OBJECTIVES
1. The amount of starch in a germinating seed decreases because the starch is used up
A. for respiration and building up of cell.
B. to build cellulose cell wall.
C. to develop meristematic tissues.
D. for the production of enzymes.
2. Which of the following types of placentation is not common amongst syncarpous pistils
A. Marginal.
B. Axile.
C. Parietal.
D. Free central.
3. Water and salts are both lost from the human body in
A. breath and sweat.
B. breath and urine.
C. breath, urine and sweat.
D. sweat and urine.
4. Which of the following features could be used to determine the growth of a seedling?
A. Number of flowers.
B. Number of leaves.
C. Length of flowers,
D. Length of radicle.
5. The main difference between a seed and a fruit is that a fruit
A. is large while a seed is small.
B. has two scars while a seed has one.
C. is pigmented while a seed is not.
D. can be dispersed by animals while a seed cannot.
6. Which of the following characteristic features is not associated with monocotyledonous plants?
A. Well differentiated sepals and petals.
B. Presence of fibrous root system.
C. Presence of narrow leaves.
D. Floral parts are in multiples of three.
7. Gymnosperms bear naked seeds because they lack
A. ovary.
B. colourful flowers.
C. pollen grains.
D. stigma.
8. In both dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants, the root hairs originate from the
A. viniferous layer.
B. epidermal layer.
C. endodermal layer.
D. cortical layer.
9. The part of the young root that pushes its way through the soil is the
A. root hair.
B. tap root.
C. root cap.
D. lateral root.
10. The diagram below illustrates the transverse section of a

A. dicotyledonous root.
B. monocotyledonous root.
C. dicotyledonousstem.
D. monocotyledonous stem.
11. Primary growth in plants is brought about by the activity of the
A. meristem.
B. endodermis.
C. epidermis.
D. mesophyll.
12. Secondary growth is brought about by the activities of the
A. phellogen and phellodern.
B. phellogen and procambium.
C. vascular cambium and phelloderm.
D. vascular cambium and phellogen.
13. A monocot root is different from a dicot root by having
A. endodermis.
B. cambium.
C. wide pith.
D. root hair.
14. The removal of all the phloem tissues of the stem of a plant close to the root system for a long period of time is likely to
A. provide more energy to the roots.
B. accumulate more Starch in the roots.
C. cause the underground roots to develop buds.
D. cause the plant to wither and die.
15. The falling off of leaves of deciduous trees is helpful to the plant because it
A. reduces the rate of transpiration.
B. enables the plant to conveniently eliminate its excretory products.
C. enables the plant to bear more fruits.
D. ensures that the limited mineral salts get to only growing regions.
16. Which of the following conditions in flowering plants enhance self-pollination?
A. Cleistogamy
B. Heterostyly.
C. Protandry.
D. Protogyny.
17. An inferior ovary of a flower is situated
A. below the floral parts.
B. above the floral parts.
C. at the same level with all the floral parts.
D. at the center of the floral parts.
18. Which of the following structures in a flower develops
into the seed?
A. Testa.
B. Integument.
C. Ovule.
D. Ovary.
19. The brightly coloured petals in some plants is an adaptive colouration for
A. feeding.
B. pollination.
C. dispersal.
D. shedding.
20. The process by which flowers produce fruit without the process of fertilization is called
A. viviparity.
B. parthenocarpy.
C. propagation.
D. metamorphosis.
21. An example of a dehiscent fruit is
A. crotolaria.
B. tomato.
C. mango.
D. orange.
22. What happens to a plant if the shoot tip is cut off and replaced by an agar block containing auxin? It will
A. stop growing.
B. grow rapidly.
C. continue to grow normally.
D. die completely.
23. Which of the following structures is not essential in a wind pollinated flower?
A. Anther.
B. Ovary..
C. Stigma.
D. Petal.
Study the diagram below and use it to answer questions 24 & 25 & 26
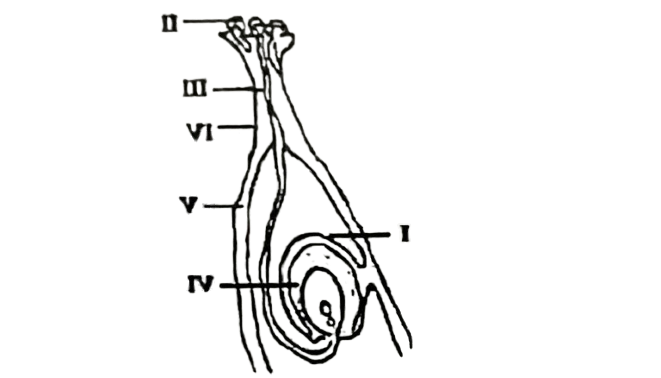
24. Which part of the flower produces the structure labelled II?
A. Carpel.
B. Pollen.
C. Stigma.
D. Anther.
25. The parts labelled III and IV respectively are called
A. Pollen tube and style.
B. Pollen grain and pollen tube.
C. Anther and filament.
D. Stigma and style.
26. Which of the labelled parts would become a component of the seed after fertilization?
A. I.
B. II.
C. IV.
D. V.
27. Bees are of great importance to the farmer because they
A. provide him with honey.
B. pollinate flowers.
C. sting crop pests to death.
D. destroy flowers by sucking nectar from them.
28. A seed of a flowering plant can best be described as
A. radicle and plumule.
B. the developed ovule.
C. the embryo and endosperm.
D. developed ovary.
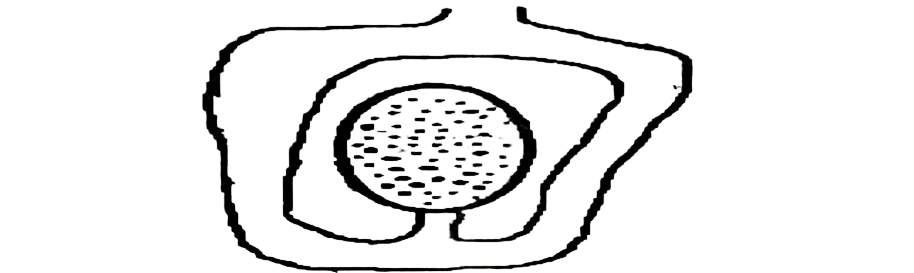
29. The type of placentation illustrated in the diagram below is
A. marginal.
B. parietal.
C. axile.
D. basal.
D. brity
30. The immediate product of meiosis in flowering plants is the
A. sporophyte.
B. gametophyte.
C. zygote.
D. pollen grain.
31. The transfer of ripe pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower is termed
A. fertilization.
B. self-pollination.
C. reproduction.
D. conjugation.
32. Double fertilization is said to occur in flowering plants because
A. two embryos are formed.
B. one egg is fertilized twice.
C. two sperms fertilize each egg.
D. one embryo and an endosperm nucleus are formed.
33. Which of the following adaptation is not found in fruits and seeds dispersed by the wind
A. Small and light body.
B. Spongy coats.
C. Turfs of hairs.
D. Wings on pericarp.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 34-36

34. What is the function of the part labelled II?
A. Attraction of insects.
B. Secretion of nectar.
C. Protection of the stigma
D. Formation of fruit wall.
35. The function of the part labelled I is to
A. receive pollen grains.
B. produce nectar.
C. store the pollen grains.
D. store the ovules.
36. How would you describe the position of the ovary in relation to the receptacle?
A. Superior.
B. Inferior.
C. Semi-inferior.
D. Gamosepalous.
37. Which of the following is the effect of using artificial pollination in plant breeding?
A. Production of healthy crops.
B. Improvement of the variety of crops.
C. Making crops susceptible to diseases.
D. Lengthening the maturity time of crops.
38. A dry indehiscent fruit containing one seed and possessing a hairy pappus is described as
A. a nut.
B. a drupe.
C. a cypsela.
D. a follicle.
39. Which of the following is not a dry indehiscent fruit?
A. Legume.
B. Cypsela.
C. Samara.
D. Caryopsis.
40. If a germinating seed is attached horizontally on a revolving klinostat, what will be the effect on the
seedling after three days? The
A. plumule will curve vertically upwards while the radicle will curve towards the ground.
B. plumule and radicle will not show any curvature.
C. radicle will curve towards the ground while the plumule will not show any curvature.
D. plumule will curve vertically upwards while the radicle will not show any curvature.
41. Which of the following is not correct about a fruit? It
A. may contain many seeds.
B. is a mature ovary.
C. is covered by the pericarp.
D. may develop from the receptacle.
42. Which structure in the maize grain stores food?
A. Radicle.
B. Embryo.
C. Cytoplasm.
D. Endosperm.
43. Which of the following fruits is a schizocarp?
A. Groundnut.
B. Desmodium.
C. crotalaria.
D. Cashew.
44. Which of the following is not a characteristic of wind dispersed fruits and seeds?
A. Light weight.
B. Wing.
C. Floss.
D. Sticky juice.
45. How many conjugants are involved in sexual reproduction of paramecium?
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 4.
D. 8.
46. Which of the following is the function of bright coloration of petals in flowers?
A. Beautifying the environment.
B. Providing warning coloration for insects.
C. Attracting pollinating insects.
D. Production of chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
47. Which of the following is not a feature of a seed or fruit dispersed by the wind?
A. Light weight.
B. Parachute.
C. Pappus.
D. Hooks.
Use the diagram below to answer this question

48. Which of the following agents is responsible for the dispersal of the seed shown above?
A. Man.
B. Water.
C. Wind.
D. Explosive mechanism.
49. Which of the following statements best describes pollination? The transfer of pollen grain from
A. anther to stigmas.
B. stigmas to stamens.
C. the anther of a flower to the stigma of another flower of a different species.
D. anther to the ovary.
50. The collective name for the female parts of the flower is
A. gynoecium.
B. androecium.
C. ovary.
D. stigma.
51. If the petals of a flowering plant are removed, which of the following processes is likely to be affected?
A. Transpiration.
B. Pollination.
C. Germination.
D. Photosynthesis.
Use the diagram below to answer this questions 52-54.
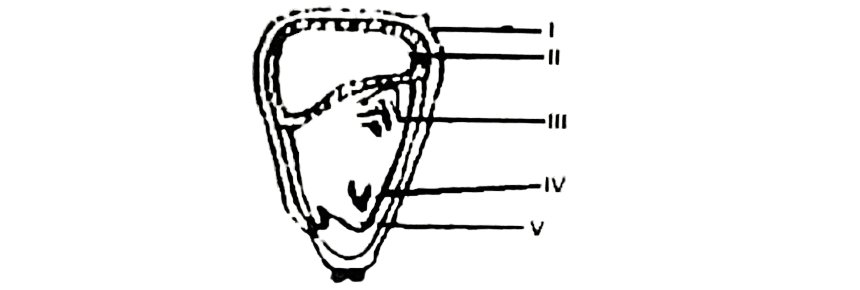
52. The part labelled II in the diagram is the
A. plumule.
B. endosperm.
C. radicle.
D. coleorhiza.
53. The part labelled IV in the diagram is the
A. plumule.
B. endosperm.
C. radicle.
D. coleoptile.
54. The function of the part labelled V in the diagram is the
A. manufacture of food.
B. storage of food.
C. secretion of digestive enzyme.
D. protection of the radicle.
55. Which of the following is a feature of wind pollinated
flowers?
A. Large and brightly coloured petals.
B. Possession of sweet scent.
C. Presence of nectar.
D. Smooth, light and numerous pollen grain.
56. Which of the following statements about the maize grain is not correct?
A. undergoes hypogeal germination.
B. is a fruit.
C. is non-endospermous.
D. has pericarp fused with the testa.
57. Which of the following is an agent of pollination of
grasses?
A. Insects.
B. Water.
C. Wind.
D. Mammals.
58. Which of the following is not a condition necessary for germination to occur in most seeds?
A. Water.
B. Air.
C. Activation of enzymes.
D. Soil fertility.
59. Which of the following structures are characteristics of insect pollinated flowers?
A. Dull coloured flowers with no nectar.
B. Very light, numerous, and pendulous stamen.
C. Brightly coloured petals, scent and nectar.
D. Flowers are usually small and inconspicuous.
60. Which of the following is an advantage of dispersal of fruits and seeds? It allows
A. fair distribution of source of food for animals.
B. growth in close association with parent plant.
C. even distribution of plants and reduction of intraspecific competition.
D. keen competition for food.
61. A dehiscent fruit formed from several fused carpels with many seeds is classified as
A. an achene.
B. a capsule.
C. a follicle.
D. a legume.
62. During the germination of seeds water is taken in by the process of
A. diffusion.
B. hydrolysis.
C. imbibition.
D. translocation.
63. Which of the following is not a characteristics feature of a wind dispersed fruit?
A. Light weight.
B. winged apparatus.
C. Flossy structure.
D. Buoyancy.
Study the diagrams below and use them to answer questions 64-66.
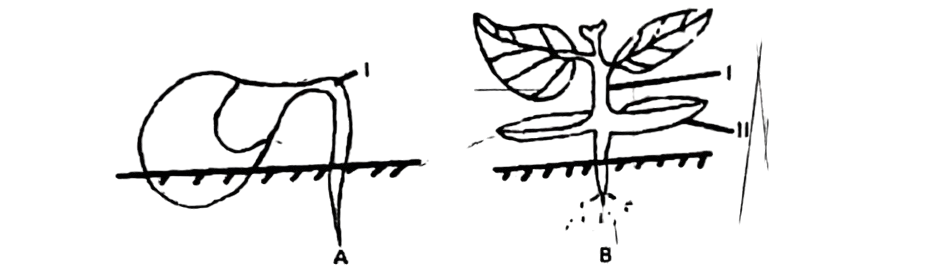
64. The part labelled I in fig. A represents the
A. root.
B. radicle.
C. hypocotyl.
D. shoot.
65. The part labelled II in fig. B represents the
A. root.
B. epicotyl.
C. hypocotyl.
D. cotyledon.
66. What is the importance of the part labelled II to the seedling? It
A. protects the foliage leaves.
B. grows into the first foliage leaves.
C. later develops into the fruit.
D. provides the seedling with food.
The diagram below is the root system of a leguminous plant.
Study and use it to answer questions 67 and 68
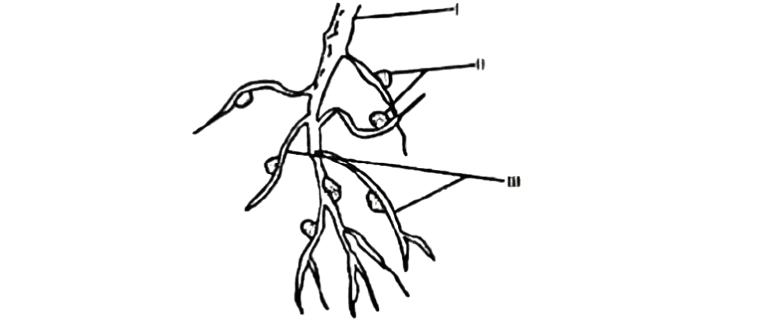
67. The structures labelled II are
A. groundnut seeds.
B. underground root nuts.
C. root tubers.
D. root nodules.
68. The structures labelled II are associated with
A. storage of plant nutrients.
B. organic acids.
C. nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
D. putrefying microbes.
69. Which of the following is not seen in the transverse section of a young monocotyledonous stem?
A. Parenchyma.
B. Phloem.
C. Xylem.
D. Cambium.
70. Which of the following tissues is not found in the stem and root of monocotyledons?
A. Xylem.
B. Cambium.
C. Pith.
D. Cortex.
The diagram below represents a cross-section through a monocotyledonous root. Use it to answer the questions

71. The part through which manufactured sugar is transported is labelled
A. I.
B. III.
C. IV.
D. VII.
72. In flowering plants, fertilization would occur when
A. the pollen grows downwards penetrating the style.
B. a pollen grain is transferred to the stigma.
C. one of the nuclei inside the pollen tube fuses with the ovum.
D. the nucleus of the pollen tube divides.
73. After fertilization in the flowering plants, the zygote develops into the
A. plumule.
B. radicle.
C. cotyledon.
D. embryo.
74. What happens to an ovule of a flower, after 88. Which part of the flower is responsible for the
fertilization? It
A. becomes a fruit.
B. withers away.de
C. becomes a seed.
D. forms the cotyledons.
75. When both ovaries of the human female ovulate simultaneously and both ova are fertilized, then
A. identical twins are produced.
B. fraternal twins are produced.
C. siamese twins are produced.
D. the other children produced are genetically identical.
76. The female part of a flower consists of the
A. stigma, style and ovary.
B. petals, sepals and anthers.
C. stigma, sepals, and anthers.
D. filaments, style and pollen grain.
77. The essential parts of a flower are
A. petals and sepals.
B. anther and filament.
C. stigma and style.
D. androecium and gynoecium.
78. The process by which fruits develop without fertilization is called
A. parthenocarpy.
B. pathology.
C. hermaphroditism.
D. layering.
79. What is the fate of the ovary of a flower after fertilization? It
A. becomes the seed.
B. withers away.
C. becomes the fruit.
D. develops more nuclei.
80. A one-seeded fruit in which the pericarp has fused with the seed coat is classified as
A. a berry.
B. a caryopsis.
C. a legume.
D. an achene.
81. Placentation of plants is best described as the
A. arrangement of ovules in the ovary.
B. arrangement of fruits on the branches.
C. development of ovules in the ovary.
D. formation of the pericarp from the ovary wall.
82. A flowering plant having both the male and female flowers on the same plant, is said to be
A. regular
B. monoecious
C. irregular
D. dioecious.
83. The term syncarpous is used to describe a flower when the carpels are
A. many and fused
B. two only
C. two and separate
D. many and free
84. The series of changes that occur in a seed by which the embryo develops into a seeding is known as
A. fertilization
B. gametogenesis
C. pollination
D. germination.
85. Which of the following is not an example of entomophilous flower?
A. Hibiscus.
B. Flamboyant.
C. Guinea grass.
D. Allamanda.
86. Underground storage stems which grow horizontally in the soil are
A. bulbs.
B. runners.
C. rhizomes.
D. corms.
87. The classes of plants the root systems in diagrams I and Il below represent respectively are

A. Dicotyledoneae and Monocotyledoneae
B. Monocotyledoneae and Dicotyledoneae
C. Dicotyledoneae and Dicotyledoneae
D. Monocotyledoneae and Monocotyledoneae
The diagram below is an illustration of the longitudinal section of a flower. Study it and answer questions 88 and 89.
88. Which part of the flower is responsible for the protection of young flower buds?
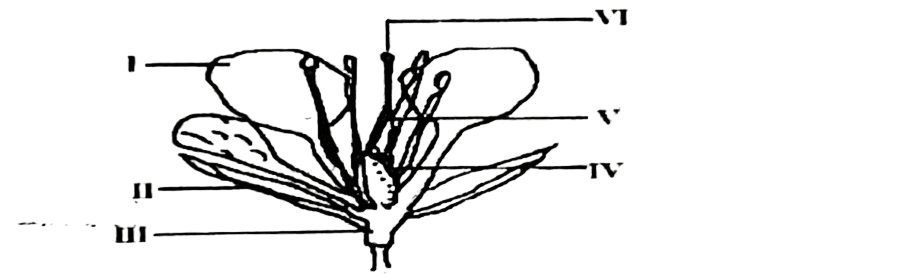
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV
89. The essential parts of the flower are labelled
A. I, II and III.
B. II, III and IV.
C. III, V and VI.
D. IV, V and VI.
The diagram below is an illustration of a part of a flower.
Study it and answer questions 90 & 91.
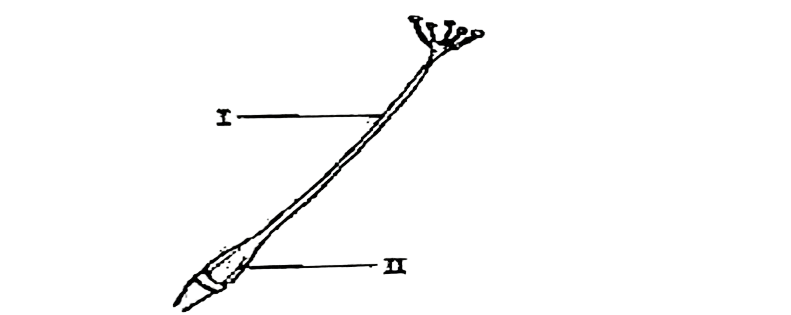
90. The function of the part labelled I is
A. Receiving the pollen grain.
B. Passage for the male gamete to the ovary.
C. Germination of the pollen grain.
D. Site for double fertilization in the plant.
91. The reagent used in testing for carbon (IV) oxide is
A. Copper sulphate solution.
B. Lime water.
C. Hydrochloric acid.
D. Sodium hydroxide solution.
The diagrams below are illustrations of different sections of a particular fruit. Study them and answer question 92 and 93.
92. The sections in X and Y respectively, are
A. longitudinal and transverse.
B. transverse and longitudinal.
C. cross and transverse.
D. transverse and cross.
93. The fruit that has illustrated sections is a
A. hesperidium.
B. capsule.
C. drupe.
D. cypsela.
94. How many gametes are produced in the pollen grain of a flowering plant before fertilization?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Diagrams X and Y below are illustrations of transverse sections of a part of plants. Study them and answer questions 95 to 97.
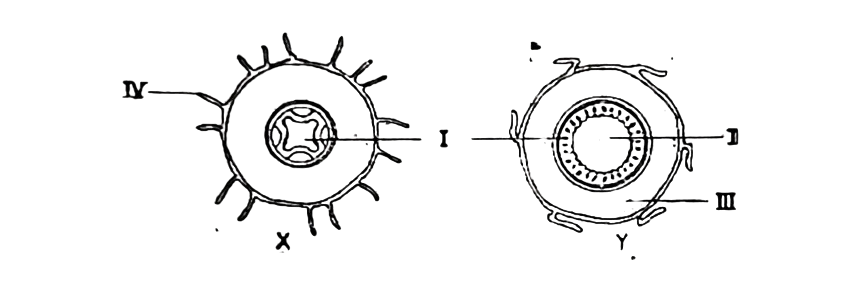
95. Which of the following statements is not correct? Diagrams X and Y are sections of
A. roots.
B. a dicotyledonous root and a monocotyledonous root respectively.
C. vascular bundles.
D. stems.
96. The part responsible for conducting water and dissolved mineral salts from the soil to the leaves is
labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
97. The part labelled II is the
A. pith.
B. xylem.
C. phloem,
D. endodermis.
98. The region of a plant stem in which cells divide to increase its diameter is the
A. cambium.
B. phloem.
C. xylem.
D. collenchyma.
99. In which of the following structures is simple sugar produced?
A. Vacuole
B. Cytoplasm
C. Chloroplast
D. Cell wall
100. The androecium in a flowering plant is a collection of
A. ovules.
B. stamens.
C. filaments.
D. sperms.
101. Placentation in fruits is referred to as the
A. part of the ovary where the ovules originate and remain till maturity.
B. formation of a single carpel joined at the two edges of an ovule.
C. arrangement of ovules in the ovary of a flower.
D. ovules borne on a central column of tissues in an ovary.
THEORY
1. (a) Name the type of germination which takes place in:
(i) monocotyledonous plants
(ii) dicotyledonous plants.
(b) In a tabular form state four differences between the forms of germination named in (a) above.
2. (a) Name two types of germination of seeds giving one example of each type.
(b) Describe a simple experiment to demonstrate that oxygen, water and warmth are necessary for germination of seeds.
3. (a) Describe epigeal germination of a seed
(b) In tabular form state three differences between epigeal germination and hypogeal germination.
4. (a) What is seed dormancy?
(b) State three ways by which dormancy in seed can be broken.
5. State three reasons why the dispersal of fruits and seeds are important.
6. Describe how the floral parts of a named flower are adapted to wind-pollination.
7. (a) List four floral parts of a flower
(b)(i) In a tabular form, state five differences between wind and insect pollinated flowers
(ii) Give one example of each
(c)(i) State three agents of fruit and seed dispersal
(ii) Give an example of fruits or seeds dispersed by each agent.
8. (a) List four types of placentation in flowering plants
(b) State four conditions necessary for seed germination.
9. Describe the processes that occur from the time a pollen grain is deposited on the stigma of a flower to the formation of a zygote.
10. (a) Distinguish between pollination and fertilization in plants
(b)(i) State five features which ensure cross pollination in plants
(ii) Name one plant example for each feature
(c)(i) Name three agents of pollination (ii) State three features of wind-dispersed fruits/seeds.
11. (a) Make a diagram 8-10cm long, of the female reproductive part of a flowering plant and label fully (b) Name three plants that are pollinated by insects.
12. Describe the structure and function of the male reproductive organ of a flowering plant.
13. Describe the process of fertilization in flowering plants.
14. Make a labelled diagram of the female reproductive organ of a flowering plant and state the function of any two of the labelled part.
15. Explain briefly the reason the following factors are necessary for germination:
(i) moisture;
(ii) viable seed.



