OBJECTIVES
1. The organism at the organ level of organization of life is.
A. Euglena.
B. Spirogyra.
C. Ginger.
D. Tapeworm.
2. The disadvantage of complexity of organization in the higher organisms is that it leads to
A. mutual interdependence between component cells.
B. internal structural specialization.
C. increased adaptation to environment.
D. slower rate of diffusion of oxygen to individual cells.
3. In which of the following multicellular organisms is interdependence of cells maintained?
A. Spirogyra.
B. Volvox.
C. Eudonna.
D. Pandorina.
4. Which of the following features does not necessarily place Paramecium at, a higher level of organization over Amoeba?
A. Presence of cilia.
B. Absence of pseudopodia.
C. Presence of micro and meganuclei.
D. Presence of more than one food vacuole.
5. Hydra is considered to be at a tissue level of organization of life because it
A. has numerous cells that perform different functions.
B. has developed organs and systems.
C. has a poorly developed nervous to system.
D. reproduces by budding.
6. An organism that operates at the cellular level of organization, carries out its physiological activities by using its
A. cell membrane.
B. organelles.
C. small size.
D. cytoplasm.
7. Which of the following structure is a tissue?
A. Vessel element.
B. Blood.
C. Sieve tube element.
D. Erythrocyte.
8. What level of organization is Spirogyra
A. Organ system.
B. Organ.
C. Cell.
D. Tissue.
9. The following organisms have structures for movement except
A. Amoeba.
B. Spirogyra.
C. Volvox.
D. Paramecium.
10. An example of an organism that exists as a colony is
A. Spirogyro.
B. Paramecium.
C. Euglena.
D. Volvox.
11. Which of the following organisms is most specialized?
A. Paramecium.
B. Amoeba.
C. Spirogyra.
D. Rhizopus.
12. Which of the following organisms is not a protozoan?
A. Amoeba.
B. Ascaris.
C. Plasmodim.
D. Paramecium,
13. The structure similarities in paramecium and Euglena are in the
A. shape of locomotory organs.
B. blunt anterior and pointed posterior.
C. Presence of micro and mega nuclei in both.
D. Presence of anterior and posterior contractile vacuoles.
14. Which of the following organisms cannot exist freely on its own?
A. Chlamydomonas.
B. Amoeba,
C. Paramecium.
D. Plasmodium.
15. Spirogyra is regarded as a multicellular plant because
A. the cylindrical cells are linked end to end.
B. its cells are linked together by cytoplasmic strands.
C. its cells are large.
D. it is an algae containing a large vacuole.
16. The epidermis of a leaf is considered an example of a tissue because the cells
A. allow sunlight to pass through.
B. are covered by a waxy cuticle.
C. all possess a similar structure and function.
D. allow water to enter them by osmosis.
17. Which of the following levels of organisation in living things is in the correct sequence, starting from the most complex to the simplest?
A. Tissue →cell→organ→ System.
B. System →organ →tissue→cell.
C. Cell→tissue→ system→ organ.
D. Cell→tissue→organ→system.
18. Which of the following best describes a colony of volvox?
A. Asexually reproduced cells held together in a mass, but independent of each other.
B. Sexually reproduced cells held together in a mass, and dependent on each other.
C. Single free-living a cellular units irrespective of their parental origin.
D. Several units of cells, held together by cytoplasmic strands and dependent on each other.
19. Which of these has the most complex level of organization?
A. Euglena.
B. Hydra.
C. Heart.
D. Virus,
20, Which of the following represents the correct sequence, from the most simple, to the most complex
of organizations?
A. Mitochondrion, Muscle, Alimentary canal, Rabbit, Heart, Neurone.
B. Mitochondrion, Neurone, Muscle. Heart, Alimentary canal, Rabbit.
C. Alimentary canal, Neurone, Muscle, Heart, Rabbit, Mitochondrion.
D. Rabbit, Mitochondrion, Heart, Neurone, Alimentary canal, Muscle.
21. The main similarity between unicellular and multicellular organisms is that both
A. perform all life activities.
B. exist as filaments.
C. are plants.
D. exist as colonies.
22. A serious disadvantage of complexity in higher organisms is
A. a high demand for food and energy.
B. ability to function in many specialized roles.
C. Little amount of energy dissipated in functioning.
D. specialization of parts of the body.
23. Which of the following pairs of organisms exist as colonies
A. Obelia and Euglena.
B. Eudorina and Volvox.
C. Chlamydomonas and Amoeba.
D. Hydra and Spirogyra.
24. The structure represented in the diagram below is

A. a colony.
B. a tissue.
C. a filament.
D. a pseudopodium.
Below is a list of the levels of organisation in organisms. Use it to answer questions 25 and 26
I. Tissue II. System Ill. Cell IV. Organ
25. The correct sequence of the levels in an increasing order of complexity is
A. I, II, III, IV.
B. III, I, IV, II.
C. II, IV, I, II.
D. V, III, I, II.
E. IV, I, II, III.
26. Which of the following organelles is used for locomotion in Paramecium?
A. Pseudopodium.
B. Trichocyst.
C. Cilium.
D. Pellicle.
27. Which of the following organisms exists as a filament?
A. Euglena.
B. Amoeba.
C. Volvox.
D. Spirogyra.
28. Which of the following is a tissue?
A. Volvox.
B. Chlamydomonas.
C. Epidermis.
D. Paramecium.
29. Which of the following statements is correct about organs
A. They are composed of specialized cells.
B. They perform a certain overall function.
C. They are not found in plants.
D. Unicellular animals have few organs.
30. Which of the following is not an organ?
A. Hair.
B. Tongue.
C. Rhizome.
D. Corn.
31. Which of the following plant parts is not a storage organ?
A. Carrot root.
B. Sugarcane stem.
C. Onion leaf.
D. Banana stem.
32. At what level of organisation is Amoeba?
A. Tissue.
B. Organ.
C. Cellular.
D. System.
33. Which of the following organisms is one-celled and free-living?
A. Volvox.
B. Spirogyra.
C. Rhizopus.
D. Chlamydomonas
34, Which of the following organisms is at the tissue level of organization?
A. Euglena.
B. Paramecium.
C. Volvox
D. Hydra
35. Which of the following organisms does not exist as a single cell?
A. Amoeba.
B. Euglena.
C. Volvox.
D. Chlamydomonas.
36. Which of the following features of Paramecium is not an advancement over Amoeba? The possession of
A. definite shape.
B. cilia.
C. oral groove.
D. nucleus.
37. Which of the following is not true of Rhizopus or mucor?
A. manufactures its own food.
B. has non-septate hyphae.
C. undergoes sexual and asexual reproduction.
D. bears spores in sporangia.
38. One of the similarities between algae and masses is their possession of
A. chlorophyll.
B. stem.
C. leaves.
D. roots
The diagram below illustrates the structure of Euglena. Use it to answer questions 39 & 40
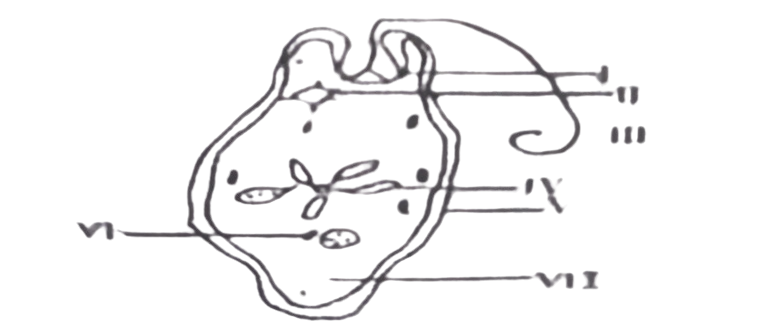
39. Excretion is carried out through the structure labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. IV.
D. V.
40. The part labelled VII is made up of
A. carbohydrates.
B. lipid materials.
C. waste materials.
D. protein materials.
41. The organelle which eliminates water from the body
of protozoa is
A. plasma membrane.
B. contractile vacuole.
C. cell wall.
D. protoplasm
42. Which of the following organisms has the largest surface area to volume ratio?
A. Man.
B. Earthworm.
C. Amoeba.
D. Grasshopper.
43. Which of these could be regarded as an advantage of complexity in higher organisms?
A. There is no cellular differentiation.
B. Cellular differentiation leads to loss of independence of the cells.
C. Complexity stops at cellular differentiation only.
D. Cellular differentiation leads to internal structural specialization.
44. Which of the following is not true about a bacterial colony growing on an agar plate?
A. They are visible without the aid of the microscope.
B. Bacterial cells found in one colony often belong to one species.
C. Different colonies have different colours.
D. Only one species of bacterial colony can grow on a culture at any time.
45. An example of organ level of organization is
A. bird.
B. kidney.
C. spermatozoon.
D. xylem.
46. A structural similarity between Paramecium and
Amoeba is the presence of
A. one food vacuole.
B. two contractile vacuoles.
C. two nuclei.
D. one gullet.
47. The organism with spiral chloroplasts and nucleus
Suspended by cytoplasmic strands is
A. Volvox.
B. Spirogyra.
C. Paramecium.
D. Euglena.
The diagram below is an illustration of a living organism. Study it and answer question 48.

48. The level of organization of the organism is
A. tissue.
B. cell.
C. organ.
D. system.
49. Organ level of organization in living things is found in
A. waterleaf plant.
B. virus particle.
C. kidney.
D. spermatozoon.
THEORY
1. Describe briefly two levels of cell organization in living organisms giving an example of each type.
2. State one difference each between Hydra and the mammals with respect to (i) level of organisation (ii) symmetry (iii) number of body layers
3. (a) State two advantages of complex structural organisation in higher organisms (b)(i) List two differences between colonial organisms and filamentous organisms (ii) Give one example each of a colonial organism and a filamentous organism
4. (a)(i) Name the four levels of organisation in living organisms (ii) Explain two of the levels of organisations named in (a)(i) above (iii) State the level of organisation of Euglena, onion bulb and blood (b) Give four advantages of complexity of organisation in higher organisms (c)(i) State one advantage Amoeba has over a cell of a lizard, in relation to their levels of organisation (ii) Give two reasons for the advantage.
5. Complete the table below by naming the classes of vertebrates in their evolutionary trend and giving one example
| Class of Vertebrates | One Example |



