OBJECTIVES
1. A pyramid of numbers is constructed by
A. comparing living and non-living things. B. measuring productivity, C. conducting census. D. labelling the living organisms.
2. Which of the following instruments is used to estimate the number of plants in a habitat?
A. Pooter. B. Pitfall trap. C. Quadrat. D. Sweep net
Use the information on capture-recapture method to calculate the total number of organisms in a habitat First capture=200. Second capture = 120 Number of organisms with the mark in the second capture = 40.
3. The total number of organisms therefore is
A. 200. B. 360, C. 600.D. 800.
4. The resolution of a microscope refers to its power to 32351
A. increase an object’s apparent size B. distinguish clearly between two objects. C. scan the surface of an object. D. focus on an object.
5. The fine adjustment of the light microscope is used to
A. admit more light into the microscope. B. focus the object under low power. C. focus the object under high. power. D. raise the stage upwards.
6. The line XZ in the diagram below represents an actual distance of 10.0 cm and the length of the diagram is 5.0 cm. What is the magnification of the diagram?
A. x 0.2. B. x 0.5. C. x 2.0. D. x 50.0.
7. Ecological investigation in a habitat includes the following procedures except
A. choosing a habitat. B. identification of specimens. C. determining the genetic make-up of specimens. D. measuring abiotic and biotic factor.
8. In a water culture experiment, the culture solution in a transparent beaker turned green. What precaution should have been taken prevent the culture solution from turning green?
A. Changing the culture solution regularly. B. increasing the number of times the culture is aerated. C. Covering the transparent beaker with black cloth. D. Adding warm alcohol to bleach the green colour
9. The frequency of andropogon in a grass lawn is 90 100. Throws were made with 1 meter square quadrate..!? What is the density of andropogon in the field?
A. 0.09m per m². B. 0.90 per m². C. 9.0 per m². D. 90 per m².
10. Which of these materials is not required for insect collection in an ecological field-trip?
A. Pooter. B. Secchi disc. C. Spreading board. D. Jar containing alcohol.
11. Which of the following is the simplest method of finding the magnification of the drawing of a specimen?
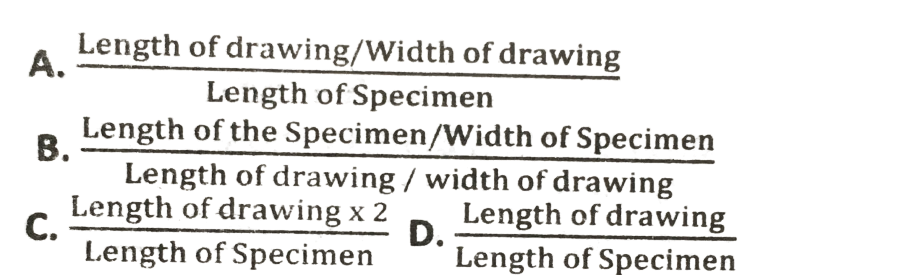
12. The number of individuals in a habitat in relation to the unit space available to each organism is referred to as the
A. birth rate. B. density. C. mortality. D. dispersion.
13. Which of the following activities is not necessary in population sampling?
A. Selecting the habitat. B. Dividing the selected habitat into portions. C. Throwing the quadrate randomly. D. Feeding the organisms.
14. Which of the following is used for the collection of small insects from soil, leaf litter and crevices?
A. Pooter. B. Quadrate. C. Sweep net. D. Drag net.
15. Which of the following methods is best for the determination of population density of Tridax in an open field?
A. transect. B. qudrat. C. sweep-net. D. pit-fall.
16. The first step in carrying out ecological studies in a as terrestrial habitat is
A. quadrat sampling. B. mapping the area. C. collection of organisms. D. measuring abiotic factors measuring abiotic factors.
THEORY
1. Describe how you can estimate the density of a plant species using a quadrate.
2. List three major steps that are usually taken in studying plants and animals in a community,
3. (i) State two reasons why ecologists use sampling techniques in population studies. (ii) State four examples of sampling techniques used in population studies.



