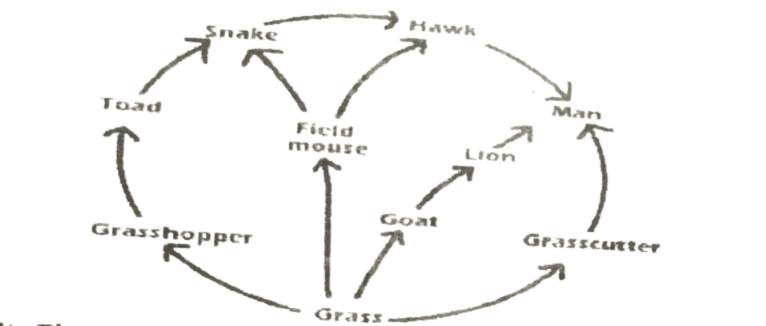
4. The best title for the above diagram is
A. terrestrial food web. B. terrestrial food chain C, aquatic food web. D. aquatic food chain.
5. How many food chains are in the agram?-
A. Three B. Four. C. Five. D. Six.
Study the food web below carefully and use it to answer questions 6 & 7
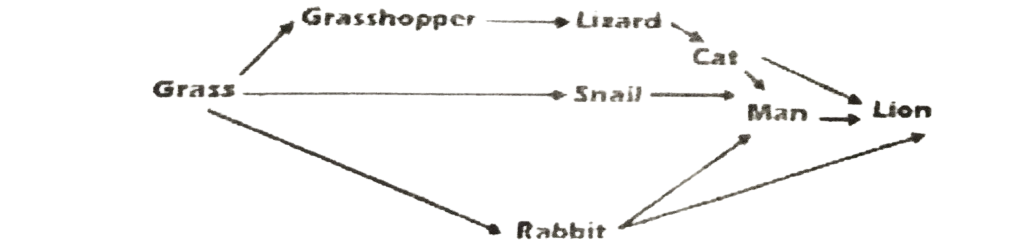
6. Tertiary consumers within the web are
A. cat and lion only. B. man and lion only. C. man and cat only. D. man, cat and lion.
7. What would be the effect of taking the lion out of the web?
A. The number of organisms at each trophic level would increase. B. Man would occupy the apex of the web. C. There would be more rabbits in the web. D. The energy reaching the remaining trophic levels would increase.
8. Which of the following organisms is a primary consumer?
A. Dog. B. Sheep. C. Grass. D. Fungus.
Study the diagram of a food chain shown below and use it to answer questions 9 & 10
9. The organism designated P in the food chain above is normally sustained by energy from
A. sunlight. B. Carbohydrates. C. green plants. D. mineral salts.
10. Which of the following statements best describes the organism designated R? It
A. feeds on S. B. is a primary consumer. C. is a producer as well as a consumer. D. is a secondary consumer.
11. Food chains are relatively short because
A. of energy recycling in the ecosystem. B. energy gain at trophic level is high energy loss at each trophic level. D. energy now in an ecosystem is unit-directional.
12. The following organisms are producers except
A. Hibiscus. B. Mushroom. C. Cactus. D. Spirogyra.
13. Food webs are complex because
A. the number of producers are large. B. many animals feed directly on producers. C. they include primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. D. some animals from part of several food chains.
14. The amount of energy passed from one trophic level to the next decreases because
A. many organisms are present at the first trophic level. B. many organisms occur at the higher trophic level. C. more energy is conserved at lower tropic level. D. parts of the organisms remain unutilized at each trophic level.
15. Which of these values in kj/m² likely represents the energy content of the producers in a habitat?
A. 5033. B. 100. C. 12. D. 10.
16. Which of the following pyramids gives the most accurate picture of the relationships between the organisms at the various trophic levels in a food chain?
A pyramid of A. numbers. B. energy. C. biomass. D. size.
17. Which of the following statements is not associated with pyramids of energy
A. Efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels can be studied. B. Comparisons of pyramids for different ecosystems can be made. C. More accurate comparisons of trophic levels D. Representation of numbers of organisms at different trophic levels.
18. Which of the following substances when lost from the body of a mammal will not be returned to the ecosystem?
A. Sweat. B. Urea. C. Heat energy. D. Carbon dioxide.
19. In an ecosystem, the least efficient energy transfer link is from the
A. secondary consumers to decomposers. B. sun to producers. C. primary consumers to secondary consumers. D. producer to primary consumers.
20. The following organisms are consumers except
A. earthworm. B. Spirogyra. C. bacteria. D. Rhizopus.
21. Which of the following statements about ecosystems is false?
A. All the energy entering the ecosystem is passed on to decomposers. B. The primary producers provide energy for herbivores and carnivores. C. Ecosystems must start with the capture of energy by autotrophs. D. Energy transfer from one trophic level to the other is not 100% efficient.
22. Which of the following organisms are the producers in an aquatic habitat?
A. Benthons. B. Phytoplanktons. C. Zooplanktons. D. Nektons.
The following are pathways of energy in the biosphere: 1. Heat energy is lost from body metabolism to the surrounding air. II. Energy passes to decomposers and parasites. III. Energy is transferred to the next higher level in a food chain IV. Energy is also passed by conduction to clothing and other objects. Use the pathways to answer questions 23 and 24
23. Which pathway directly leads to transfer of useful energy within a biological community?
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
24. Which of the following pathways will energy follow to reach plasmodium in the red blood cells?
A. I, II and III. B. I and II. C. il only. D. Ill and IV.
25. Changes in energy flow between organisms in a habitat can be represented by a
A. pyramid of biomass. B. pyramid of numbers. C. pyramid of energy. D. food chain.
26. Which of the following explains the term pyramid of numbers?
A. The number of organisms in atrophic level. B. The relationship between plants in different trophic levels. C. The number of saprophytes and parasites in a habitat. D. The number of predators in a habitat,
27. In any food chain, the first member must be a
A. carnivore. B. herbivore. C. zooplankton. D. autotroph.
28. The total amount of energy entering a food chain is that which is present in the
A. consumer. B. ecosystem. C. producer. D. decomposer.
29. Which of the following would be the primary producer in a food chain
A. Saprophytes. B. Herbivores.vel C. Carnivores. D. Green plants.
30. In the marine food web, the source of energy to the producer comes from
A. sea waves. B. sea water. C. sun. D. air.
31. Which of the following organisms is a producer?
A. Spirogyra. B. Mucor. C. Rhizopus. D. Yeast.
32. Which of the following does not contribute to the biomass in an ecosystem?
A. Producers. B. Food chains. C. Consumers. D. Micro-organism.
33. Which of the following organisms will not bring about decomposition?
A. Earthworm. B. Bacterium. C. Mould. D. Spirogyra.
34. In an ecosystem the organism which changes light energy into stored chemical energy is the
A. consumer. B. decomposer. C. producer. D. carnivore.
35. Which of the following organisms will have the highest biomass?
A. Small fish. B. Tadpole. C. Hawk. D. Phytoplankton.
36. Which of the following is the correct sequence for energy transfer and nutrient cycling among livingnthings in an ecosystem?
A. Consumers producers → decomposers. B. Producers decomposers → consumers. C. Decomposers producers → consumers. D. Producers consumers → decomposers.
37. A food web can be described as a
A. complex feeding relationship in a community. B. transfer of food energy from one community to another. C. complex pattern of food production in a community. D. group of many populations competing for the same type of food.
38. Which of the following represents the correct order in a possible food chain?
A. Crustacean -> diatom -> fish -> man. B. Fish crustacean man diatom. C. Man r> fish S crustacean -> diatom. D. Diatom crustacean →fish man.
Study the diagram below showing three food chains Use it to answer question 39
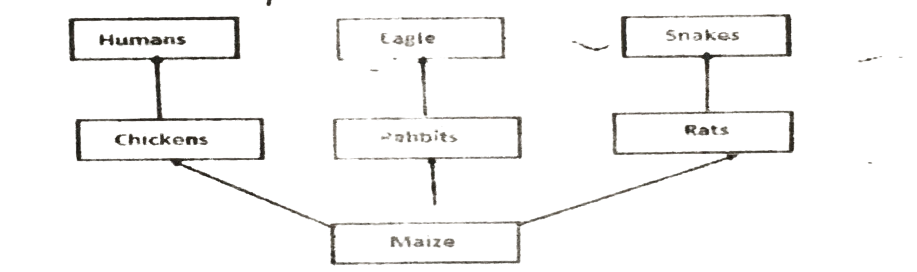
39. Which of the following are consumers in these food chains?
A. maize and rabbits. B. chicken, rats and maize. C. eagle, maize and snakes. D. humans, eagle and snakes.
40. An importance of food web is that living organisms
A. use web to collect food. B. can live on their own. C. have to form a web. D. depend on one another for their existence.
41. The continuity of an ecosystem depends on constant flow of energy and circulation of matter. However, the amount of energy passed on from decomposers to producers should be
A. great. B. small. C. reversible. D. zero.
42. Which of the following components of an ecosystem does not contribute to the biomass of the system
A. Producers. B. Consumers. C. Micro-organisms. D. Habitat.
43. Organisms that feed essentially on plants within any ecosystem may be referred to a
A. carnivores. B. herbivores. C. saprophytes. D. omnivores.
44. In a food chain, each stage in the chain is a
A. chain level. B. web level. C. consumption level. D. trophic level.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 45-47.

45. The diagram above illustrates
A. the size of various organisms. B. types of organisms in a habitat. C. the flow of energy In a habitat. D. the food chain.
46. Which of these organisms occupies the 3rd trophic level?
A. King fisher. B. Small fish. C. Phytoplankton. D. Big fish.
47. Which of these organisms is a herbivore?
A. Tadpole. B. Phytoplankton. C. King fisher. D. Small fish.
48. Which of the following statements about feeding relationships is correct
A. In a food web on land, grasshopper feeds on praying mantis and on predator bugs. B. In a food chain on land, green plant is the producer. C. In an aquatic food chain, mollusc larvae are the producers. D. In an aquatic food web, various copepods feed on mollusc larvae and on sand eel.
49. Which of the following values showing the total biomass of organisms in a food chain represents the secondary consumer?
A. 40,000. B. 3,000. C. 20. D. 1.
50. The gas produced during decomposition of matter is
A. hydrogen sulphide. B. carbon monoxide. C. chlorine. D. oxygen.
51. The substances recycled in the soil by the activities of micro-organisms during the decay of dead organisms are first utilised by the
A. carnivores. B. herbivores. C. scavengers. D. autotrophs.
52. In complex food relationships in a community, the primary, secondary and tertiary consumers are
referred to as
A. symbionts. B. omnivores. C. heterotrophs. D. autotrophs.
53. In a food chain the position occupied by an organism is called
A. the trophic level. B. energy level. C. the feeding level. D. the habitat level.
54. Which of these statements about food chain is not correct?
A. Animals in the chain are consumers. B. A food chain usually begins with a green plant. C. All organisms in a food chain are animals. D.. Living things are dependent on one another.
55. Which of the following statements is not correct about food chains?
A. All food chains start with a green plant. B. Food chains involve feeding relationships among organisms. C. Shorter food chains indicate more effective utilization of energy than longer ones. D. There is no energy loss in a food chain.
56. Which of the following groups of organisms feeds directly on green plants?
A. Producer. B. Decomposer. C. Primary consumer. D. Secondary consumer.
Use the diagram to answer questions 57 and 58.
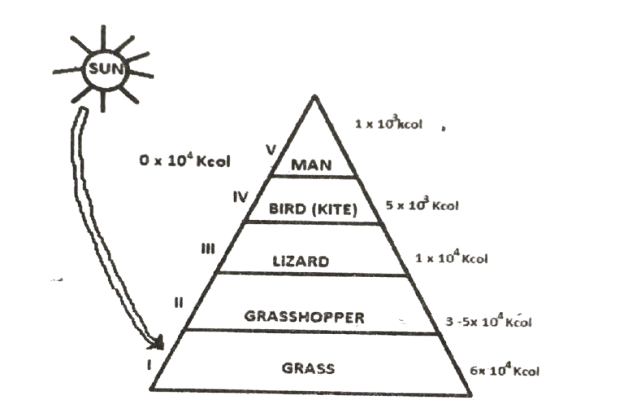
57. What phenomenon in ecosystem does the diagram illustrate?
A. Pyramid of numbers. B. Food web among organisms. C. Pyramid of energy. D. Pyramid of biomass.
58. Which of the following effect would desertification have on the ecological balance represented in the diagram above? The calorific value of the energy
A. 10 x 10k cal obtained from the sun would decrease. B. 10 x 10k cal obtained from the sun would increase. C. 6 x 10k cal obtained at level would increase. D. 1 x 10k cal obtained at level V would increase.
59. Which of the following is a means of measuring primary production?
A. Rate of reproduction of animals. B. Life span of an organism. C. Number of predators in an environment. D. Harvested plants in a unit area.
60. Micro-organisms which break down dead organisms and absorb their contents are called
A. decomposers. B. consumers. C. parasites. D. commensals.
61. Which of these groups of organisms is responsible for capturing energy for the biotic community?
A. Decomposers. B. Omnivores. C. Consumers. D. Producers.
62. If a pond contains water weed, tadpoles, Tap-minnows (fish) and is visited after by Herons (bird) what would be the possible
A. Tap-minnow → Heron → Tadpole. B. Water weed → Tadpole Tap-minnow → Heron. C. Water weed → Heron Tap-minnow →W Tadpole. D. Water weed → Tadpole Heron Tap- minnow.
63. Which of the following is the correct chain for the organism found in an aquatic community?
A. Paramecium, Phytoplankton, Prawn, Waterflea, Tilapia, Shark. B. Waterflea, Paramecium, Phytoplankton, Prawn, Tilapia, Shark. C. Phytoplankton, Waterflea, Paramecium, Prawn, Shark, Tilapia. D. Phytoplankton, Paramecium, Waterflea, Prawn, Tilapia, Shark.
64. Organisms in an ecosystem are usually grouped according to their trophic level into
A. carnivores and omnivores. B. consumers and parasites. C. producers and saprophytes. D. producers and consumers.’ Turn over.
65. In the pyramid of energy illustrated below, the organism with the least amount of transferred energy is
A. Spirogyra. B. tadpole. C. fish. D. bird.
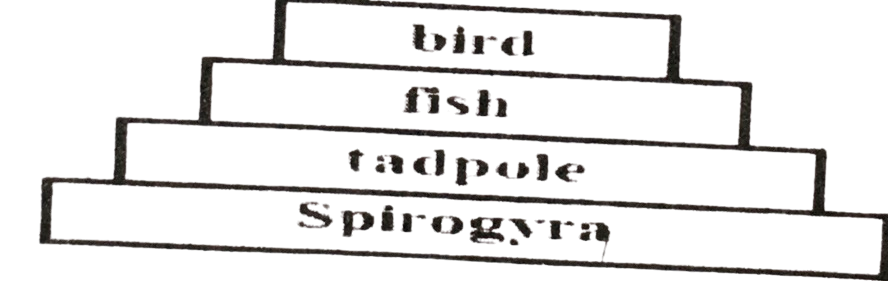
66. The position occupied by an organism in a food chain is the
A. Energy level. B. Niche. C. Trophic level. D. Biomass.
67. The illustration below is a food chain. Grass->grasshopper-» domestic fowl->hawk What would happen if the population of domestic fowl decreases? The population of
A. grasshoppers would decrease B. hawks would increase C. grasshoppers would increase D. grasses available to grasshoppers would increase.
68. Which of the following pyramids is not used in ecology? Pyramid of
A. energy B. numbers C. biomass D. organisms.
Study the food chain illustrated below and use it to answer questions 69 to 70.
J → K → L → M → N
69. Organism J is normally sustained by energy from
A. green plants. B. carbohydrates. C. organism K. D. sunlight.
70. Which of the following statements about organism L is correct? It
A. feeds on organism M B. is a primary consumer C. is the producer D. is a secondary consumer.
71. The position occupied by each of organisms J, K, L, M and N in the food chain is known as the
A. energy level. B. trophic level. C. food web. D. pyramid of numbers.
72. Which of the following organisms would be the producer in a food chain?
A. Goat. B. Maize. C. Man D. Bacterium.
The diagrams below are illustrations of organisms in a habitat. Study them and answer questions 73 and 74.

73. The feeding relationship between the organisms labelled ill and IV in the diagrams is
A. mutualism. B. parasitism. C, predation. D. saprophytism.
74. The producer in the diagrams is
A. I because it contains the least amount of energy. B. I because it uses sunlight to manufacture food. C. IV because it is the largest organism in the diagram. D. IV because it is the organism that receives the highest amount of sunlight.
THEORY
1. (a) What is meant by the term Food chain? (b) Draw a food chain involving four trophic levels which can be found in a terrestrial habitat. (c) Explain the flow of energy through the food chain drawn in (b) above; (d) How energy in the chain is lost to the environment.
2. (a) State the second law of thermodynamics. (b) Use the second law of thermodynamics to explain the flow of energy across different trophic levels in a food chain.
3.’ Construct a food chain typical of an Estuarine habitat.
4. (a) Explain briefly energy flow in a freshwater habitat. (b) Explain briefly three roles of a decomposer in an ecosystem.
5. (a) What is the importance of decomposers in the ecosystem? (b) Name one plant and one animal decomposer.
6. With reference to the food chain, explain the role of the following: (a) green plants (b) herbivores (c) carnivores (d) decomposers.
7. (a) State the two laws of thermodynamics (b) Use the second law of thermodynamics to explain the energy flow across trophic levels.
8. Explain the following terms: (a) Producer (b) Consumer (c) Community (d) Decomposer.
9. Describe the energy flow in a freshwater habitat.
.



