OBJECTIVES
1. A vaccine is introduced into a person’s body to
A. destroy all disease-causing organisms in the body. B. stimulate the body to produce antibodies. C. enhance the production of red blood cells. D. isolate disease-causing pathogens from the blood.
2. Many diseases caused by bacteria can be treated and cured by using
A. antiseptics. B. antibiotics. C. antigens. D. antibodies.
3. Viruses are economically important because they
A. do not have cell structures. B. can only reproduce inside living cells. C. cause diseases in plants and animals. D. exist as crystals outside living cells.
4. The main reason for immunizing children is to
A. destroy pathogens in their bodies. B. increase the production of white blood cells. C. stimulate the production of antibodies. D. simulate the production of antigens.
5. A pandemic is an outbreak of disease that
A. is confined to a town. B. is widespread. C. will not spread. D. has limited spread.
6. Which of the following diseases is caused by a bacterium
A. Ringworm. B. Poliomyelitis. C. Syphilis. D. Malaria.
7. Vaccination results in
A. aiding red Blood cells to carry more oxygen. B. production of antibodies which destroy toxins of germs. C. arresting excessive bleeding. D. production or white blood cells which engulf and digest bacteria.
8. The vector of the sleeping sickness disease parasite is the
A. cockroach. B. mosquito. C. black fly. D. tsetse fly.
9. Which of the following infections would not respond to an antibiotic treatment?
A. Gonorrhoea. B. Measles. C. Diarrhoea. D. Tuberculosis.
10. Which of the following activities constitutes biological control? A.
A small bony fish transported on the back of a shark B. Adding manure to crops in a garden C. Tilapia feeding on the larvae and pupae of mosquito D. A vulture feeding on the carcass of a goat.
11. The following are useful effect of micro-organisms except
A. production of vaccines. B. curing of tobacco. C. tanning of leather. D. decay of meat.
12. One of the ecological conditions which favour the spread of malaria is
A. improper disposal of decaying organic matter. B. clearing bushes around dwelling A S houses. C. presence of water weeds. D. presence of HT stagnant water in ponds.
13. Only specially adapted micro-organisms are found in
A. salty water. B. humid air. C. moist soil. D. mouths cavities.
14. Which of the following organisms causes syphilis
A. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. B. Bordetella pertusis. no C. Treponema pallidium. D. Clostridium tetani.
15. Infective hepatitis is a disease of the
A. heart. B. kidney. C. liver. D. stomach.
16. Which of the following substances cannot control the growth of harmful microorganisms?
A. Antibiotics. B. Hypertonic salt solution. C. Disinfectants. D. Isotonic sugar solution.
17. Measles in infants can be prevented by
A. sleeping under mosquito nets. B. providing clean water supply. C. taking anti-malaria tablets. D. vaccinating young children.
18. Micro-organisms are important in recycling nutrients because
A. they are capable of multiplying quickly. B. they are eaten by large organisms. C. they break down dead organic materials. D. many of them are parasites.
19. I. Plasmodium II. Vibrio choleroe III. Gonococcus sp IV. Poliomyelitis virus. V. Syphilis bacteria.
Which of the following organisms are transmitted by houseflies?
A. I and II only. B. II and V only. C. Ill and IV only, D. II and IV only.
20. The causative organism of sleeping sickness is the
A. Trypanosome. B. Plasmodium. C. Vibrio bacterium, D. penicillin.
21. Which of the following are not causative organisms of Plant diseases?
A. Fungi. B. Viruses. C. Bacteria. D. Cercariae.
22. The vector of the malaria parasite is the
A. male Anopheles. B. female Culex. C. male Culex. D. female Anopheles.
23. Trypanosomiasis is associated with
A. cockroach. B. mosquito. C. housefly. D. tsetse fly.
24. Which of the following infections is unlikely to respond to antibiotic treatment
A. Typhoid fever. B. Ring worm. C. Measles. D. Tetanus.
25. Transmission of the malaria parasite is effected through the bite of the
A. male Anopheles mosquito. B. female Anopheles mosquito. C. infected male Anopheles mosquito. D. infected Aides mosquito.
26. The drugs which inhibit the growth of disease-causing organisms and thus used in the treatment of infections are a referred to as
A. antibodies. B. antibiotics. C. antitoxics. D. septic.
27. Which of these diseases cannot be spread by an insect
A. Cholera. B. Malaria. C. Trypanosomiasis. D. Measles.
28. Which of the following statements about poliomyelitis is not correct? It
A. is a bacterial disease. B. is capable of paralysing the limbs. C. can be prevented by immunization. D. is an infant disease.
29. Oil is sprayed over stagnant water in which mosquitoes breed in order to
A. provide landing surface for the adult. B. prevent larva or pupa from attaching itself to the surface. C. prevent the water from overheating. D. lubricate the larva for easy movement.
30. Viruses are pathogens of the following diseases. Except
A. measles.B. smallpox. C. poliomyelitis. D. tuber culosis.
31. Which of the following structures in a housefly aids in the transmission of diseases in man?
A. Hairs. B. Spiracles. C. Antennae. D. Wings.
32. Which of these is not correct about the tse-tse fly and mosquito? They
A. harbour protozoa as disease agents. B. possess piercing and sucking mouth parts. C. have intermediate hosts. D. inject disease causing organisms into the blood stream.
33. Which of these is a vector of malaria fever?
A. Female anopheles mosquito. B. Male anopheles mosquito. C. Female culex mosquito. D. Male culex mosquito.
34. In medicine, bacteria have proved very useful due to the production of
A. nitrate. B. antibiotic. C. cured tobacco. D. tanned leather.
35. Sickle-cell anaemia has persisted in the human race due to
A. lack of proper medical care for sicklers. B. carriers being more resistant to malaria. C. mosquito vectors. D. wildlife intermediate hosts.
The diagrams below represent the shape of major groups of bacteria. Use them to answer question 36
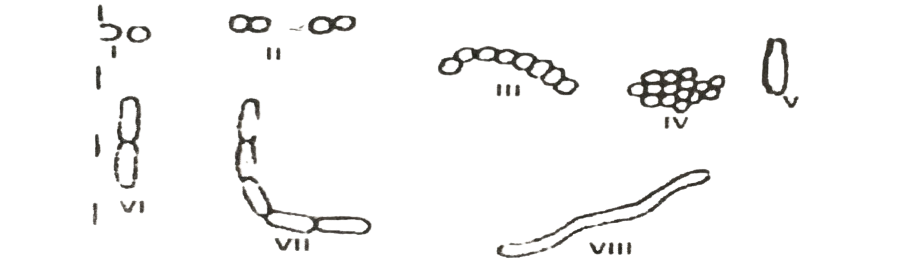
36. The groups staphylococci and streptobacilli are represented by
A. I and II. B. II and IV. C. Ill and V. D. IV and VI.
37. One of the methods of preventing/measles is by
A. sleeping under mosquito net. B. attacking the vectors. C. attacking the secondary host. D. vaccinating young children.
38. Which of the following parasites is a flatworm?
A. Plasmodium.B. Trypanosome. C. Ascaris. D. Schistoso ma.
39. Cholera is mostly spread by
A. air. B. soil. C. water. D. noise.
40. Which of the following behaviours is correctly matched with the corresponding diseases?
| Behaviour | Diseases | |
| A. | Smoking cigarette | liver cirrhosis, lung cancer, AIDS. |
| B. | Having multiple sexual partners | liver cirrhosis, syphilis, AIDS. |
| C. | Living near dirty gutter | lung cancer, syphilis, river blindness. |
| D. | Eating uncooked meat | dysentery, cholera, food poisoning. |
The diagrams below are illustrations of forms in which a particular group of organisms exist. Study them and answer questions 41 and 42.
41. Which group of organisms is illustrated?
A. Bacteria. B. Viruses. C. Fungi. D. Protozoa.
42. In which of the illustrated forms docs the organism that causes cholera exist?
A. II. B. III. C. IV. D. V.
THEORY
1. (a) What is immunity? (b) Name four diseases for which babies are immunized. (c) Explain two ways by which a person becomes immune to yellow lever.
2. (a) Explain the following terms: (i) a disease (ii) symptoms of diseases (b) List two physical and two chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from penetrating the body of an organism. (c) Explain how vaccination protects the body from contracting infectious diseases. (d) Distinguish between an antibody and an antigen. (e) Name the causative agents of: (i) Malaria (ii) Cholera (iii) AIDS
3. Name two viral diseases of humans.
4. State five functions of the World Health Organization.
5. State four functions of a public health authority.
6. (a) State three harmful effects of microorganisms to plants. (b) State six beneficial effects of microorganisms to humans.
7. (a) List four bacterial diseases associated with poor food hygiene. (b) State three effects of poor food hygiene.
8. (a) List two diseases each of plants and animals caused by bacteria (b)State three ways in which bacteria are useful (c) State three methods by which mosquitoes can be controlled and state the reason for each method. (d) Describe an experiment to demonstrate the presence of bacteria under the finger nails.
9. (a) Explain the terms first aid? (b) State three objectives of first aid (c) Name two ways of stopping bleeding from an open wound.
10. State four economic importance of insects and name an example of each of the insects involved,
11. (a) Mention: (i) one fungal parasite of a plant and its host (ii) One bacterial parasite of humans (b) List four symptoms of malaria (c) Mention six methods of controlling malaria in West Africa.
12. List seven ways by which microorganisms can be controlled to maintain good health.
13. The following are the names of some common diseases; malaria, typhoid, amoeboid dysentery, tuberculosis, tetanus, leprosy, cholera, yellow fever, poliomyelitis, measles, common cold, small pox, influenza, chicken pox, whooping cough and trypanosomiasis. Use the format below to classify the diseases according to their causative organisms.
| Viral | Bacterial | Protozoan |
| Diseases | Diseases | Diseases |
14. Explain briefly the following diseases (a) hepatitis (b) kidney stones.
15. Complete the table below
| Disease | Causative organism | Vector | Control |
| Cholera | |||
| Trypanosome | |||
| Female Anopheles mosquito | |||
| Ringworm | None |



