Summary of the Topic:
The interaction between a cell and its environment is fundamental to understanding biological processes. This topic delves into the mechanisms by which substances move into and out of cells, including:
- Diffusion: Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- Osmosis: Movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration.
- Active Transport: Movement of substances against a concentration gradient, requiring energy.
These processes are vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis and are frequently tested in WAEC Biology examinations.
Key Concepts Explained:
1. Diffusion:
A passive process where molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration until equilibrium is achieved. It does not require energy.
2. Osmosis:
A specific type of diffusion involving water molecules moving through a semi-permeable membrane from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one.
3. Active Transport:
An energy-dependent process where cells transport molecules against a concentration gradient, from areas of lower concentration to higher concentration.
4. Plasmolysis:
Occurs when a plant cell loses water in a hypertonic solution, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the cell wall.
5. Turgidity:
The state of being swollen or firm due to water intake, crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of plant cells.
6. Cyclosis:
The streaming movement of the cytoplasm within a cell, aiding in the distribution of nutrients and organelles.
7. Contractile Vacuole Activity:
In freshwater protozoa like Amoeba, contractile vacuoles expel excess water to prevent bursting due to osmotic pressure.
Example WAEC-Style Questions (With Explanations):
Q1: The opening of the guard cells of the epidermis in plants is by the process of:
Answer: Osmosis
Explanation: Water enters guard cells by osmosis, making them turgid and causing the stomata to open.
Q2: When a Spirogyra filament is placed in a concentrated salt solution for 30 minutes, the cell would become:
Answer: Plasmolysed
Explanation: Water leaves the cell due to osmosis, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall.
Q3: The streaming movement of cytoplasm within Paramecium is known as:
Answer: Cyclosis
Explanation: Cyclosis facilitates the movement of materials within the cell.
Q4: If Amoeba is placed in a salt solution, the contractile vacuoles would:
Answer: Be formed less frequently
Explanation: In a hypertonic solution, less water enters the cell, reducing the need for expulsion by contractile vacuoles.
Q5: Active transport can be defined as the movement of:
Answer: Substances from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration across a living cell membrane, using energy.
Explanation: This process requires energy to move substances against the concentration gradient.
(Continue with additional questions as provided in your original post, ensuring each is accompanied by a clear explanation.)
Study Tips:
- Understand Key Processes: Grasp the differences between diffusion, osmosis, and active transport, including their energy requirements and directions of movement.
- Visual Aids: Utilize diagrams to visualize processes like plasmolysis and turgidity.
- Relate to Real-Life Examples: Connect concepts to everyday phenomena, such as the wilting of plants due to water loss.
- Practice Past Questions: Regularly solve past WAEC questions to familiarize yourself with the question patterns and improve your answering techniques.
- Create Summary Tables: Develop comparative tables for different transport mechanisms to reinforce understanding.
Conclusion:
A thorough understanding of how cells interact with their environment is crucial for mastering biology concepts. This topic not only explains fundamental life processes but also lays the groundwork for more advanced studies. To reinforce your learning, proceed to the WAEC past questions provided below, which offer practical application of the concepts discussed.
OBJECTIVES
5. The opening of the guard cells of the epidermis in plants is by the process of
A. osmosis.
B. diffusion.
C. active transport.
D. transpiration.
6. When a spirogira filament is placed in a concentrated salt solution for 30 minutes, the cell would become
A. plasmolysed.
B. turgid.
C. shortened.
D. elongated.
7. The streaming movement of cytoplasm withi Parames is known as
A. transpiration.
B.Digestion
C. cyclosis.
D, osmosis.
8. If Amoeba is placed a salt solution the contractile vacuoles would
A. be bursting more frequently.
B. be more numerous.
C. be formed less frequently
D. grow bigger before they burst.
9. Active transport can be defined as the movement of
A substances from a region of high concentration to a Environment region of low concentration.
B. substances from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration across a living cell membrane.
C. substances across a living cell membrane using energy from the cell.
D. movement of molecules in a medium.
10. In which of the following yam tissues will osmosis occur?
A. Boiled and peeled.
B. Raw and peeled.
C. Boiled and unpeeled.
D. Roasted and peeled
11. Which of the following processes takes place when a plant cell is put in a hypotonic solution?
A. Water moves into the cell and the cell bursts.
B. Water leaves the cell and the cell becomes flabby.
C. Water moves into the cell and the cell becomes turgid.
D. The cell becomes plasmolysed.
12. Which of the following processes involves diffusion?
A. Opening and closing of stomatal pores.
B. Turgidity of herbaceous plants.
C. Absorption of water through the root hairs.
D. Absorption of digested food into the villi.
13. The mechanism of opening and closing of stomata in plants is based on
A. turgidity and diffusion.
B. turgidity and flaccidity.
C. osmosis and diffusion.
D. diffusion and flaccidity.
14. An example of osmosis in plants is the
A. movement of water through the xylem.
B. loss of water vapour from the stomata.
C. translocation of food through the phloem.
D. absorption of water from the soil by the root.
15. Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a weaker solution to a stronger
solution is known as
A. transpiration.
B. diffusion.
Cactive transport.
D. osmosis.
16. Amoeba obtains its oxygen requirements
A. from oxidising food substances.
B. from air trapped in vacuoles.
C. through diffusion of air into its body.
D. through an air cavity in the ectoplasm.
17. Which of the following will cause wilting in plants?
A. Humidity.
B. Coldness.
C. Adequate soil water.
D. Excessive transpiration.
18. Which of the following statements is incorrect about diffusion?
A. It involves degradation of soluble particles in solvents.
B. it occurs mainly in gaseous and liquid media.
C. No membrane is needed to effect the movement of molecules.
D. Molecules move from region of lower concentration to that of higher concentration.
19. Diffusion is most effective in living organisms, when the surface area is
A. large and the thickness is also large.
B. small while the thickness is large.
C. large while the thickness is small.
D. the same as its thickness.
20. Which of the following is used to measure the rate of water uptake in plants?
A. Potometer.
B. Hydrometer.
C. Hygrometer.
D. Aspirator.
21. In active transport, molecules move against a concentration gradient therefore
A. molecules move from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration.
B. molecules move from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
C. the concentration gradient has little effect on the movement of molecules.
D. molecules force their way through special channels.
22. Which of the following substances pass through the root cell membrane by osmosis
A. Cell sap.
B. Carbon dioxide.
C. Oxygen.
D. Water.
23. Which of the following statements defines plasmolysis
A. Shrinking of a plant cell in a solution.
B. Shrinking away of cytoplasm from an animal cell membrane.
C. Shrinking away of the cytoplasm from the plant cell wall.
D. Shrinking of the vacuole and leaving the cytoplasm attached to the cell wall.
24. Which of the following processes occurs by diffusion?
A. Reabsorption of water in kidney tubules.
B. Entry of water into the cytoplasm of unicellular animals.
C. Absorption of water in the large Intestine.
D. Exchange of nutrients between a mother and the foetus.
The diagram below illustrates the structure of Euglena. Use it to answer questions 25
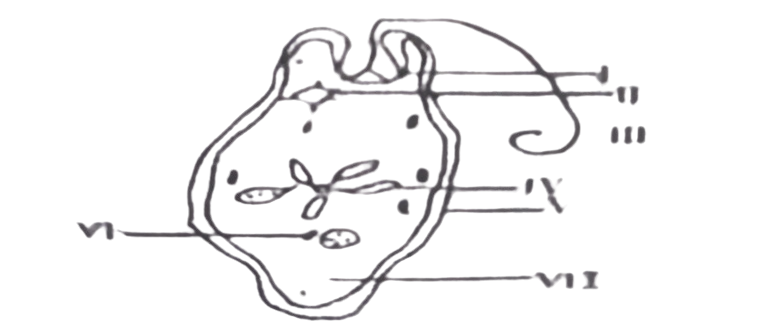
25. Which of the following structures is responsible for osmoregulation?
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
26. The process by which a drop of ink spreads uniformly In a beaker of water is called
A. absorption.
B. osmosis.
C. plasmolysis.
D. diffusion.
27. Osmosis can be defined as diffusion of
A. atoms and molecules through a membrane to an area of higher concentration.
B. water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution across a permeable membrane.
C. water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
D. water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi-permeable membrane.
28. Green plants lose water to the atmosphere through the process of
A. respiration.
B. photosynthesis.
C. transpiration.
D. translocation.
Study the diagram below. Use it to answer questions 29 – 31.
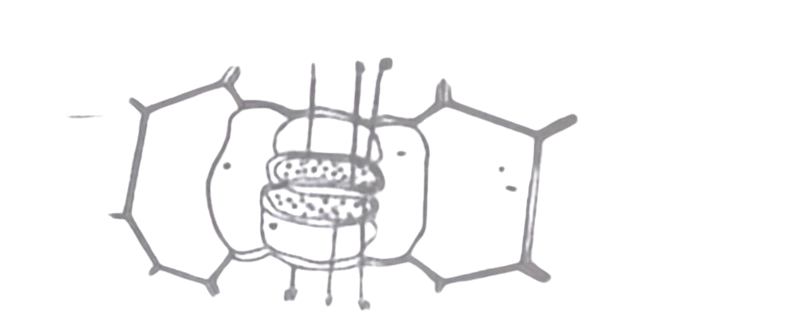
29. Which of the labelled structures in the diagram will shrink when plasmolysis occurs
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
30. The condition shown in the above diagram is due to
A. conversion of starch to sugar.
B. conversion of sugar to starch.
C. excess water in structure labelled 1.
D. presence of carbon dioxide in the structure labeled 1.
31. Which of the following solutions will induce the condition shown in the diagram?
A. Hypertonic solution.
B. Hypotonic solution.
C. Isotonic solution.
D. Distilled water.
32. One major difference between osmosis and diffusion is that diffusion
A. does not need a semi permeable membrane.
B. does not take place in living tissues.
C. takes place only in a liquid medium.
D. takes place only in a gaseous medium.
33. During the process of osmosis a semi-permeable membrane allows
A. only solute molecules to pass through it.
B. both solute and solvent molecules to pass through it.
C. solvent molecules to pass through it.
D. only gaseous molecules to pass through it.
34. A piece of yam weighing 1.0 gm was put into some salt solution. After 3 hours, it was removed and
weighed. The recorded weight was 1.2gms. This simple experiment demonstrates that the
A. salt solution is more concentrated than the cell sap of the yam.
B. cell sap of the yam is more concentrated than the salt solution.
C. salt solution has the same concentration as the cell sap of the yam.
D. the yam lost some water molecules to the salt solution.
35. Which of the following environmental conditions is ideal for plant cells to remain turgid
A. Hot, dry weather.
B. Windy weather.
C. Cold, dry weather.
D. Cool, humid weather.
36. Four cells with osmotic potential equivalent to that of 3% salt solution were immersed respectively in
solutions of different concentrations labelled as follows: I=4% salt solution; II = 6% salt solution; III =
1% salt solution; IV = 10% salt solution; V = 5% salt solution. Which of the solutions will cause an increase in osmotic pressure within the cell?
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
37. Which of the following statements is not true of osmotic process?
A. There must be a selectively permeable membrane.
B. The two solutions must be of different concentrations initially.
C. It involves only the movement of water molecules.
D. The two solutions are of equal concentration at the beginning of experiment.
38. Which of the following statements is correct about diffusion?
A. It involves the movement of water molecules only.
B. Molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
C. Differentially permeable membrane must be present for diffusion to occur.
D. it involves the movement of only solute molecules into the Bowman’s capsule.
39. The main reason why rotten eggs should be separated from fresh eggs is that
A. foul air from the rotten eggs could easily diffuse through the shells of fresh eggs.
B. fresh eggs could easily crack if foul air diffuses into it.
C. It is difficult to get rid of foul air on egg shells.
D. a fresh egg shrinks if foul air diffuses into it.
40. Transpiration in plants results in the A. closure of the stomata at night.
B. continuous streaming of water through the plant.
C. pale, green Colouration of portions of the leaves.
D. opening of stoma.
41. The loss of water vapour through the aerial parts of the plant to the atmosphere is called
A. respiration.
B. guttation.
C. osmoregulation.
D. transpiration.
42. Turgidity in the cell of plant does not easily lead to bursting of the cell because the
A. cell membrane can resist the turgidity.
B. large vacuole contained in the cell, can continuously take in water.
C. cellulose cell wall can resist the turgidity.
D. cytoplasm is jelly- like.
43. The cell membrane of a cell is said to be semi-permeable because
A. it allows only large molecular substances to pass through it into the cell.
B. it is actively involved in energy production in the cell.
C. it actively allows all substances to pass through it by diffusion.
D. it is actively selective in allowing substances pass through it.
44. Turgor pressure occurs in a cell when the
A. volume of its cell sap increases.
B. cell loses water to its environment.
C. volume of cell decreases.
D. cell is put in an isotonic solution.
The diagram below illustrates an experimental set up. Use it to answer questions 45 and 46

45. The part labelled I is
A. a microorganism.
B. a developing insect.
C. a water droplet.
D. an oil droplet.
46. The function of the part labelled II is to
A. prevent the entry of Insects into the soil.
B. prevent the entry of light into the soil.
C. make the container air tight.
D. prevent evaporation from the soil.
47. Which of the following can be used to detect the loss of water vapour from the leaves of plants?
A. Hydrated copper sulphate.
B. Blue litmus paper.
C. Red litmus paper.
D. Blue cobalt chloride paper.
48. Which of the following is not true about a potted plant left in the laboratory for one week without
watering?
A. the cells of the plant will be turgid.
B. there will be wilting of the plant.
C. the leaves are likely to turn yellow.
D. plant will not take in enough nutrient.
49. The rate of diffusion of molecules between two media will be higher if
A. the difference in concentration of the two media is low.
B. the difference in concentration of the two media is negligible.
C. the difference in St concentration of the two media is high.
D. there is no difference in the concentration of the two media.
50. Which of the following materials is not a living semi-permeable membrane?
A. Pig’s bladder
B. Unripe pawpaw fruit
C. Yam tuber
D. Sheet of cellophane.
51. A plant cell placed in the a solution with a higher water potential will
A. expand and then shrink.
B. enlarge and become.
C. expand and then burst.
D. decrease in size and become flaccid.
52. The process that brings about the shrinking of a Spirogyra cell when placed in a strong solution is
A. osmosis
B. autolysis.
C. plasmolysis.
D. diffusion.
53. The process by which the amount of water and solutes in the blood are controlled is known as
A. haemolysis.
B. diffusion.
C. turgidity.
D. osmoregulation.
54. An example of a process that involves osmosis is the
A. movement of digested food from ileum into blood capillaries.
B. translocation of starch from leaves to all parts of a plant.
C. reabsorption of food nutrients from the kidney into blood capillaries.
D movement of water from root hairs into cortical cell.
THEORY
1. What role do the following processes play in the activities of a living cell?
(i) osmosis (ii) diffusion
2. (a) Explain the term osmosis (b)(i) Explain what happens to a red blood cell when placed in a hypotonic solution (ii) Mention three conditions that may cause haemolysis.


