Summary of the Topic:
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biological process through which cells convert nutrients into energy (ATP), essential for various cellular activities. This process occurs in all living organisms and can be classified into two main types:
- Aerobic Respiration: Requires oxygen and produces a significant amount of energy.
- Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs without oxygen and yields less energy.
Understanding the stages, products, and differences between these types is crucial for mastering this topic.
Key Concepts Explained:
1. Definition of Respiration:
- Respiration is the biochemical process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to release energy in the form of ATP.
2. Types of Respiration:
- Aerobic Respiration:
- Occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Produces a large amount of ATP.
- Involves three main stages:
- Glycolysis: Breakdown of glucose into pyruvate.
- Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Further breakdown of pyruvate, releasing CO₂, and transferring electrons to carrier molecules.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): Electrons from carriers are transferred through protein complexes, producing ATP and water.
- Overall Equation:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP)
- Anaerobic Respiration:
- Occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- Produces less ATP compared to aerobic respiration.
- In animals, results in the production of lactic acid.
- In yeast and some plants, produces ethanol and CO₂.
- Overall Equations:
- In animals:
C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₃H₆O₃ + Energy (ATP) - In yeast:
C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂ + Energy (ATP)
- In animals:
3. Importance of Oxygen in Respiration:
- Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling the production of a large amount of ATP.
- Without oxygen, cells resort to anaerobic pathways, which are less efficient.
4. Oxygen Debt:
- Oxygen debt refers to the amount of extra oxygen the body needs to oxidize lactic acid to carbon dioxide and water after anaerobic respiration, particularly following intense physical activity.
5. Differences Between Gaseous Exchange and Aerobic Respiration:
| Feature | Gaseous Exchange | Aerobic Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Lungs, gills, skin | Mitochondria |
| Purpose | Exchange of gases (O₂ and CO₂) | Production of ATP |
| Process | Passive diffusion | Biochemical reactions |
| Energy Produced | None | ATP |
Example WAEC-Style Questions (With Explanations):
Q1: In cellular respiration, energy is made available to organisms by:
A. Removal of a phosphate group from ADP.
B. Breaking off a phosphate group from ATP.
C. Adding a phosphate group to glucose.
D. Breaking off a hydrogen ion from NADPH.
Answer: B. Breaking off a phosphate group from ATP.
Explanation: ATP releases energy when a phosphate group is removed, forming ADP.
Q2: Respiration is an essential life process providing living cells with:
A. Oxygen.
B. Sugars.
C. Energy.
D. Carbon dioxide.
Answer: C. Energy.
Explanation: The primary purpose of respiration is to provide energy for cellular activities.
Q3: A group of rats placed in an airtight box for some hours died because they:
A. Breathed in air containing nitrogen.
B. Produced carbon dioxide.
C. Ran short of energy.
D. Used up the available oxygen.
Answer: D. Used up the available oxygen.
Explanation: In an airtight box, oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide accumulates, leading to suffocation.
Q4: The muscle cell fluid of an athlete was tested immediately after a 100 m race and was found to contain a high concentration of lactic acid. This indicates that the:
A. Athlete must have eaten food containing lactic acid just before the race.
B. Athlete must have injected lactic acid into his blood just before the race.
C. Athlete’s muscles must have carried out anaerobic respiration during the race.
D. Athlete must have inhaled lactic acid from the environment during the race.
Answer: C. Athlete’s muscles must have carried out anaerobic respiration during the race.
Explanation: Intense exercise can lead to anaerobic respiration in muscles, producing lactic acid.
Q5: Anaerobic respiration results in the production of:
A. More energy than aerobic respiration.
B. No energy.
C. An equal amount of energy to aerobic respiration.
D. Less energy than aerobic respiration.
Answer: D. Less energy than aerobic respiration.
Explanation: Anaerobic respiration produces less ATP compared to aerobic respiration.
Q6: Krebs cycle occurs in the:
A. Mitochondria.
B. Cytoplasm.
C. Nucleus.
D. Ribosomes.
Answer: A. Mitochondria.
Explanation: The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
Q7: Which of the following are the final products of aerobic respiration?
A. Water, carbon dioxide, and energy.
B. Pyruvic acid, carbon dioxide, and water.
C. Glucose, energy, and urea.
D. Energy and carbon dioxide.
Answer: A. Water, carbon dioxide, and energy.
Explanation: The end products of aerobic respiration are water, carbon dioxide, and ATP.
Q8: In aerobic respiration, oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the:
A. Cytoplasm.
B. Mitochondria.
C. Lysosome.
D. Vacuoles.
Answer: B. Mitochondria.
Explanation: Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Q9: The role of ATP includes all the following activities except:
A. Provision of energy to do work in living organisms.
B. Transmission of nerve impulses.
C. Keeping the body warm in homeothermic animals.
D. Producing water during aerobic respiration.
Answer: D. Producing water during aerobic respiration.
Explanation: While water is a byproduct of aerobic respiration, ATP’s primary role is energy transfer.
Q10: When a mammal respires anaerobically for a long time:
A. Pyruvic acid is converted into acetyl CoA.
B. More energy is released from fats in the body.
C. Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles.
D. The Krebs cycle is fully completed.
Answer: C. Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles.
Explanation: Prolonged anaerobic respiration leads to the accumulation of lactic acid in muscles.
Q11: In cellular respiration, energy is stored in the form of:
A. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
B. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
C. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
D. Heat energy.
Answer: C. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Explanation: ATP is the primary energy carrier in cells.
Q12: The process of anaerobic respiration in yeast in sugar solution is known as:
A. Oxidation.
B. Fermentation.
C. Tissue respiration.
D. Alcohol production.
Answer: B. Fermentation.
Explanation: Yeast undergoes fermentation in the absence of oxygen, producing ethanol and CO₂.
Q13: In the anaerobic stage of respiration, the net ATP molecules produced per glucose molecule is:
A. One.
B. Two.
C. Three.
D. Four.
Answer: B. Two.
Explanation: Anaerobic respiration yields 2 ATP per glucose molecule.
Q14: During anaerobic respiration in skeletal muscles, pyruvic acid is:
A. Reduced to lactic acid.
B. Oxidized to ethanol.
C. Oxidized to lactic acid.
D. Reduced to water.
Answer: A. Reduced to lactic acid.
Explanation: In anaerobic conditions, pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid in muscles.
Q15: Muscle fatigue in the body of an athlete is due to:
A. Low pH.
B. High oxygen content.
C. Accumulation of lactic acid.
D. Accumulation of carbonic acid.
Answer: C. Accumulation of lactic acid.
Explanation: Lactic acid accumulation lowers pH, leading to muscle fatigue.
Q16: Anaerobic respiration in the organism illustrated in the diagram below produces carbon dioxide and:
A. Ethanol.
B. Water.
C. Oxygen.
D. Glucose.
Answer: A. Ethanol.
Explanation: Yeast produces ethanol and CO₂ during anaerobic respiration.
Q17: In an experiment, mould and yeast cells were transferred into an environment with low oxygen concentration. After a few days, the mould died while the yeast cells did not. Which of the following statements best explains the above observation?
A. The yeast cells carried out photosynthesis while the mould did not.
B. Photosynthesis does not take place in the absence of oxygen.
C. Respiration can take place in yeast cells in the absence of oxygen.
D. Respiration does not occur in the mould.
Answer: C. Respiration can take place in yeast cells in the absence of oxygen.
Explanation: Yeast can perform anaerobic respiration, while mould requires oxygen.
Q18: The reagent used in testing for carbon (IV) oxide is:
A. Copper sulphate solution.
B. Lime water.
C. Hydrochloric acid.
D. Sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer: B. Lime water.
Explanation: Lime water turns milky in the presence of CO₂.
Study Tips (continued):
- Understand the Stages: Familiarize yourself with the stages of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration — glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and fermentation. Know where each occurs and what happens.
- Memorize Key Equations: Learn the overall chemical equations for aerobic and anaerobic respiration, including products formed.
- Use Diagrams: Draw and label mitochondria and the stages of respiration to visualize the processes.
- Practice Past Questions: Regularly answer WAEC-style questions on cellular respiration to get comfortable with the question formats and commonly tested concepts.
- Focus on Definitions: Be clear on terms like oxygen debt, fermentation, ATP, and lactic acid.
- Compare and Contrast: Create tables comparing aerobic vs anaerobic respiration, including energy yield, products, and conditions.
- Relate to Real Life: Connect concepts to real-life examples, like muscle fatigue during exercise and yeast fermentation in baking.
Conclusion:
Studying cellular respiration is essential for mastering WAEC Biology. The questions above cover many important areas, and practicing them will boost your confidence and understanding.
Past WAEC questions on cellular respiration and other related topics are available below for you to study with. Use them to test yourself and prepare well for the exams.
OBJECTIVES
1. In cellular respiration energy is made available to organisms by
A. removal of a phosphate group from ADP.
B. breaking off a phosphate group from ATP.
C. adding a phosphate group to glucose.
D. breaking off a hydrogen ion from NADPH.
2. Respiration is an essential life process providing the living cells with
A. oxygen.
B. sugars.
C. energy.
D. carbon dioxide.
3. A group of rats placed in an air-tight box for come hours died because they
A. breathed in air containing nitrogen.
B. produced carbon dioxide.
C. ran short of. energy.
D. used up the available oxygen.
4. The muscle cell fluid of an athlete was tested immediately after a 100 m race and was found to contain a high concentration of lactic acid. Explain what could have caused this. The
A. athlete must have eaten food containing lactic acid just before the race.
B. Athlete must have injected lactic acid into his blood just before the race.
C. athlete’s muscle must have carried out anaerobic respiration during the race.
D. athlete must have inhaled lactic acid from the environment during the race.
5. Anaerobic respiration results in the production of
A. more energy than aerobic respiration.
B. no energy.
C., an equal amount of energy to aerobic respiration.
D. less energy than aerobic respiration.
6. Kreb’s cycle occurs in the
A. mitochondria.
B. Cytoplasm.
C. nucleus.
D. ribosomes.
7. Which of the following are the final products of aerobic respiration?
A. Water, carbon dioxide and energy.
B. Pyruvic acid, carbon dioxide and water.
C. Glucose, energy and urea.
D. Energy and carbon dioxide.
8. In aerobic respiration, oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the
A. cytoplasm.
B. mitochondria.
C. lysosome:
D. vacuoles.
9. The role of ATP include all the following activities except
A. provision of energy to do work in living organisms.
B. transmission of nerve impulse.
C. keeping the body warm in homoithermic animals.
D. producing water during aerobic respiration.
10. When a mammal respires anaerobically for a long time
A. pyruvic acid is converted into acetyl COA.
B. more energy is released from fats in the body.
C. lactic acid accumulates in the muscles.
D. the Kreb’s cycle is fully completed.
11. In cellular respiration, energy is stored in the from
A. adenosine diphosphate (AD).
B. adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
C. adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
D. heat energy.
12. The process of anaerobic respiration of yeast in. sugar solution is known as
A. oxidation.
B. fermentation.
C. tissue respiration.
D. alcohol production.
13. In the anaerobic stage of respiration, the net ATP molecules produced per glucose molecule is
A. one.
B. two.
C. three.
D. four.
14. During anaerobic respiration in skeletal muscles, pyruvic acid is
A. reduced to lactic acid.
B. oxidised to ethanol.
C. oxidised to lactic acid.
D. reduced to water.
15. Muscle fatigue in the body of an athlete is due to
A. low pH.
B. high oxygen content.
C. accumulation of lactic acid.
D. accumulation of carbonic acid.
16. Anaerobic respiration in the organism illustrated in the diagram below produces carbon dioxide and

A. ethanol.
B. water.
C. oxygen.
D. glucose.
17. In an experiment, mould and yeast cells were transferred into an environment with low oxygen concentration. After a few days, the mould died while the yeast cells did not. Which of the following statements best explains the above observation?
A. The yeast cells carried out photosynthesis while the mould did not
B. Photosynthesis does not take place in the absence of oxygen
C. Respiration can take place in yeast cells in the absence of oxygen
D. Respiration does not occur in the mould.
18. The reagent used in testing for carbon (IV) oxide is
A. Copper sulphate solution.
B. Lime water.
C. Hydrochloric acid.
D. Sodium hydroxide solution.
The diagram below is an illustration of a mango leaf drawn by a student in a Biology test. The student failed the test. Study it and answer questions 19 and 20.
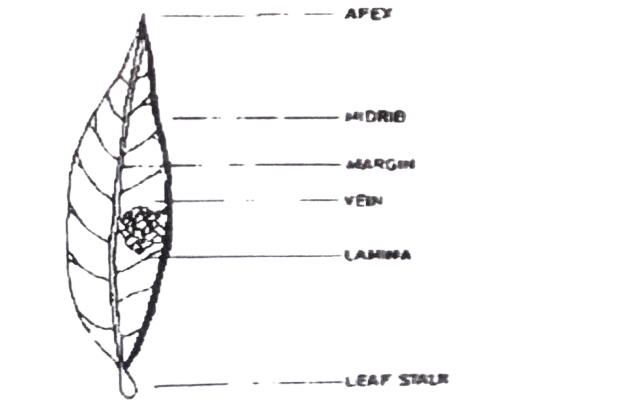
19. The likely reason why the student failed the test was that the
A. labels were wrong and the guidelines were not touching the structures.
B. net venation shown were few, rough, not properly drawn and wrongly placed.
C. leaf was too tapered at the apex, the leaf stalk was too short and the shape of leaf was wrong.
D. leaf venation should have been parallel and the midrib should be thicker.
20. Which other features of the diagram, if shown, would have earned the student more marks? The
A. colour and size.
B. title and magnification.
C. habitat and agricultural qualities of leaf.
D. spelling of label and length of midrib.
THEORY
1. (a) What is respiration? (b) What is oxygen debt. (c) Outline three activities that can result in oxygen debt. (d) In a tabular form, state four differences between gaseous exchange and aerobic respiration.
2. Write the chemical equation for each of the following processes (a) aerobic respiration (b) anaerobic respiration in plant (c) anaerobic respiration in animal.
3. (a) Describe briefly the process involved in the breakdown of glucose in the cell of living organisms to produce energy (ATP) (b) State two conditions under which glycogen can be converted to glucose to produce energy.
4. Name the two types of respiration and write a balanced equation to summarize each of them.


