OBJECTIVES
1. Which of the following processes occurs in the second phase of meiosis?
A. Homologous chromosomes separate.
B. Two daughter cells are formed.
C. Fertilization occurs.
D. Segregation of genes occurs.
2. Which of the following statements about chromosomes is correct?
A. All the chromosomes of a species are the same in shape.
B. The number present in a species is constant.
C. They are neatly arranged in the cytoplasm.
D. They bear ribosomes on their outer membranes.
The following diagrams show the sequence of events in early cell division. Study the diagrams and answer question 3.

3. In which of the following cells is this division likely to take place?
A. sperm cell.
B. blood cell.
C. muscle cell.
D. uterine cell.
4. In the structure of DNA, which of the following statements is true?
A. Ac double helix are held together by covalent bonds.
B. Nucleotide is made up of ribose, phosphate and an organic nitrogen compound.
C. Guanine is the opposite of cytosine.
D. Adenine is the opposite of cytosine.
5. What name is given to a sudden change in a gene or chromosome?
A. Allele.
B. Genotype.
C. Mutation.
D. Phenotype.
6. The sudden change in a gene structure or chromosome number in an organism likely to cause an inheritable change in the phenotype is known as
A. migration.
B. mutation.
C. mitosis.
D. meiosis.
7. How many chromosomes will be in a gamete if the normal cell has four chromosomes?
A. 2.
B. 4.
C. 6.
D. 8.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 8&9
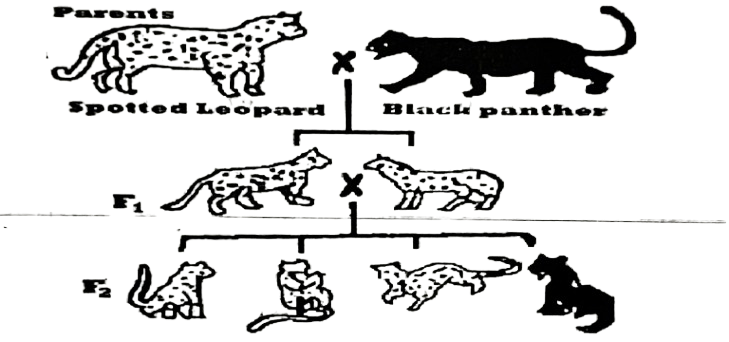
8. Which of the following statements about the cross is correct?
A. the gene for the spotted coat is recessive to the gene for the black coat.
B. black coat and spotted coat are dominant.
C. the gene for the spotted coat is dominant over the gene for the black coat.
D. the genotype for the F1 are homozygous dominant.
9. What are the genotypes of the parents if the gene for skin colour is H?
| Spotted Leopard | Black Panther | |
| A | HH | Hh |
| B | HH | Hh |
| C | Hh | Hh |
| D | Hh | Hh |
10. Which of the following statements about sex-linked characters is not true?
A. They are usually borne on the X-chromosome.
B. They are more common in males.
C. Males are usually carriers.
D. They are not usually carried on the Y chromosomes.
11. DNA formation is associated with
A. Golgi bodies
B. tysosomes.
C. mitochondria.
D. nucleus.
12. In genetics, linkages refer to the linking of genes of the
A. same chromosomes.
B. different chromosomes.
C, same nucleus.
D. different nuclei.
13. A gene that is only located on X-chromosome is said to be
A. expressed in females only.
B. defective.
C. sex-linked.
D. expressed in males only.
14. An apple plant can produce sexually and asexually and it has 40 chromosomes in its leaf cells. How many chromosomes would be in each gamete and somatic cell
A. 20 chromosomes in the gametes and 10 in the somatic cells.
B. 40 chromosomes in the gametes and 20 in the somatic cells.
C. 20 chromosomes in the gametes and 40 in the somatic cells.
D. 40 chromosomes in the gametes and 40 in the somatic cells.
15. What will be the chromosome number of the hybrid for two varieties of a plant with 36 chromosomes in the endosperm cell?
A. 12.
B. 24.
C. 36.
D. 48.
16. In a family of eight (8), all the children are girls. Which of the following reasons correctly explains this?
A. The woman cannot produce male children.
B. The man has a low sperm count.
C. The Y component of the man’s sex chromosome was always involved.
D. The X component of the man’s sex chromosome was always involved.
17. Which of the following statements is correct about the structure of a chromosome? A chromosome consists of
A. two chromatids joined at the centromere.
B. two chromatids joined at the spindle.
C. two chromatin threads joined at the centrioles.
D. thread-like structures not joined together.
18. The exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes is called
A. crossing over.
B. back cross.
C. test cross.
D. mutation.
The diagrams below are illustrations of the inheritance of coat colour in mice. J, K, L, M and N are parents. The cross between two parent mice gave rise to offspring P,Q, R and S.
Study the diagrams and answer questions 19 & 20

19. Which parent mouse is heterzygnous for coat colour
A. M. B. J. C. K. D. L.
20. Which of the offspring are all homozygous
A. P.
B. Q.
C. S.
D. R.
21. A plant cell has 14 chromosomes prior to mitosis. What is the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells
A. 14.
B. 56.
C. 28
D. 7.
22. What does the chemical composition of the genetic material of all living organisms consist of?
A. Deoxyribonucleic acid.
B. Adenosine diphosphate.
C. Adenosine triphosphate.
D. Follicle stimulating hormone
23. Which of the following occurrences is not a feature of meiosis?
A. Formation of four haploid cells.
B. Two successive nuclear cell divisions.
C. Pairing of homologous chromosomes at prophase.
D. Formation of two diploid cells.
24. The chemical bond that holds the bases of the two strands of DNA together is
A. oxygen bond.
B. hydrogen bond.
C. electrovalent bond.
D.-covalent bond.
25. Which of the following statements is true about mutation
A. Phenotype is not involved.
B. Genotype is not involved.
C. Artificial induction is not possible.
D. Genotype is involved.
26. The following statements about mitotic cell division are correct except that
A. it occurs only in young cells
B. it occurs in somatic cells
C. the chromosome number of the daughter cell is the same as that of the parent.
D. the genetic composition of the mother cell is the same as that of the daughter cell.
27. Cytokinesis of mitosis Is a process that ensures that
A. each daughter cells gets the necessary organelle
B. there is distribution of a complete set of genes into each daughter cell.
C. daughter cells inherit new genetic combinations
D. worn out organelles are excluded from daughter cells.
28. In which of the following structures will cells undergoing meiosis be seen?
A. At the apices of stem and root.
B. In the cortex of the stem.
C. In the palisade mesophyll of the leaf.
D. In the ovary of a flower.
Study the diagram below and use it to answer Questions 29
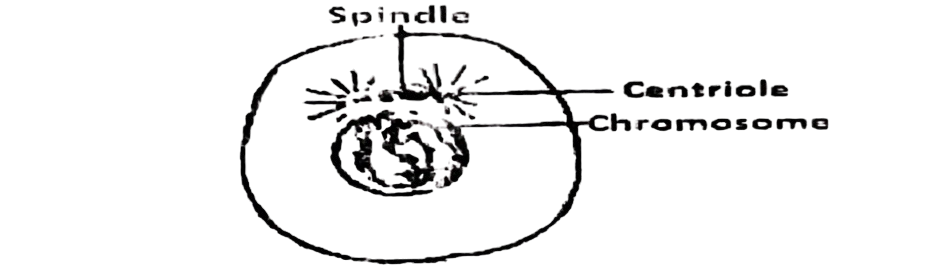
29. What stage of mitotic division is represented in the diagram of the cell illustrated above?
A. Prophase.
B. Telophase.
C. Anaphase.
D. Metaphase.
30. This stage of mitosis is characterized by the.
A. movement of the chromosomes to the poles.
B. arrangement of chromosomes on the equatorial plate.
C. centromeres moving apart along the spindle.
D. condensation.
31. At the end of mitosis the number of cells produced from a parent cell is
A. four.
B. six.
C. eight.
D. two.
32. At which of the following stages of mitosis do the two daughter chromosome separate completely
A. Early prophase.
B. Telophase.
C. Anaphase.
D. Metaphase.
Below is a drawing of a Stage in mitosis. Use to answer questions 33 and 34.
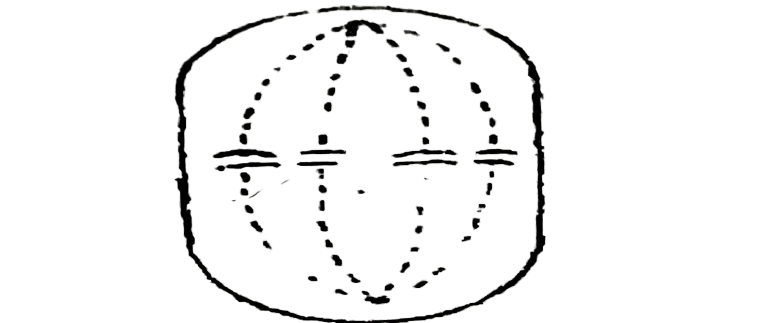
33. Which of the following processes is not evident from the drawing?
A. Lining up of the chromosomes at the equatorial plate.
B. Centromere attaching a pair of chromatids to a spindle fibre.
C. Chromatids held by centromere.
D. Absence of nuclear membrane.
34. The stage of mitosis represented in the diagram is known as the
A. telophase.
B. metaphase.
C. anaphase.
D. interphase.
35. Which of the following statements is not true about chromosomes?
A. Each chromosome is made up of two chromatids.
B. Body cells have diploid numbers of chromosomes.
C. Homologous chromosomes do not occur in pairs naturally.
D. The sex cells have haploid number of chromosomes.
36. Which of the following is the unit of transmission of hereditary traits in living organism
A. Nucleus.
B. Nucleolus.
C. Gametes.
D. Genes.
37. The name given to a sudden change in a gene or chromosome that can be passed on to the offspring
is
A. inheritance.
B. linkage.
C. alleles.
D. mutation.
38. In humans, sex is determined by
A. two homologous chromosomes.
B. a dominant gene for maleness present in a male.
C. two similar sex chromosomes in the male and dissimilar in the female.
D. the differences in the nature of the X and Y chromosomes in the male.
39. The genes affecting the same trait and are located at the same position on the homologous chromosomes are called
A. autosomes.
B. alleles.
C. loci.
D. chromatids.
40. Which of the following is a function of the chromosome?
A. Transmission of hereditary traits.
B. Protein synthesis.
C. Excretion.
D. Energy production.
41. Which of the following statements best explains the meaning, of homologous chromosomes?
A. Product of division of chromosomes.
B. Two identical chromosomes from each parent.
C. Chromosomes arranged on spindle fibre during cell division.
D. Chromosomes arranged on the equatorial plate of the cell.
42. Which of the following statements about mutation is true
A. The genotype is not affected.
B. The genotype is affected.
C. The phenotype is not affected.
D. It cannot be induced by artificial means.
43. Which of the following is not a correct base pairing on the DNA strand
A. Adenine, Thymine.
B. Cytosine, spring Guanine.
C. Guanine, Cytosine.
D. Uracil, Thymine.
44. Which of the following processes is responsible for the increase in length and dry mass in a root tips?
A. Meiosis.
B. Absorption.
C. Mitosis.
D. Conjugation.
45. Which of the following is found in Meiosis but not in Mitosis?
A. Chromatids.
B. Prophase.
C. Crossing over.
D. Spindle fibres.
46. Which of the following statements is not correct about sex-determination
A. Females contribute half of the sex chromosomes.
B. Males contribute an X or Y chromosome.
C. Females contribute only the X chromosome.
D. Females alone determines the sex of child.
47. Which of the following is the precise location of the gene
A. Chromosome.
B. Centresome.
C. Centriole.
D. Ribosome.
48. How many chromosomes are found in the human ovum
A. 46.
B. 23.
C. 33.
D. 13.
49. Which of the following is not a constituent of DNA?
A. Purine.
B. Phosphate.
C. Cystocine.
D. Uracil.
50. Which of the following best describes the homologous chromosomes? They are
A. a product of the division of a chromosome.
B. two identical chromosomes from each parent.
C. chromosomes arranged on spindle fibres during cell division.
D. daughter chromatides formed during meiotic division.
51. The haploid number of chromosomes in man is by
A. 48.
B. 46.
C. 42.
D. 23.
52. Which of the following is a difference between mitosis and meiosis?
A. Alignment of chromosomes along the equitorial plane.
B. Replication of the chromosome and the cell organelles.
C. Pairing of homologous chromosomes.
D. Formation of spindle fibres.
53. Which of the following structures are visible in the cell of a plant during mitosis?
A. Centrioies, chromatids and nucleolus.
B. Homologous chromosomes, nuclear membrane and spindle fibre.
C. Celt wall centrioles and chromatids.
D. Chromosomes, nuclear membrane and centromere.
54. Which of the following is not true about gene mutation? It
A. introduces new traits into a population.
B. causes changes in the DNA.
C. may have unnoticeable effect on the phenotype.
D. always affects the chromosome number.
55. In man, sex is determined by the inheritance of
A. a pair of homologous chromosomes.
B. an extra chromosome in the cells of a female.
C. a dominant gene for maleness present in man.
D. two similar X chromosomes in the female and X and Y chromosomes in the male.
56. Which of the following statements is correct about the chromosomes in the gametes? At the end of the
second meiotic division.
A. each gamete contains only paternal hereditary information.
B. chromosomes contain a random mixture of paternal and maternal chromosomes.
C. chromosomes in the four gamete cells are diploid in number.
D. chromosomes contain only maternal hereditary information.
57. How many chromosomes will be present in a gamete if the somatic cell has eight(8) chromosomes?
A. 4.
B. 6.
C. 8.
D. 10.
58. The contrasting pair of genes affecting a trait and located at the same position on homologous
chromosomes is referred to as
A. chromatids.
B. mutams.
C. alleles.
D. chromatin.
59. The haploid number of chromosomes in humans is
A. 48.
B. 46.
C. 24.
D. 23.
60. At which of the following stages of cell division can the cell be said to be resting
A. Anaphase.
B. Telophase.
C. Prophase.
D. Interphase.
The diagram illustrates a stage of mitosis. Use it to answer question 61 and 62

61. What stage is illustrated by the diagram?
A. Interphase.
B. Prophase.
C. Metaphase.
D. Anaphase.
62. What is the name given to the structure labelled A at this stage of cell division?
A. Chromatin.
B. Chromosome.
C. Chromatid.
D. Gene.
63. Which of the following is not a reason why an offspring looks different from its parents?
A. Random reorganisation of chromosome during gamete formation.
B. Existence of multiple alleles in organisms.
C. Formation of chasmata in chromatics during meiosis.
D. Mutation which gives rise to new combination of gene.
64. The pair of genes expressed in a heterozygous individual is described as
A. allele.
B. chromatid.
C. dominant gene.
D. centrosome.
65. Which of the following statements about sex determination is correct? At fertility
A. the probability of male to female offspring is 1/2.
B. the Y chromosome of the father decreases the probability of having a male child to 3/4.
C. the XX chromosome of the mother decreases the probability of having a female child to 3/4.
D. the vigour of either parents determines the sex of the offspring.
66. Which of these statements is correct?
A. Recombination at fertilization does not occur between two homologous chromosome.
B. In homologous chromosome two genes very close to each other are more likely to form recombinants at meiotic prophase I.
C. A dominant gene masks the presence of a recessive gene.
D. Meiosis leads to the formation of daughter cells with diploid chromosome number.
67. Which of the following factors is not a source of variation in living organisms?
A. Environment
B. Inheritance
C. Mitosis
D. Meiosis.
68. Which of the following nucleotides is not found in the DNA molecule?
A. Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. Uracil.
The diagram below is an illustration of a stage in a biological process. Study it and answer questions 70 and 71.
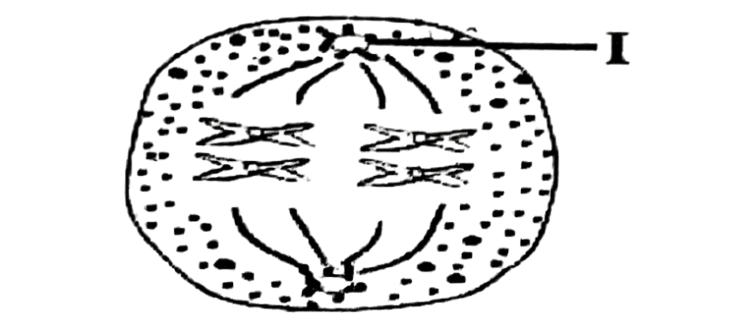
70.What stage of cell division is illustrated in the diagram?
A. Prophase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase.
71. The part labelled I is the
A. centromere.
B. spindle fibre.
C. centriole.
D. chiasmata.
The diagram below is an illustration of a process occurring in a living animal cell. Study it and answer
questions 72 and 73.
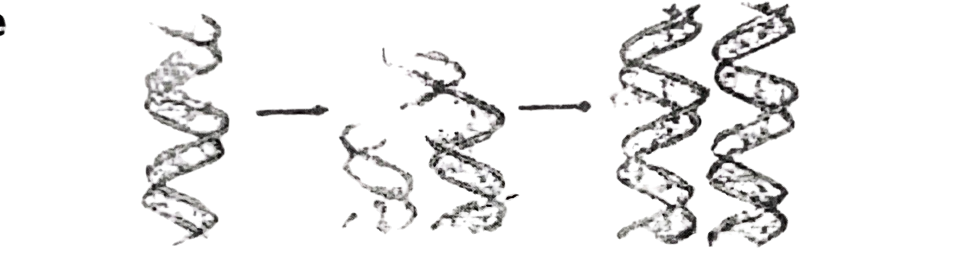
72. The process occurs in the
A. nucleus.
B. mitochondrion.
C. Golgi body.
D. cytoplasm.
73. The process is called
A. replication.
B. cell maturation.
C. crossing over.
D. mutation.
74. Which of the following statements about chromosomes is correct?
A. All the chromosomes of a species are the same in shape
B. The number present in a species is constant
C. They are neatly arranged in the cytoplasm
D.They bear ribosomes on their outer membranes.
75. Replication of DNA molecules is catalysed by an enzyme called
A. Polymerase.
B. Ptyalin.
C. Pepsin.
D. Amylase.
76. Which of the following statements about mitosis is not correct?
A. Chiasmata are not formed
B. Bi-valents are not formed
C. It does not lead to variation
D. Fourdaughter cells are produced.
77. A sudden change in the genetic composition of an organism is termed
A. epistasis.
B. linkage.
C. mutation.
D. variation.
THEORY
1. (a) What is a gene?
(b) Explain the following terms:
(i) hybrid
(ii) pure breeding
(iii) nucleotide.
2. State three reasons why mitosis is important to living organisms
3. Explain the following terms:
(i) test cross;
(ii) monohybrid cross.
4. (a) Define the following terms:
(i) gene;
(ii) gene mutation.
(b) Name two structures each of plants and animals where the following processes take place:
(i) mitosis;
(ii) meiosis.
5. (a) Describe the main stages of mitotic division
(b) State four ways in which mitosis is important to living organisms.
6. (a) Explain briefly the following terms:
(i) gene
(ii) hybrid
(iii) trait.
7. (a) Name two sites each in plants and animals where meiosis occurs.
(b) State two differences between meiosis and mitosis.
8. State two differences between mitosis and meiosis.
9. Describe the process of mitosis.
10. (a) Explain the role of Mutation.
(b) Isolation in the formation of new species.
11. (a) Name the two types of cell divisions
(b) Give two examples each of life processes involved in each type of the cell divisions.
12. What is the importance of mitosis to living organisms?
13. Explain briefly how the process of meiotic division contributes to variation in a population.
14. If there were twenty (20) chromosomes in the leaf cell of a plant, how many chromosomes would be in each of the following cells of the plant?
(i) pollen grain
(ii) guard cell
(iii) ovule
(iv) root cell.



