OBJECTIVES
1. Special modification which enable an organism to survive in its habitat is known as
A. adaptation. B. tolerance. C. mimicry. D. colouration.
2. The inability of an organism to adapt to its habitat can lead to
A. dormancy. B. adaptation. C. extinction. D. survival.
3. An animal which is active during the day is known as
A. nocturnal animal. B. diurnal animal. C. terrestrial animal. D. homoeothermic animal.
In explaining the term camouflage, to a class, the diagram below showing four varieties, P, Q, R, and S of the same species of fish living amongst water plants in a river were used. Use the diagram to answer questions 4, 5 & 6

4. Which of the varieties is likely to decrease most in number if a predatory fish is introduced into the river?
A. P. B. Q. C. R. D. S
5. Which of the varieties is most likely to outlive the
others?
A. P. B. Q. C. R. D. S.
6. The variety selected in question above will outlive the others because the
A. variety is the most beautiful B. variety does not have markings. C. markings of the variety are similar to those of the environment. D. predator does not like eating the variety
7. Which of the following features is used by chameleons to escape predation?
A. Fearsome appearance. B. Coiling tail. C. Offensive smell. D. Adaptive colouration.
8. Which of the following organisms does not show colour adaptation to its environment?
A. Chameleon. B. Earthworm. C. Fish. D. Toad.
9. The main reason for nuptial flight in termites is to
A. escape unfavourable conditions. B. search for food. C. form new colonies. D. communicate with one another.
10. Which of the following organisms is not a social insect?
A. Termites. B. Ants. C. Grasshoppers. D. Bees.
11. The function of the drone in a colony of bees is to
A. clean the cells. B. mate with the queen. C. protect the colony. D. lay eggs.
12. The following are the major reasons why the butterfly lays eggs under the surface of a leaf except to
A. shade the eggs from the direct rays of the sun. B. protect the eggs from predators. C. protect the eggs from being washed away by rain drops. D. camouflage the eggs.
13. In which of the following insects is group instinct not displayed
A. Soldier ants. B. Cockroaches. C. Honeybees. D. Termites.
14. Which of the following traits is not characteristic of social insects
A. All members are identical. B. There is division of labour. C. The members dwell in the same habitat. D. Some members protect the queen.
15. The importance of courtship in animals includes the following except
A. ensuring that the female chooses the right male species. B. arousing both male and female partners. C. protection of territory. D. to coincide with the ovulation period and ensure fertilization.
16. Which of the following insects is not a social insect
A. Termite. B. Housefly. C. Honeybee. D. Ant.
17. A characteristic feature of plant parasites is the
A. possession of hold fast. B. possession of rhizoids. C. development of hanging roots. D. development of haustoria.
18. The following adaptations are associated with the might of birds except
A. reduced body weight. B. streamlined shape. C. presence of powerful muscles. D. clawed digits.
The diagram below is an illustration of a crocodile. Use it to answer questions 19 & 20
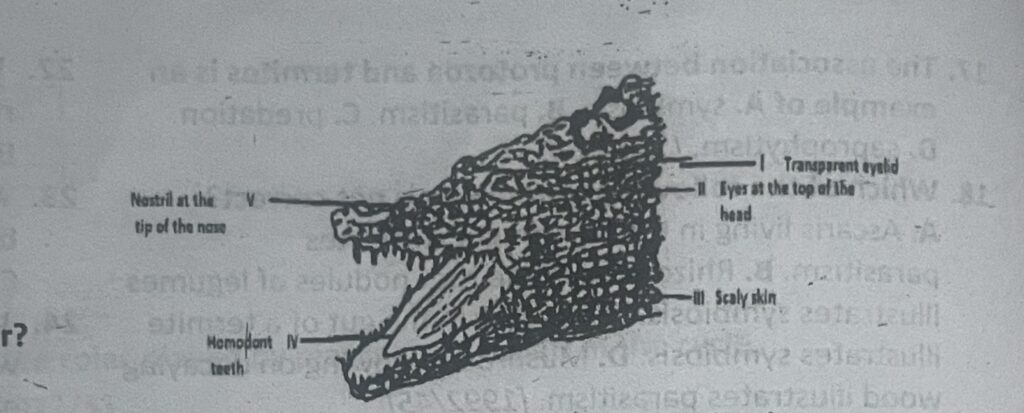

19. Which of the labeled parts enable the animal to stay under water most of the time?
A. I, IV and V. B. I, II and V. C. I, III and IV. D. III, IV and V.
20. Two characteristic features of the class to which the crocodile belongs are labeled
A. II and II. B. III and IV. C. II and IV. D. II and V.
21. The resemblance of a palatable insect to a poisonous insect is an example of
A. a chemical deterrent to a predator. B. an escape from the predator by camouflage. C. an escape from the predator by mimicry. D. a defence against the predator by warning colouration.
22. Which of the following statements in not true of the worker termites? They
A. build and repair the nest. B. produce enzymes to digest cellulose. C. search for food to feed the colony. D. look after the nymph.
Study the diagrams below carefully and use them to answer questions 23 & 24

23. What is the likely food of the bird in 1?
A. Worms. B. Seed. C. Nectar. D. Fishes.
24. The food of the bird in II is
A. worms. B. seed. C. nectar. D. fishes.
25. The frog is considered a better shimmer than the toad because it
A. has more pronounced webbed digits. B. has much longer and stronger, hind limbs. C. lives in water most of the time. D. is more streamlined than the toad.
26. One of the structural adaptations of mammals for movement on land is the development of the
A. hollow bones. B. pentadactyl limb. C. fused thoracic bones. D. streamlined body.
27. A termite with a relatively large head and powerful jaws is likely to be a
A. king. B. queen. C. soldier. D. reproductive.
28. A xerophyte conserves water by possession of the following features except
A. thick cuticle. B. sunken stomata. C. broad leaves. D. fleshy stem.
29. Xerophytes have the following characteristics aimed at conserving water except
A. thick cuticle. B. broad leaf surfaces. C. sunken stomata. D. waxy cuticle.
30. A moss plant can withstand drought by means of its
A. spores. B. rhizoids. C. antheridia. D. achegonia.
31. The absence of alimentary canal in the parasitic flatworm can be attributed to the fact that
A. its body does not feed. B. it has no enzymes.C. its body absorbs digested food. D. it has suckers on the scolex.
32. An animal which possesses scales, hairs and a backbone is likely to be
A. toad. B. lizard. C. rat. D. bat
33. Which of the following animals exhibits territoriality?
A. Rabbit B. Earthworm C. Lizard D. Toad.
34. The organ which is sensitive to light in Euglena is the
A. gullet. B. chloroplast. C. eye spot. D. contractile vacuole.
35. Euglena moves by the
A. whipping action of its flagellum. B. beating of its cilia. C. rotating action of the flagella. D. pushing out a jet of water from an organelle.
36. Which of the following depicts the external features of a rat as a mammal?
A. Long intestine and tail. B. Diaphragm and lungs. C. Milk and sweat production. D. Fur and whiskers
37. Which of the following is not a courtship behavior exhibited by animals?
A. Pairing. B. Display. C. Seasonal migration. D. Hibernation.
38. Hydra captures small crustaceans by means of
A. pseudopodia. B. musculo-epithelial cells. C. tentacles. D. enteron.
39. Adaptive radiation as illustrated by the variety of forms in insects can be regarded as
A. a behavioural modification. B. a case of rapid population growth. C. aphysiological process. D. an evidence of evolution.
40. The process by which plants and animals are modified in structure, physiology and behaviour in order to survive is known as
A. evolution. B. adaptation. C. succession. D. aggregation
41. What is the significance of the bee dance to other bees?
A. Warning signal. B. Presence of food. C. Mating signal by the male. D. Scaring the enemies away.
42. Which of the following is a social insect?
A. Mosquito B. Butterfly. C. Honey bee. D. Grasshopper.
43. Which of the following is not an adaptation of plants or animals to desert environment?
A. Well developed taproot system. B. Small leaves with thick epidermis. C. Stems with spike-like leaves. D. Broad leaves for storage.
44. Which of the following terms ensures the survival of an organism in its environment?
A. Hibernation B. Succession. C. Adaptation. D. Competition.
45. The concave shape of a birds wing during flight, ensures that the greater air pressure under the wings will
A. counteract the effect of gravity. B. lift the bird so that it can remain airborne. C. enable the pectoral muscles to contract easily. D. change the direction of the flying bird.
46. The adaptations for water conservation in organisms include the following except
A. scales in fishes. B. scales on leaves. C. thick leaves. D. spine in plant.
47. Which of the following structures is a protective adaptive feature of the Agama lizard to terrestrial
habitat?
A. Claws. B. Gular fold. C. Scaly skin. D. Nuchal crest.
48. Which of the following statements best explains the term aestivation?
A. A device for survival during the period of extreme food and water shortage. B. A method of survival adopted by plants during the dry season. C. Movement of animals over long distances. D. A method of survival adopted by animals under favourable condition.
49. Which of the following organisms is well adapted for fluid feeding
A. Cockroach. B. Mosquito. C. Grasshopper. D. Ants.
50. During mating, the male toad holds the female with its
A. sticky tongue. B. jelly. C. webbed hind limbs. D. nuptial pad.
51. The phenomenon whereby some organisms with certain features get established in an environment is known as
A. partial selection. B. artificial selection. C. natural selection. D. mutation.
52. Which of the following is an adaptation by plants to reduce the rate of water loss in a dry habitat?
Possession of
A. a few sunken stomata on the lower epidermis only. B. long leaf tendrils. C. leaves with serrated edges. D. strong tap root.
53. Which of the following does not illustrate adaptation to the environment?
A. Colour changes by chameleon. B. Streamline shape of fishes. C. Light bones in birds.
D. Development of big muscles by a weightlifter.
54. Which of the following best describes the adaptation of the earthworm to its habitat?
A. Living in burrow during the day to prevent desiccation. B. Burrowing into soft soil to store food. C. Possession of segmented body to reduce movement. D. Possession of a few bristles for defence.
55. The following are social insects except
A. wasps. B. termites. C. bees. D. cotton strainer.
56. The changing of colour by a chameleon to that of the environment is an example of
A. adaptive radiation. B. protective coloration. C. courtship display. D. display of body colour.
57. The division of labour in social insects is an example of
A. structural adaptation. B. physiological adaptation. C. commensalism. D. behavioural adaptation.
58. The swarming especially at the beginning of the rainy season is a courtship behaviour shown by
A. migratory birds. B. pigeons. C. crickets. D. winged termites.
59. The process in which insects undergo conspicuous changes in form and appearance during development is known as
A. ecdysis. B. metamorphosis. C. aestivation. D. migration.
60. Which of the following organisms is a social insect
A. Grasshopper. B. Honey bee. C. Butterfly. D. Housefly.
61. Territoriality is a phenomenon among
A. lower organisms. B. plants of different species. C. male animals with a group of females. D. animals and plants.
62. A honey bee worker communicates with others on locating a source of food by
A. dancing. B. stinging. C. instinct. D. flares.
Diagrams Use them I, II and III below illustrate the feet of birds adapted to various modes of feeding and
movement. Use them to answer 63, 64 and 65

63. What is the foot labeled I adapted to?
A. Feeding on flesh. B. Eating grains. C. Swimming in water. D. Perching on trees.
64. The foot labeled III is strong and has blunt claws on its digits. This implies that the bird
A. is a scavenger. B. is a bird of prey. C. is a marine bird. D. uses the foot to scratch the soil.
65. The long and sharp claws in the foot labeled II show that the bird uses them to
A. hold onto its prey. B. paddle in water. C. glide in the air. D. scratch the earth for worms.
66. The following insects undergo incomplete metamorphosis except
A. termite. B. cockroach. C. butterfly. D. locust.
67. Which of the following is not a structural adaptation of desert plants for water conservation?
A. Tiny leaves. B. Sunken stomata in leave. C. Stems and leaves with heavy cuticle. D. Broad leaves with numerous stomata.
68. Which of the following characteristics distinguishes the soldier termite from other members of the caste?
A. Wingless, strong mandibles and large head. B. Small head, small thorax and large abdomen. C. Small head, wingless, and small thorax. D. Small head, winged and small thorax.
69. Bees communicate with one another to obtain information about the direction of food source
through
A. complicated set of dances. B. smell. C. contract notes. D. sounds.
70. Which of the following behavioral patterns describes adaptive colouration?
A. Counter shading. B. Hibernation. C. Aestivation. D. Aggregation.
71. The structure used for movement in Amoeba is
A. cilia. B. pseudopodia. C. flagella. D. endoplasm.
72. The structure used by fishes to detect the presence and movement of other animals by the vibration they produce is the
A. eye. B. nostril. C. lateral line. D. scales.
73. Increasing specialization of structure and function among animals of the same class or order for survival in new and different environments is called
A. adaptive radiation. B. phylogeny. C. homology D. Analogy
74. Display is a phenomenon which occurs when an animal
A. ready for mating. B. fighting to defend itself. C. approaching puberty. D. chasing away an intruder.
75. The change in colour of the chameleon serves as a means of
A. attraction to the opposite sex. B. repulsion of the enemy. C. a camouflage from a predator. D. regulation of body temperature.
Use the diagrams below to answer questions 76 and 77
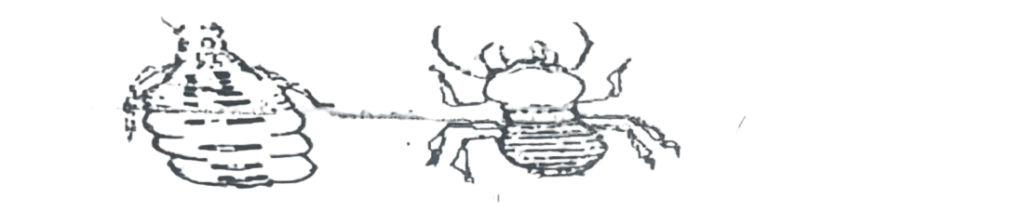
76. The diagrams above represent a group of insects known to be
A. colonial. B. parasitic. C. social. D. carnivorous.
77. In their system of organization, the diagram labeled II plays the role of a
A. worker. B. soldier. C. queen. D. drone.
Study the diagrams below carefully. Use them to answer Questions 78.
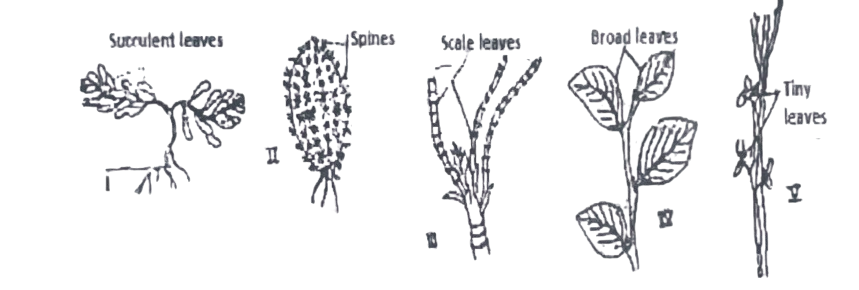
78. The plants best adapted for life in the desert are
A. I and IV only. B. II and IV only. C. IV and V only. D. I, II, III and V.
79. Which of the following organisms exhibit division of labour?
A. houseflies. B. butterflies. C. cockroaches. D. termites.
80. Which of the following vertebrates incubate their eggs?
A. Mammals. B. Birds. C. Amphibians. D. Reptiles.
81. The spinneret found in the caterpillar of butterfly is used for?
A. Protection against predators. B. Feeding on vegetation. C. Movement on twigs. D. Production of silk thread
82. In which of the following organisms is the siphon found?
A. Tadpole. B. Pupa of mosquito. C. Tilapia. D. Crayfish.
83. Which of the following structural features in animals does not affect control of body temperature?
A. Scales B. Skin. C. Fur. D. Capillaries.
84. Which of the following structural features adapts Drosera (Sundew) to its carnivorous mode of
nutrition?
A. Long root with glandular hairs. B. Club-shaped glandular hairs on leaves. C. Prominent lenticelon the stem. D. Broad leaves with long spines.
85. Courtship behaviour in animals may include all of the following except
A. howling of a dog. B. dancing of the worker bee. C. croaking of a toad. D. basking in the sun by a lizard.
86. Termites are called social insects because
A. the nests are built by the nasute soldiers. B. they live together in communities. C. the queen allocates duties to the workers. D. the king and queen do mate.
87. Honey-bee workers carry out the following functions except
A. laying eggs. B. building nests. C. cleaning the nest. D. gathering food.
88. Which of the following makes up the bee caste?
A. Soldiers and Queen. B. Drones, soldiers and workers. C. Queen, workers and soldiers. D. Queen, drones and workers.
89. Fish cannot survive on land because it has
A. a body covered with scales. B. a streamlined body. C. no lungs. D. no walking appendages.
90. Rabbits cannot survive in an aquatic habitat because they have
A. fore and hind-limbs. B. no gills. C. no fins. D. no scales.
91. Which of the following is not a behavioural adaptation used by social animals?
A. Cryptic. B. Mimicry. C. Flash. D. Season.
92. Which of the following animals exhibits territoriality?
A. Bees. B. Bats. C. Lizards. D. Rabbits.
93. Which of the following examples best describes camouflagic colouration in organisms?
A. A butterfly which has a red colouration on the wing. B. A green snake in a green grass. C. A. zebra with vertical stripes on the body. D. Certain tree frogs with bright colour patterns.
94. The statement that the environment determines which organisms survives to reproduce
A. explains the theory of acquired characters. B. support Jean Lamarck’s theory of use and disuse. C. supports the idea of survival of the fittest. D. is refuted by fossil records.
95. The following structures are adaptation for water conservation except
A. sunken stomata. B. scales in animals. C. lenticels in stems. D. spines in plants.
96. Group instinct or social behaviour is not displayed in
A. soldier ants. B. bees. C. chickens. D. weaver birds.
97. Which of the following is an example of reproductive adaptation?
A. Succulent stems of cactus plant. B. Changing colour of chameleon. C. Possession of spines by desert plants. D. Neck colouration in Agama lizard.
98. A situation whereby some mammals remain inactive throughout dry and hot seasons is known as
A. aestivation. B. dormancy. C. burrowing. D. incubation.
99. In fishes, the brooders return to their parents mouth for
A. feeding. B. respiration. C. breeding. D. protection.
100. Which of the following features enables the tapeworm to live successfully in the small intestine of
human?
A. Hooks and suckers for strong attachment. B. A long neck for forming young proglottis. C. The absence of segmentation and appendages. D. Possession of flame cells for excretion.
101. The yellow and black stripes on the body of wasps is an example of
A. mimicry. B. courtship behaviour. C. camouflage. D. warning colouration.
102. The biological importance of the dance by the worker honeybee is that it
A. acts as a signal for mating. B. serves as a warning signal C. signals the availability of food. D. serves as a means of identifying members of the caste.
103. Which of the following statements best explains the reason why termites swarm at night?
A. Light is not necessary for swarming B. They avoid day-flying birds C. Light destroys their wings D. They can only see in the dark.
104. Which of the following organisms does not undergo incomplete metamorphosis?
A. Locust B. Grasshopper C. Butterfly D. Cockroach
The diagram below is an illustration of the foot of an animal.
105. The adaptation of this type of foot is that it is
A. usedas a bait to catch fish in water. B. used as a paddle for swimming. C. effective in scratching the soil for food. D.used for killing prey in water.
106. Which of the following features is not an adaptation of plants to aquatic habitats?
A. Breathing roots for entry of air B. Flowers are raised above water to attract pollinators C. Spongy tissues containing gases for buoyancy D. Hairy structures on the leaves to reduce water loss serves as a warning signal.
107. Which of the following organisms exhibits adaptive colouration?
A. Rabbit B. Chameleon C. Mouse D. Dog
108. The mouth parts of a grasshopper are adapted for
A. chewing. B. grinding. C. sucking. D. absorption.
109. Fishes survive in water mainly because they possess
A. streamlined body. B. scales. C. paired fins. D. gills.
110. The following activities are associated with termites except
A. nuptial flight. B. communication. C. pollination. D. searching for food.
THEORY
1. (a) Explain the term adaptation in relation to the mode of life of an organism
(b) Explain how each of the following structures adapt the organisms that possess them to their modes of life:
(i) succulent leaves in Aloe sp;
(ii) succulent stems and reduced leaves in cactus plants
(iii) short strong beaks in fowls
(iv) tiny scale leaves on needle-like branches of pine trees.
(v) counter shading in fish.
2. State two differences each between: metamorphosis in housefly and toad.
3. Describe briefly three ways each by which animals in arid habitats are adapted to:
(i) drought;
(ii) high temperatures.
4. (a) State five reasons why animals move from place to place.
(b) State one function each of the following structures found in plants:
(i) epidermis
(ii) phloem
(iii) Sclerenchyma
(c) State two adaptive features of plants which inhabit salt water swamp.
5. Name two forms of adaptive communication in animals.
(b) State two reasons why organisms communicate with one another.
6. (a) What is courtship behaviour in animals?
(b) List three courtship behaviours in animals.
7. Write short notes on the following:
(a) territoriality
(b) seasonal migration.
8. (a) Explain the term adaptation.
(b) Explain two ways each by which the following organisms adapt to their habitats:
(I) hydrophytes
(II) xerophytes.
9. Explain how each of the following organisms are adapted for obtaining food:
(i) Mosquito larva
(ii) Dodder plant
(iii) Grasshopper.
10. State the adaptive features of the egg of a domestic fowl.
11. Explain how each of the following behaviours in animals affect the reproduction process
(i) territoriality
(ii) display
(iii) seasonal migration.
12. State three behavioural adaptations of animals to seasonal changes.
13. (a) Explain the term courtship behaviour in animals
(b)How does courtship aid reproduction in animals?
14. Explain two ways each by which the toad/frog is structurally adapted to the following:
(i) obtaining food
(ii) protection
(iii) movement.
15. (a) Mention four castes found among the termite nests
(b) State one role of each caste to the two types of courtship behaviour in lower animals
(c) State two importance of courtship behaviour in the reproduction of lower animals
(d)Describe briefly the courtship behaviour exhibited by Agama lizard.
16. (a) Define the term metamorphosis
(b) Name the two types of metamorphosis that organisms undergo and mention two organisms that undergo each type
(c) List four peculiar features of social insects.
17. State three adaptive features of sea weeds.
18. State the adaptation of tapeworm (Taeniasolium) to its habitat in the gut of human.
19. List four adaptive features of animals that climb rain forest trees.
20. Describe six protective adaptations used by animals against predation and give one example in each case.
21. List the functions of a typical foliage leaf.
22. (a) Give two reasons why termites are described as social insects
(b) Name four castes found in the termite nest, stating one role of each caste
(c) Describe five behavioural adaptations of termites which enable them to survive in their environment.
23. (a) What is metamorphosis
(b) State the type of metamorphosis exhibited by each of the following insects listed below:
Grasshopper, Cockroach, Butterfly, Mosquito and Housefly.
24. Name three animals each that exhibit:
(a) territoriality
(b) seasonal migration
(c) display.
25. List three animals each that exhibit the following courtship behaviours.
(a) territoriality
(b) pairing.



