1. Increasing adrenaline content of the blood would be expected to decrease the flow of blood to the
A. liver.
B. heart.
C. lungs.
D. brain.
2. The presence of glucose in the urine of a patient is an indication of malfunctioning of the
A. pancreas.
B. gall bladder.
C. liver.
D. spleen.
3. Which of the following statements is not true about hormones?
A. Hormones are manufactured in ductless glands and poured straight into the blood stream.
B. Hormones are carried by the blood plasma to the required target organs.
C. Hormonal responses are usually swift, instant and electrical.
D. Once the effects of hormones are over, they are inactivated and excreted
from the body.
4. Which of the following actions is not a function of adrenaline? It increases
A. body blood sugar by conversion of liver glycogen into glucose.
B. muscular power and resistance to fatigue.
C. the rate of heartla heat.
D. the dilation of the pupils of the eye.
5. Which of the following conditions would result in ad decrease in the production of antidiuretic hormone?
A. Abnormally high blood sugar level.
B. Drinking large quantities of water.
C. Increase in osmotic pressure of blood.
D. Period of strenuous exercise.
6. Which of the following organs is responsible for the production of insulin?
A. Spleen.
B. Adrenal gland.
C. Thyroid gland.
D. Pancreas.
7. The endocrine gland which co-ordinates the action of other glands and is also associated with the nervous system is the
A. adrenal gland.
B. thyroid gland.
C. pituitary gland.
D. thymus gland.
8. Insulin is produced by the
A. adrenal gland.
B. gonads.
C. pituitary gland.
D. pancreas.
9. Which of the following glands also serves as an exocrine gland
A. Ovary.
B. Pancreas.
C. Adrenal.
D. Thyroid.
10. The thyroid gland is located at the base of the
A. midbrain.
B. kidney.
C. neck.
D. liver.
11. A person had an accident that affected the skull but not the nose and later lost the sense of smell. The accident must have affected the
A. nose by extension.
B. olfactory lobes of the brain.
C. passage from the nose to the brain.
D. part of the skull near the nose.
12. A farmer who wants to keep seeds for three years before planting and wants to prevent them from
sprouting uses
A. auxin
B. gibberellins.
C. abscisin.
D. cytokinins.
13. Plant hormones include the following except
A. insulin
B. auxin.
C. cytokinin.
D. gibberelin.
14. The process of regulating the amount of water and solutes in the body fluids is called
A. osmosis.
B. diffusion.
C. osmoregulation.
D. homeostasis.
15. The maintenance of a stable internal environment within the body of a mammal is known as
A. osmosis.
B. plasmolysis.
C. homeostasis.
D. excretion.
16. The reason why hospitals use saline solutions as drip instead of water is
A. because salt is a preservative.
B. to prevent contamination of the body.
C. to maintain the composition of body fluids.
D. to increase the number of blood cells.
17. The maintenance of a constant internal environment in an organism is known as
A. homeostasis..
B: homoiothermy.
C. diuresis.
D. dialysis.
18. An example of homeostasis in living organisms is
A. cooling effect resulting from evaporation of water from the body surface.
B. root hairs of a plant growing towards a source of light.
C. changing of the body colour of chameleon to match the colour of the foliage on which
it is resting.
D. the release of phosphorus into the phloem of a plant growing in a phosphorus-deficient
soil.
19. More sweat is produced during muscular exercise because
A. the contracting muscles produce water.
B. fermentation occurs in muscles.
C. the temperature of the body rises.
D. the muscle fatigues.
20. Which of the following processes is not a function of the mammalian skin?
A. Regulation of body total temperature.
B. Reception of external stimuli.
C. Excretion.
D. Gaseous exchange.
21. Protection of the body cells of mammals against ultra-violet rays of the sun is brought about by
A. keratin.
B. melanin.
C. sebum.
D. scales.
22. The inability to maintain proper balance of the body in humans may be due to a defect in the
A. cochlea.
B. Eustachian tube.
C. semi-circular canals.
D. oval window.
The graph below shows the results of a laboratory investigation which measured the body temperatures of
a lizard and a bird under changing artificial conditions.
Use it to answer questions 23 & 24
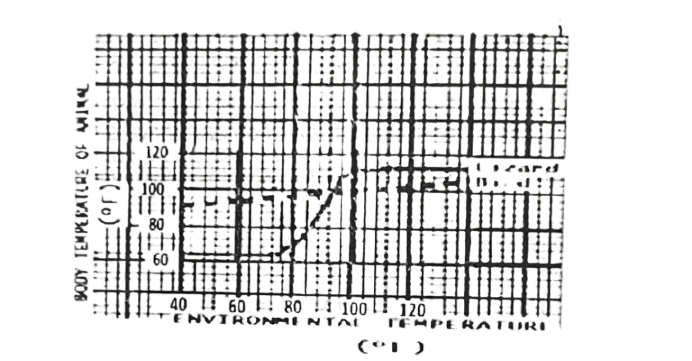
23. Which of the statements below is valid?
A. The bird’s blood was always warmer than that of the lizard.
B. The body temperature of the bird varied less than that of the lizard during changes in environmental
temperature.
C. The body temperature of the bird remained constant despite changes in environmental
temperature.
D. The body temperature of the lizard was always close to that of the environmental temperature.
24. What physiological term can be used to describe the regulation of the body temperature of the lizard?
A. Homeostasis.
B. Homoithermy.
C. Poikilothermy.
D. Osmoregulation.
25. Flaccidity in plants is associated with
A. cessation of photosynthesis.
B. wilting.
C. turgidity.
D. discolouration of leaves.
26. Which of the following diseases is caused by deficiency of insulin in the body?
A. Malaria.
B. Diabetes mellitus.
C. Hepatitis.
D. Gonorrhoea.
27. The maintenance of a constant internal environment of an organism is known as
A. homeostasis.
B. homeorhesis.
C. homoiothermy.
D. turgidity.
28. The ability of organisms to maintain a constant internal environment is known as
A. diuresis.
B. endosmosis.
C. plasmolysis.
D. homeostasis.
29. The condition known as cretinism is caused by the deficiency of
A. adrenalin.
B. vitamin A.
C. insulin.
D. thyroxin.
30. Which of the following is not true about auxins? They
A. are manufactured by plants.
B. are used in the site of production.
C. are normally present in minute quantities in the cells of plants.
D. regulate growth rate of plants.
31. Adrenalin is considered as a hormone for “fright and flight” because it
A. controls the fluid content of the body.
B. is used in protein metabolism.
C. plays a role in the pH balance of the body fluids.
D. prepares the body for action.
32. In humans, which of the following pairs of hormones correspond to male and female respectively?
A. Oestrogen and adrenalin.
B. Progesterone and testosterone.
C. Testosterone and oestrogen.
D. Adrenalin and progesterone.
33. Which of the following conditions will cause a decrease in body temperature?
A. Increased metabolism.
B. Shivering.
C. Vasoconstriction of capillaries of the skin.
D. Relaxation of the erector muscles.
34. The organs constantly in touch with the liver are
A. pancreas, colon and caecum.
B. duodenum and stomach.
C. ileum, stomach and colon.
D. stomach and gall bladder liver.
35. Which of the following is responsible for the increased heartbeat of a boy who saw a python?
A. adrenalin.
B. insulin.
C. pituitrin.
D. thyroxin.
36. Which of the following organs is responsible for controlling the body temperature regulation and water balance in mammals?
A. Kidney.
B. Hypothalamus.
C. Parathyroid.
D. Adrenal.
37. Which of the following statements is correct of hormones? Hormones are
A. secreted into blood through ducts.
B. secreted directly into the blood stream.
C. inactive chemical substances in the blood stream.
D. non-specific in their mode of action.
C. production of fibrinogen.
D. production of vitamin D.
38. The pituitary is called ‘master gland’ because
A. it is located in the brain.
B. its secretions are more numerous than those of any other gland.
C. its secretion controls other glands.
D. it is the only organ that produces hormone.
39. Which of the following takes place when a person’s body temperature rises above 37°C
A. Sweating and vasoconstriction.
B. Panting and vasoconstriction.
C. Sweating and vasodilation,
D. Panting and vasodilation.
40. Auxins are produced in the
A. petiole of leaves.
B. parenchyma of roots and shoots.
C. epidermis of roots and shoots.
D. apical regions of roots and shoots.
41. The pituitary is regarded as the master gland because
A. it is located in the brain.
B. its secretions are the most numerous.
C. its secretions control other endocrine glands.
D. it is the biggest endocrine gland.
42. Over-secretion of thyroxin is likely to lead to
A. thinness of body.
B. sluggishness.
C. cretinism in infants.
D. reduced metabolism.
43. Which of the following glands secretes a substance into the blood stream of a frightened person
A. Adrenal glands.
B. Salivary glands.
C. Gastric glands.
D. Parathyroid glands.
44. The early removal of the pituitary gland in animals may cause
A. cessation of growth.
B. gigantism.
C. poor mental development.
D. goitre.
45. A high concentration of auxin in the root will
A. inhibit growth.
B. stimulate growth.
C. not affect growth.
D. cause the root to rot.
46. The body temperature of a mammal has to be maintained at a fairly constant level because
A. excessive heat is continually lost by the body to the environment.
B. their body temperature is always higher than that of the environment.
C. evaporation of sweat cools the body.
D. metabolic activities function best at certain temperature.
47. Which hormonal deficiency is likely to cause an accumulation of reducing sugar in the urine?
A. thyroxine.
B. insulin.
C. secretin.
D. testosterone.
48. An organism which maintains a constant temperature irrespective of environmental temperature fluctuation is
A. an insect.
B. a mammal.
C. an amphibian.
D. a fish.
49. The hormone that promotes secondary sexual characteristics in females is
A. insulin.
B. thyroxin.
C. testosterone.
D. oestrogen.
50. Which of the following processes occurs when the body temperature of a mammal rises above the
normal? I. The arterioles in the skin dilate II. Sweat production is reduced III. The erector muscles contract.
A. I only.
B. II only.
C. I and Ill only.
D. II and Ill only.
51. The following functions are associated with the liver except
A. regulation of blood sugar.
B. production of heat
C. production of fibrinogen
D. production of vitamin D
52. The pancreatic duct opens into the
A. caecum.
B. colon.
C. ileum.
D. duodenum.
53. The control of water and salt requirements of the body in order to maintain a stable internal ROSHT
Bid environment is known as
A. osmosis.
B. excretion.
C. plasmolysis.
D. homeostasis.
54. Which of the following is the function of the hormone in the Islets of Langerhans? It
A. is used in protein metabolism.
B. is involved in sugar synthesis.
C. aids the rate at which glucose is converted to glycogen.
D. controls the fluid content of the body.
55. Which of the following endocrine glands is a master gland?
A. Pituitary gland.
B. Thyroid gland.
C. Pancreas.
D. Ovary.
56. The endocrine gland secreting hormone that induces the thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine is
A. islets of Langerhans.
B. adrenal gland.
C. pituitary gland.
D. parathyroid gland.
57. Which of the following is not a function of insulin?
A. Accelerates the rate at which glucose is converted to glycogen.
B. Promotes the uptake of glucose by tissues.
C. Regulates the amount of glucose in the blood.
D. Stimulates muscles to oxidise glucose.
58. Which of the following diseases results from the deficiency of insulin?
A. Cretinism.
B. Goitre.
C. Beri-beri.
D. Diabetes.
59. lodine is needed by a patient suffering from a malfunctioning of the
A. salivary gland.
B. thyroid gland.
C. adrenal gland.
D. sebaceous gland.
60. The process of maintaining a steady internal environment is known as
A. osmoregulation
B. equilibration.
C. homeostasis.
D. plasmolysis.
61.The properties of endocrine system include the following except
A. Secretion of hormones.
B. Transportation by blood to target organs.
C. Having specific effect.
D. Release of secretions into ducts.
62. Which of the following hormones is suddenly secreted into the bloodstream of a frightened person?
A. Insulin
B. Adrenaline
C. Thyroxine
D. Parathormone
63. The temperature control centre in mammals is located in the
A. skin
B. hypothalamus
C. pituitary gland
D. adrenal gland
The table below shows the effect of hormones I, II, III and IV on some parts of the human body. Where (V) represents effect and (X) represents no effect of hormone on the corresponding part of the body. Study it and answer questions 64 and 65.
| Hormone | Effect on | |||
| Heart | Digestive System | Kidney | Uterus | |
| I | ||||
| II | X | X | X | |
| III | X | X | X | |
| IV | X | X | X | |
64. Which of the following hormones are I, II, III and IV respectively?
A. ADH, Glucagon, Oestrogen, Adrenaline
B. Adrenaline, Glucagon, Oestrogen, ADH
C. Glucagon, ADH, Oestrogen, Adrenaline
D. Adrenaline, ADH, Oestrogen, Glucagon
65. The hormone responsible for anxiety is
A. I.
B. II
C. III.
D. IV
66. The ability of organisms to maintain a constant internal environment is known as
A. diuresis.
B. endosmosis.
C. homeostasis.
D. plasmolysis.
67. Which of the following hormones is wrongly paired with its secretory organ?
A. Insulin and pancreas.
B. Oestrogen and ovary.
C. Oxytocin and hypothalamus.
D. Adrenalin and kidney.
THEORY
1. (a) Name one hormone each involved in:
(i) plant growth
(ii) animal growth.
(b) State the effects of the hormones named in (a) above
2. State five functions of the pituitary gland,
3. (a) What are hormones?
(b) In a tabular form, state four differences between nervous coordination and hormonal
coordination in humans.
(c) State three effects each of:
(i) Over-secretion;
(ii) Under-secretion of thyroxin on mammals.
4. (a) A student suddenly stepped on a big snake, he cried for help and ran away, name the hormone produced in the body for the reaction.
(b) In which part of the human body is the hormone named in (a) produced?
(c) State five changes that must have taken place as a result of the hormone named in (a).
5. Name one appropriate hormone each responsible for the following conditions in plants:
(i) ripening of fruits;
(ii) breaking dormancy in seeds;
(iii) weed control;
(iv) leaf fall.
6. Explain briefly how the level of sugar in the mammalian blood can be regulated
7. Copy and complete the table below on endocrine glands and their functions.
| S/N | Endocrine Gland | Hormone Production | Function |
| 1 | Thyroid | ||
| 2 | Insulin | ||
| 3 | Development of secondary sexual characters of females |
8. (a) Describe an experiment to demonstrate the influence of auxins on the growth of plant shoot (b) List three uses of auxins in agriculture
9. (a) State three functions each of
(i) insulin
(ii) auxin.
10. (a) Describe an experiment to demonstrate the effect of auxin on growth of a plant shoot
(b) List three uses of auxin in agriculture.
11. (a) Define the term hormone
(b)(i) Name one plant hormone
(ii) State two effects of plant hormones.
12. State five processes by which the mammalian body reduces its temperature.
13. (a) Describe an experiment to show that auxins are produced in the apical cells of a shoot.
(b) Name two plant hormones, other than auxins.
14. Describe the role of pancreatic juice in the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins in à mammal
15. (a) What is a hormone?
(b) Outline the role played by adrenaline in an emergency situation
(c)(i) In a tabular form, list five differences between hormonal co-ordination and nervous co-ordination
(ii) Name three animal hormones and two plant hormones.
16. Describe the process of osmoregulation in
(i) a named unicellular organism
(ii) man.



