OBJECTIVES
1. When fertilization occurs that leads to formation of a zygote, which of the following processes takes place?
A. The tail of the sperm fuses with the egg cell. B. Both tail and head of the sperm fuse with the egg cell. C. The nucleus of the sperm fuses with the egg cell. D. The egg cell develops on its own without the sperm.
2.An illustration of a human male reproductive system is shown below. Which of the labelled parts can be cut to ensure permanent sterility?

A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
3.In which of the following organisms is parental care manifested?
A. Tilapia. B. Toad. C. Cockroach. D. Snail.
4. Which of the following statements about the development of the foetus is not correct?
A. The circulatory system of the foetus is directly connected to the maternal blood vessels. B. The foetus depends on the mother’s blood for its food and oxygen. C. The foetus is surrounded by a water sac. D. Food and oxygen are carried across the placenta to the embryo’s blood.
5. Which of the following pairs of cells carry out the same function?
A. Cheek cell and red blood cell. B. Spermatozoa and ovum. C. Palisade cell and epidermal cell. D. Root tip cell and guard cell.
Use Diagram for questions 6 and 7

6. The function of the part labeled II is to
A. fuse with the ovum during fertilization. B. generate the energy for the sperm to swim to the fallopian tube. C. help the sperm to swim forward. D. dissolve the membrane of the egg during fertilization.
7. The part labelled I is the
A. acrosome. B. nucleus. C. mitochondrion. D. tail.
8. The testes in male mammals descend into the scrotal sac because
A. there is congestion in the lower abdomen. B. they run the risk of being destroyed. C. they need special support. D. they require a relatively low temperature.
9. The following substances pass into the blood of the foetus from the mother’s blood via the placenta except
A. carbon dioxide. B. glucose. C. viruses. D. antibodies.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 10 & 11

10. The parts that supply food and water to the developing embryo are labeled
A. I and II. B. III and V. C. V and VI. D. II and III.
11. The part labelled III is the
A. albumen. B. chalaza. C. yolk. D. airspace.
The above is the drawing of a mammalian spermatozoon. Use it to answer questions 12 to 14

12. Which of the labelled structures is the nucleus?
A. 1. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
13. Which of the following labelled structures secretes enzymes which facilitate penetration of the egg?
A. I B. II. C. III. D. V.
14. Which of the following labelled structures is similar to the locomotory structure In Euglena?
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. V.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 15 and 16.
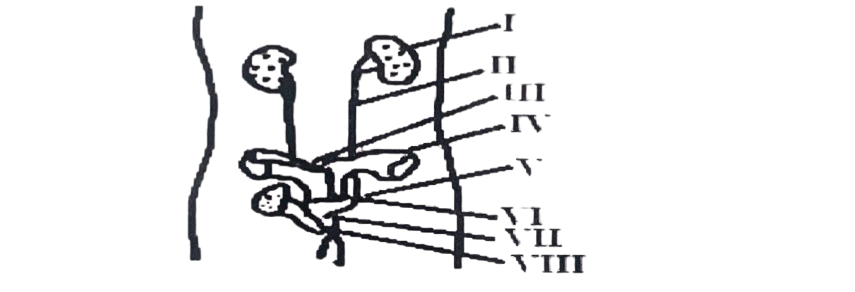
15. The structures labelled III, VI, IV and II respectively represent the
A. uterus, cervix, oviduct and ureter. B. cervix, oviduct, uterus and ureter. C. oviduct, uterus, ureter and cervix. D. vagina, cervix, oviduct and uterus.
16. The gamete is produced in the structure labeled
A. I. B. II. C. IV. D. V.
17. What is the difference between viviparous and oviparous animals?
A. Possession of yolked egg. B. Laying of unfertilized egg. C.. Possession of yolkless eggs. D. Laying and brooding of eggs.
18. The structure of the embryo which develops and makes contact with the uterine wall is known as the
A. umbilical cord. B. placenta. C. allantois. D. amnion.
19. Which of the following is not part of the female reproductive system?
A. Ovary. B. Seminal vesicle. C. Uterus. D. Vagina.
20. Which of the following substances from the mother’s blood diffuse through the placenta into the blood vessels of the foetus?
A. Carbon dioxide and oxygen. B. Glycogen and starch. C. Urea and carbon dioxide. D. Glucose and oxygen.
21. Which of the following describes an example of the fertilization in higher organisms
A. Fusion of sperm and egg nuclei. B. Ejaculating of sperm into a female body. C. Ejaculating of sperm into a female body. D. A pollen grain landing on a sticky stigma.
22. The correct route through which the ovum passes from the ovary to the vagina is
A. ovary cervix → fallopian tube fallopian funnel vagina. B. ovary fallopian funnel uterus cervix → vagina. C. ovary fallopian tube cervix uterus vagina. D. ovary → cervix uterus fallopian tube vagina.
23. The series of activities preceding mating of the male and female animals is generally known as
A. conjugation. B. pairing. C. courtship. D. nuptial flight.
24. Which of the following mammalian features acts as a shock-absorber to the developing embryo?
A. Amniotic fluid. B. Umbilical cord. C. Placenta. D. Amnion.
25. In mammals fertilization usually occurs in the
A. cervis. B. vagina. C. uterus. D. oviduct.
26. Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis are both terms used to describe
A. mitosis. B. meiosis. C. mating. D. gametogenesis.
27. The function of the amniotic fluid in humans is to
A. protect the foetus against shocks. B. remove waste products from the foetus. C. supply food and water to foetus. D. carry oxygen to the foetus.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 28-31

28. The structure labelled I is the
A. oviduct. B. ovary. C. uterus. D. funnel.
29. In which of the labelled structures does implantation take place?
A. I. B. II. C. IV. D. VI.
30. Which of the following indicates the direction of the movement of a sperm introduced into the female reproductive system?
A. III > II > I > IV. B. VI > V > IV > I. C. V > IV > I > II. D. VI > IV > I > II.
31. Which of the labelled parts is responsible for the release of ripe ovum?
A. VI. B. Ill. C. II. D. I.
32. The main function of the amniotic fluid is for
A. respiration in the foetus. B. protection of the foetus from shock. C. lubricating the birth canal. D. nourishing the foetus.
The diagrams below are illustrations of two different cells involved in a biological process in mammals. Study them and answer questions 33 to 35.

33. Which parts of P and Q fuse to complete the biological process?
A. Ill and I B. IV and I C. III and II D. IV and II.
34. Which of the following statements about P and Q is correct?
A. Both cells are structures for asexual reproduction B. Both cells normally belong to the same individual C. Both cells are found in plants D. The union of both cells gives rise to a new mammal.
35. If the number of chromosomes in the skin cells of mammals is 46, how many chromosomes would be found in P and Q respectively?
A. 23 and 23 B. 23 and 46 C. 46 and 23 D. 46 and 46.
THEORY
1. Make a drawing 8 to 10cm long of the reproductive system of a human female and label fully.
2. (a) Name two organs associated with the human placenta. (b) Write short notes on the viviparity.
3. (a) What is placentation? (b) State five functions of the human placenta.
4. (a) Explain briefly how the Sperm cell relate to its functions (b) Make a drawing, 8 cm – 10 cm long of the front view of the female reproductive system in humans and label fully. (c) State two difference between reproduction in mammals and in amphibians.
5. Describe briefly the female reproductive system of a named mammal (A diagram is essential) (b) List three differences between reproduction in mammals and in amphibian.
6. Explain briefly the importance of meiosis and fertilization in the reproduction of organisms.
7. (a) Make a labelled diagram of the female reproductive organ of a mammal (man) (b) State the functions of any two of the labelled parts in (a) above (c) Compare reproduction in mammals, amphibians and birds with respect to (i) number of eggs produced (ii) method of fertilization; (iii) parential care.
8. Draw and label the human sperm cell, (b) State where the sperm cell is produced and where it is stored, (c) Explain how the structure of the sperm cell enables it to function effectively in fertilization.
9. State five functions of the placenta and four functions of the umbilical cord of a mammal.
10. Explain the importance of the amniotic sac to the mammalian embryo.
11. Make a large, labelled diagram 8-10 cm long of the human spermatozoon to show its structure (b) State one function each of any three organelles found in the spermatozoon.
12. (a) Explain briefly the following types of fertilization in animals: (i) external fertilization; (ii) internal fertilization. (b) Name two groups of animals each that exhibit the types of fertilization in 6 (a): (i) external fertilization; (ii) internal fertilization. (c) (i) If the placenta in a pregnant woman is detached from the uterine wall, give three effects this would have on the foetus. (ii) Name three other features present in the uterus of a pregnant woman that are useful for the development of the foetus.
13. (a) State one similarity between the eggs of toads and the eggs. (b) State three differences between the eggs of toads and the eggs of birds.



