OBJECTIVES
1. Differences in characteristics that exist among individuals of the same species is referred to as
A. genetics. B. dominance. C. hybrid. D. variation.
2. Which of the following traits is not a morphological variation in humans?
A. Ability to taste PTC. B. Colour. C. Fingerprints. D. Size.
3. A noticeable physical appearance of individuals of the same species is called
A. physical variation. B. physiological variation. C. morphological variation. D. discontinuous variation.
4. Which of the following is an example of variation?
A. Blood. B. Tongue rolling. C. Reproduction. D. Growth
5. The parameters of size, height, weight and colouring a population of living things are example of
A. environmental variation. B. non-heritable variations. C. continuous variations. D. discontinuous variations.
6. Which of the following characters is not a morphological variation
A. Shape of the nose. B. Colour of skin. C. Colour of hair. D. Tongue rolling.
7. Which of the following statements is not true about continuous variation? It
A. is usually controlled by several genes. B. can be influenced by environmental factors. C. follows a normal distribution curve. D. is usually controlled by one or two pair(s) of genes.
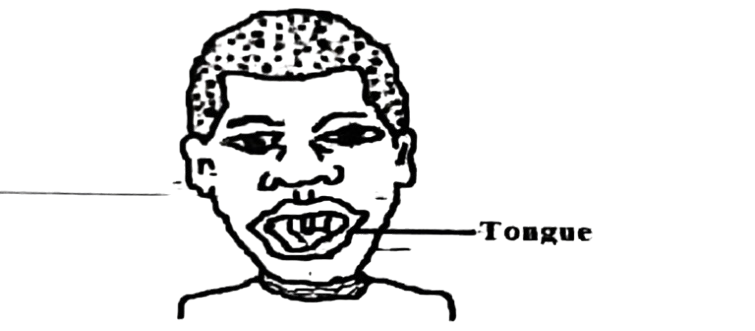
8. The type of variation illustrated above is
A. continuous variation. B. discontinuous variation. C. morphological variation. D. environmental variation.
9. Differences in characteristics observed between individuals of the same species is known as
A. trait. B. phenotype. C. mutation. D. variation
10. The following pairs of traits are examples of continuous and discontinuous variations respectively except
A. eye colour and body weight. B. height and blood group. C. skin colour and fingerprints. D. body weight and tongue rolling.
11. The classes of fingerprints in man are
A. whorl, alternate, opposite and compound. B. compound, loop, whorl and alternate. C. whorl, arch, compound and loop. D. arch, simple, compound and opposite.
12. Which of the following statements about phenyithiocarbamide (PTC) is not correct?
A. Some people find the taste of PTC to be bitter. B. Others find this substance to be tasteless. C. Ability to taste this chemical is heritable. D. Ability to taste the chemical is not heritable.
13. Which of the following characters is not an example of discontinuous variation?
A. Skin colour. B. Fingerprint. C. Ability to roll tongue. D. Sex type.
14. Which of the following traits is not inheritable? Ability to
A. taste PTC. B. roll the tongue. C. move the ear. D. roll the eyeball.
15. Which of the following forms of variation will give a normal distribution?
A. Blood groups. B. Tongue rolling. C. Body weight. D. Finger prints.
16. Characteristics that exhibit continuous variation are generally controlled by
A. a single gene. B. recessive genes. C. epistatic interactions. D. multiple genes.
17. The F1 generation of a cross between a red cock and white hen were all red because the gene for the
A. white colour did not segregate. B. red colour was dominant. C. white colour was dominant. D. red colour was recessive.
18. In dihybrid inheritance, Mendel considered
A. a pair of contrasting characters. B. two pairs of contrasting characters. C. three pairs of contrasting characters. D. four pairs of contrasting characters.
19. The observable characteristics of an individual usually resulting from the interaction between the gene composition and the environment is referred to as
A. allele. B. genotype. C. phenotype, D. chromosome.
20. Which of the following statements about human blood groups is not true?
A. A is dominant over B. B. O is recessive. C. B is dominant over O. D. A and B are co-dominant.
21. An example of continuous variation is
A. fingerprint. B. tongue rolling. C. blood grouping. D. body size
22. The outward appearance of an organism is referred to as
A. phenotype. B. genotype. C. dominance. D. recessiveness.
23. Which of the following statements about heredity is not true? In heredity the traits are
A. carried by genes. B. contained in the ovum and sperm. C. always transmitted by one parent. D. transmitted from parents to offspring.
24. Which of the following inherited conditions usually shows incomplete dominance? A. Sickle cell anaemia. B. Haemophilia. C. Tongue rolling ability. D. Baldness.
25. Acquired characters are
A. received from parents. B. passed to offspring. C. caused by the environment. D. caused by mutation.
26. The greatest contribution to genetic studies was made by
A. Gregory Mendel. B. Thomas Morgan. C. Charles Darwin. D. Robert Hooke.
27. According to Mendel’s first law of inheritance, segregation of genes occur when
A. tall plants are crossbred. B. short plants are crossbred. C. tall plants and short plants are crossbred. D. plants are crossbred.
28. Scientists who study genetics are known as
A. genealogists. B. geneticists. C. mendelists. D. gene scientists.
29. Which of the following scientists did not contribute to the development of genetics
A. Wilhem Johannsen. B. Thomas Morgan. C. Gregory Mendel. D. Felix Durjadin.
30. Which of the following diseases is transmittable through genes?
A. HIV/AIDS. B. Sickle cell anaemia. C. Diabetes. D. Presbyopia.
31. The character that is manifested in an organism in the presence of a contrasting character is known as
A. genotype. B. phenotype. C. recessive. D. dominant.
32. If a cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant produced red-flowered plants, the result can be described as an example of
A. partial recessiveness. B. dominance. C. incomplete dominance. D. out-breeding.
33. Which of these is not a hereditary variation?
A. Infant paralysis. B. Blood group. C. Sickle cell. D. Shape of face and nose.
34. A pair of genes which controls a trait is described as
A. dominant. B. recessive. C. allele. D. variant.
35. The genetic make-up of an organism is described as its
A. phenotype. B. genotype. C. character. D. chromosome.
36. Which of these statements is true about fingerprint patterns?
A. Consistent for a lifetime. B. May be exactly the same for two individuals. C. Prominent only at puberty. D. Correlate with the individual blood group.
37. Which of the following is a continuous variation, in human population?
A. Sex. B. Rh factor. C. Height. D. Down’s syndrome.
38. Which of the following statements about blood groups in human is not correct?
A. Siblings may not belong to the same blood group. B. there are for possible blood groups. C. people with blood group O can receive blood from all other groups. D. people with blood group AB are universal recipients
39. One of the major criticisms against Mendelian laws is that they do not recognize that
A. one trait is often controlled by many pairs of genes.
B. single factor inheritance is never a reality.
C. complete dominance is always possible.
D. incomplete dominance is not possible.
40. Identical twins inherit their genes from
A. the same ovum and different sperms.
B. the same sperm and different ova.
C. different sperms and many ova.
D. the same ovum and the same sperm.
41. The offspring produced when pure strains interbreed is described as
A. dominance.
B. phenotype.
C. allele.
D. genotype.
42. Which of the following is not a morphological variation in human beings?
A. Size.
B. Bloodoja groups.
C. Colour.
D. Fingerprints.
43. Character which falls to express itself in the first filial generation but emerges in the second iss
A. heterozygote.
B. homozygote.
C. dominant.
D. recessive.
44. Variation which exhibits a wide range from one extreme to the other with very little difference
between the intermediates is described as
A. phenotypic.
B. discontinuous.
C. continuous.
D. genotypic.
45. Which of the following is an example of physiological variation
A. Blood groups.
B. Skin colour.
C. Finger prints.
D. Human height.
46. Which of the following represents Mendel’s second law of inheritance? The factors for two pairs of
contrasting characters are
A. dependent on each other.
B. on homologous-chromosomes.
C. allelomorphic.
D. inherited independently of each other.
47. Which of the following terms is not associated with fingerprint and classification?
A. Whorl.
B. Contour.
C. Arch.
D. Loop.
48. Which disease is sex-linked and mainly afflicts male offspring
A. Sickle cell anaemia.
B. Haemophilia.
C. Diabetes.
D. Malaria.
49. In a living cell, factors which are responsible for inheritance are located
A. on the nuclear membrane.
B. on the nucleolus.
C. on the chromosomes.
D. in the nucleoplasm.
50. Which of the following is not a morphological variation
A. Shape of nose.
B. Colour of skin.
C. Colour of eyes.
D. Tongue rolling.
51. Which of the following major ideas were proved by Gregor Mendel?
A. There is a tendency among organisms to increase rapidly in number if conditions are favourable.
B. There is a struggle for existence,among a very large number of offspring.
C. Nature selects organisms which will survive to produce their kind.
D. Characteristics of an organism are controlled by genes occurring in pairs.
52. Blood groups and tongue-rolling are examples:
A. continuous variation.
B. discontinuous variation.
C. variation due to environment.
D. adaptive variation.
53. Which of the following is not a type of finger-print?
A. Whorl.
B. Compound.
C. Simple.
D. Loop.
54. The morphological, physiological and behavioural characteristics which enable an organism to survive in its environment is called
A. heredity.
B. ecology.
C. competition.
D. adaptation.
55. Which of these physiological variations is sex-linked?
A. albinism.
B. blood groups.
C. sickle-cell anaemia.
D. haemophilic condition.
56. Which of the following traits in humans can be affected by environmental factors?
A. skin colour.
B. eye colour.
C. baldness.
D. tongue-rolling.
57. Which of the following is not a continuous variation?
A. Height of plants.
B. Skin colour.
C. Ability to roll tongue.
D. Length of fingers.
58. Which of the following terms is not associated with finger prints?
A. Arch.
B. Loop.
C. Suture.
D. Whorl.
59. Variation is a factor which
A. differentiates between individuals of the same species.
B. qualifies an organism to live with others.
C. enables organisms to adapt to the environment.
D. states the external features of an organism.
60. Which of the following is the carrier of hereditary materials?
A. Centriole.
B. Cytoplasm.
C. Nucleolus.
D. Chromosome.
61. Which of the following traits in humans is not a morphological variation
A. Height.
B. Shape of head.
C. Colour of skin.
D. Ability to roll the tongue.
62. Which of the following is an example of continuous variation?
A. Human blood groups.
B. Sex differences in humans.
C. Haemoglobin types.
D. Height in humans.
63. Which of the following is an example of discontinuous variation?
A. The range in height of a pea plant from 30 cm to 50 cm.
B. Offspring, including the two male cats and three female cats.
C. The colour of pear plants grown in the dark.
D. The adult body weight ranging from 50 kg to 95 kg.
64. A sudden loss of black pigment from the skin of an African can be attributed to
A. a blending of black arid white genes.
B. recombination of genes.
C. loss of the 30 epidermis.
D. mutation in the skin cells.
Use the following human characteristics to answer questions 65 and 66.
I Complexion, II. Height III. Blood Rh factor IV. Colour blindness
65. Which of the above human characteristics are discontinuous variations?
A. I and III only.
B. II and IIIonly.
C. II and IV only.
D. III and IV only.
66. Which of the characteristics can be expressed phenotypically?
A. I and II only.
B. III and IV only.
C. II and IV only.
D. I, II and III only.
67. Which of the following variations is applicable of a weight lifter?
A. Continuous variation.
B. Discontinuous variation.
C. Hereditary variation.
D. Acquired variation.
68. The character that expresses itself in the presence of the contrasting character is
A. hybrid.
B. allele.
C. recessive.
D. dominant
69. Which of the following is an example of discontinuous variation?
A. Height.
B. Size of head.
C. Blood group.
D. Skin colour.
70. Hereditary variation is best described as
A. characters transmitted from generation to generation.
B. traits acquired from diseases.
C. characters that show up due to social conditions.
D. traits acquired from habits and environmental conditions.
71. The inability of some individuals to perceive the taste of some substances is an example of
A. individual adaptation.
B. physiological variation.
C. morphological variation.
D. morphological adaptation.
72. The major types of man’s finger prints do not include
A. arch.
B. compound.
C. simple.
D. loop.
73. Which of the following statements is correct about variation?
A. Offsprings are different from their parents only.
B. Offsprings from the same parents look alike.
C. Offsprings differ from their ancestors but look like their immediate parents.
D. Offsprings differ from their ancestors and from each other.
74. The ability of some individuals to taste phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) is a
A. morphological adaptation.
B. morphological variation.
C. physiological adaptation.
D. physiological variation.
75. The branch of science deals with resemblances, origin and expression of biological variations is called
A. embryology.
B. ecology.
C. entomology.
D. genetics.
76. Which of the following is a definition of heredity? It is the
A. non-resemblance of closely related organisms.
B. total absence of parents to offspring.
C. absence of variation in organisms.
D. transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
77. Individuals with blood group AB can donate blood to individuals with blood group(s)
A. A and B.
B. A and O.
C. AB only.
D. O only.
78. Variation which exhibits a wide range from one extreme to the other is
A. Phenotypic variation.
B. Discontinuous variation.
C. Continuous variation.
D. Genotypic variation.
79. Measurements of height and weight of students in a class show
A. Discontinuous variation.
B. continuous variation.
C. Shortness is more prevalent.
D. Fatness is less prevalent.
80. Which of the following diseases can be inherited?
A.Pneumonia
B. Whooping cough
C. Sickle cell anaemia
D. Malaria.
81. Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variation than those formed by asexual reproduction because
A. greater amount of DNA is involved in sexual reproduction.
B. gametes of parents have different genetic
C. genetics materials come from parents of two different species.
D. sexual reproduction is a lengthy process.
The diagrams below are illustrations of types of comb found in domestic fowl.
Study them and answer questions 82 and 83.
82. The types of comb show
A. variation.
B. inheritance.
C. cell theory.
D. courtship behaviour.
83. Which factor is most likely responsible for the various types of comb?
A. Environment
B. Genetics
C. Physiology
D. Morphology
84. An accident victim was successfully transfused with blood from the father whose blood group is AB. The blood group of the accident victim is
A. B.
B. O.
C. AB.
D. A.
85. Which of the following traits in humans is a example of physiological variation?
A. Skin colour
B. Fingerprint
C. Tongue rolling
D. Height
86. Individuals belonging to blood group O are universal donors because
A. antigens are absent in their blood cells.
B. members of the group constitute the highest number of humans.
C. there are no antibodies in their blood plasma.
D. the antigens in their blood cells are easily destroyed.
87. Which of the following characteristics shows discontinuous variation in plants?
A. Colour of flower.
B. Height of plant.
C. Leaf size.
D. Fruit size.
THEORY
1. (a) What is variation?
(b) State five advantages of variation within a species.
(c) In a tabular form, outline four differences between continuous and discontinuous variations
(d) Explain the following terms:
(i) Sex-linked characters;
(ii) Co-Dominance;
(iii) Hybrid vigour.
2. List four characteristics which can be genetically transmitted in humans.
3. (a) What is the difference between the genotype and phenotype of an individual?
(b) State two factors each which determine each of the terms.
4. Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype.
5. List four characters which can be transmitted from parent to offspring in man.
6. (a) List three transmittable characters in human beings
(b)List three transmittable characters in plants
(c) Define the law of independent assortment
(d)State the findings from Mendel’s experiment involving white-flowered and red-flowered pea plants
(e) Illustrate these findings by means of simple diagrams.
7. Explain briefly the following terms:
(i) Phenotype;
(ii) hybrid;
(iii) dominant character.
8. Explain the term:
(i) trait
(ii) recessive gene
(iii) test cross
(iv) heterozygous.
9. State Mendel’s first and second laws of inheritance.
10. Explain briefly:
(i) independent assortment of genes.
11. (a) Name four types of fingerprints in humans.
(b) (i) Name the plant used by Gregor Mendel in his experiment.
(ii) State two reasons why the plant named in (b)(i) was used.



