OBJECTIVES
1. The function of the convex lens in the correction of eye defects is to
A. diverge light rays from far objects to focus image on the retina.
B. converge light rays to focus Image behind the retina.
C. converge light rays to focus the image before the retina.
D. converge light rays from far objects to focus their image on the retina.
2. Which of the following parts of the eye contains light sensitive cells?
A. Choroid.
B. Iris.
C. Retina.
D. tens.
3. The hair on the human skin will stand erect when the person is
A. In an air-conditioned room.
B. strolling in the sun.
C. taking a hot drink.
D. doing strenuous exercise.
4. Ability of the human eye to focus images accurately on the retina is called
A. astigmatism.
B. myopia.
C. adjustment.
D. accommodation.
5. The eyes can properly focus images of objects or various distances on the retina by a process called
A. refraction.
B. reflection.
C. accommodation.
D. correction.
6. Spectacles with convex lenses correct long-sightedness by
A. converging the light rays before they enter the eye.
B. diverging the light rays before they enter the eye.
C. reducing light intensity before it enters the eye.
D. Increasing tight intensity before it enters the eye.
7. Which of the following parts of the ear does not contain endolymph?
A. Semi-circular canals.
B. Utriculus.
C. Tympanum.
D. Sacculus.
8. The ear pinna is strengthened by
A. blood pressure.
B. cartilage.
C. bone.
D. turgor pressure.
9. The relationship between the retina and the brain is similar to that between the
A. cochlea and the auditory nerve.
B. cochlea and the brain.
C. cochlea and the semi-circular canals.
D. eardrum and the brain.
10. When viewing an object that is close to the human eye, the
A. eye lens becomes thin.
B. the cilliary muscles contract and become thicker and fat.
C. suspensory ligaments become taut.
D. eye lens become fat.
11. Which of the following is an effector organ?
A. Tongue.
B. Skin.
C. Nose bridge.
D. Ear glands.
12. Which of the following practices may lead to infection of the eye? Use of
A. contact lenses.
B. convex lenses.
C. blconcave lenses.
D. concave lenses.
13. Which of the following sensations may not be detected by the skin?
A. Touch.
B. Pressure.
C. Stress.
D. Pain.
Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows

14.The diagram above is an illustration of
A. normal sight,
B. short sightedness.
C. correction of long sightedness,
D. correction of short sightedness.
15. The most sensitive part of the retina is called
A. blindspot.
B. conjuctiva.
C. fovea centralis.
D. choroid coat.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 16 and 17

16. Which type of eye defect is illustrated in the diagram above?
A. Hypermetropia.
B. Myopia.
C. Cataract.
D. Astigmatism.
17. This defect can be corrected by the use of
A. convex lens.
B. concave lens.
C. cylindrical lens.
D. surgical operation.
18. Which of the following stimuli are not perceived through the skin of mammals?
A. Light.
B. Pressure.
C. Pain.
D. Heat.
19. Which of the following parts of the tongue does not correspond to the taste Indicated against it?
A. Tip-sweet.
B. Centre-salt.
C. Back-sour.
D. Side-sour.
20. Which of the following best explains why it is difficult to see clearly in dim light
A. Initially the eyes cannot operate when the light is dim.
B. The choroid reflect all the light that enters the eye.
C. Too little light reaches the retina and so the cones may not be stimulated at all.
D. Dim light causes the pupil to close up so that not much light enters the eye.
21. The structure of the ear that is responsible for balancing is the
A. semi-circular canals.
B. pinna.
C. auditory nerve.
D. fenestra ovalis.
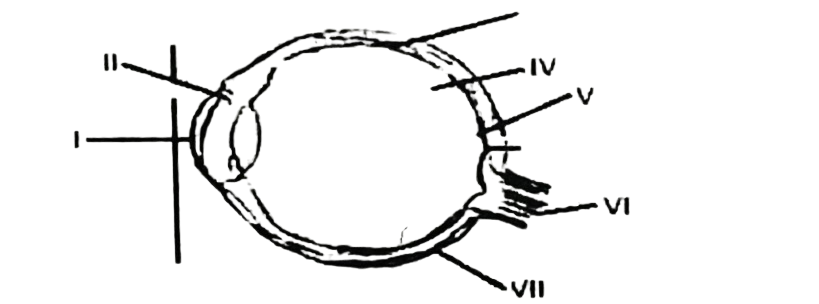
Use the diagram below to answer questions 22-24.

22. The parts labelled IV, V and VI respectively are the
A. ciliary body, optic nerve and yellow spot.
B. blind spòt, optic nerve and suspensory ligament.
C. vitreous humour, yellow spot and optic nerve.
D. blind spot, optic nerve and pupil.
23. The light ray entering the eye goes through the – following route
A. II, III, I, IV, V.
B. II, I, VII, III, V.
C. II, I, III, IV, V.
D. V, IV, III, I, II.
24. Which of the following structures are adjusted in focusing the image of a distant or near object on the retina?
A. I and II.
B. II and III.
C. Ill and VII.
D. IV and V.
25. When a person moves from a darkroom into bright light, the pupil becomes
A. red.
B. larger.
C. white.
D. smaller.
26. The pigment in the malphigian layer responsible for skin coloration is known as
A. haemoglobin
B. haemocyanin.
C. chlorocruorin.
D. melanin.
27. Which of the following parts of the eye is sensitive to light?
A. Retina.
B. Cornea.
C. Choroid layer.
D. Optic nerves.
D. ampulla.
28. The human skin is regarded as a sense organ because it
A. separates the body from the outside world.
B. protects the body from cold and heat.
C. regulates the water content of the body.
D. has nerve endings.
29. Which part of the ear is responsible for the brig maintenance of balance?
A. Ossicles.
B. Tympanicos) membrane.
C. Eustachian tube,
D. Semicircular bio canals
Use the diagram below to answer questions 30 and 31.
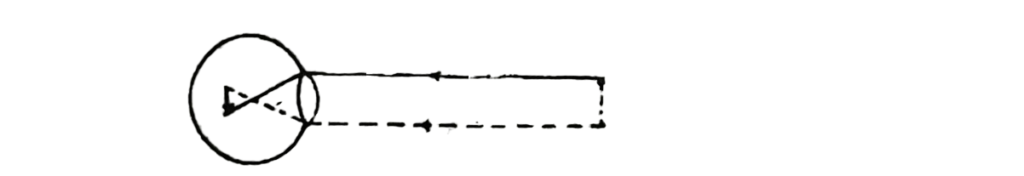
30. The eye defect represented in the diagram is
A. myopia.
B. hypermetropia:
C. presbyopia.
D. astigmatism.
31. The above defect is corrected by using a
A. concave lens.
B. converging lens.
C. cylindrical lens.
D. bi-focal lens.
32. The mammalian skin can insulate the body from cold because it has
A. epidermal cell.
B. nerve endings.
C. the subcutaneous fatty layer.
D. sebaceous glands.
33. Which of the following parts of the tongue is sensitive to sugar
A. Tip.
B. Back.
C. Right side.
D. Left side
34. The organ which is sensitive to smell in a cockroach is the
A. nostril.
B. pedipalp.
C. antenna.
D. mandible
35. Which of the following is the most sensitive spot of the retina?
A. Conjuctiva.
B. Cornea.
C. Lens.
D. Yellow spot.
36. The epidermis of the mammalian skin is an example of a tissue because the cells
A. prevent light from passing through them.
B. have a similar structure and function.
C. prevent excessive loss of water.
D. arrest impregnated with keratin.
37. Which of the following occurs when a person looks at a distant, dim object and then looks at a much closer, bright object? In each eye, the pupil becomes
A. larger, while the lens becomes thicker.
B. larger, while the lens becomes thinner.
C. smaller, while the lens becomes thicker.
D. smaller, while the lens becomes thinner.
38. The ability of the eye to alter the focal length of the lens, with regard to the distance of the object from the eye is known as
A. binocular vision.
B. nocturnal vision.
C. distortion.
D. accommodation.
39. The part of the ear in mammals responsible for the detection of sound is the
A. utriculus.
B. tympanum.
C. cochlea.
D. semi-circular canal.
40. If the mucus in the air track of mammals dry up and the hairs in the nostrils are removed
A. air would be breathed into their lungs.
B. the speed of air movement into their lungs would increase.
C. breathing air into their lungs would be difficult.
D. more air would be taken into their lungs.
41. The part of the ear which equalises air pressure on either side of the eardrum is the
A. auditory meatus.
B. malleus.
C. eustachian tube.
D. oval window.
42. Short-sight could be corrected with the use of
A. convex lens.
B. cylindrical lens.
C. concave lens.
D. bifocal lens.
43. Which pair of structures contributes to balance in mammals?
A. Útriculus and Sacculus.
B. Malleus and Stapes.
C. Sacculus and cochlea.
D. Utriculus and pinna.
44. In cold condition, the mammalian body reacts in the following ways except
A. shivering of the body.
B. dilation of the capillaries supplying blood to the skin.
C. constriction of blood capillaries in the skin.
D. increased rate of chemical Changes in the body.
45. The layer of light-sensitive cells in the human eye is called the
A. cornea.
B. sclerotic layer.
C. retina.
D. conjunctiva.
46. Which of the following is the function of the iris of the mammalian eye?
A. Closes and opens the eye.
B. Absorbs dangerous rays from sunlight.
C. Regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
D. Bringing light rays to focus on the retina.
47. A person who fails to detect the bitter taste of a substance swallowed, is more likely to have
A. dead a taste buds on the tongue.
B. avoided the substance from contacting the back of his/her tongue.
C. fewer taste buds on the tongue.
D. swallowed the substance without any water.
48. Which of the following statements is false?
A. Human sense of smell is easily fatigued.
B. The skin can perceive the sensations of touch, pain, pressure and temperature.
C. Taste buds and olfactory cells are active when wet as well as when dry.
D. Sensory nerve endings receive stimuli and send to the central nervous system.
Use the diagram below to answer questions 51 to 53.
50. The light-sensitive layer is labelled
A. I.
B. III.
C. IV.
D. VII.
51. The greatest concentration of light receptors is found in the part labelled
A. VI.
B. V.
C. IV.
D. III.
52. The aqueous humour is represented by the part labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. VI.
53. Which of the following statements about short sight is not correct?
A. The eyeball is too short.
B. The cornea of the eyeball is too curved.
C. The images fall in front of the retina.
D. It can be corrected by using concave lenses.
54. Hypermetropia is corrected by the use of
A. concave lenses.
B. convex lenses.
C. cylindrical lenses.
D. contact lenses.
55. The groups of sensory cells found on the upper surface of the tongue are called
A. ampullae.
B. taste buds.
C. nerve cells.
D. somatic cells.
56. To focus on a distant object, the ciliary muscle of the eye
A. contracts and the eye lens gets thicker.
B. relaxes and the eye lens gets thinner.
C. contracts and the eye lens gets thinner.
D. relaxes and the eye lens gets thicker.
57. What happens when the ciliary muscles of the eye contract? The
A. Lens becomes more concave.
B. Lens becomes more convex.
C. Lens gets a longer focal length.
D. Suspensory ligament becomes tight.
The diagram below is illustration of a type of eye defect in humans. Study it and answer question 58 and 59.
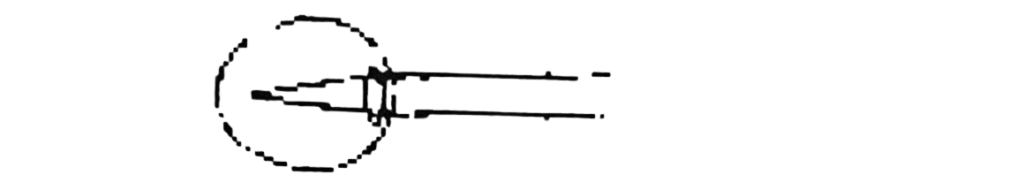
58. The eye defect illustrated in the diagram is
A. hypermetropia.
B. astigmatism.
C. presbyopia
D. myopia
59. The eye defect can be corrected by the use of
A. convex lens.
B. concave lens.
C. bifocal lens.
D. cylindrical lens.
The diagram below is an illustration of some parts of a mammalian ear.
Study it and answer questions 60 to 62.

60. The parts labelled I are the
A. semicircular canals.
B. ossicles.
C. cochlea.
D. external auditory meatus.
61. Which of the parts are correctly grouped?
| Inner Ear | Middle Ear | Outer Ear | |
| A | I, IV | III | II |
| B | III | II, IV | I |
| C | I | II | III, IV |
| D | II | I, III | IV |
62. The middle ear is connected to the pharynx by the part labelled
A. I.
B. II.
C. III
D. IV.
63. The eye defect caused by an uneven curvature of the cornea or lens or both is
A. myopia.
B. astigmatism.
C. presbyopia.
D. hypermetropia.
THEORY
(a) What is a sense organ?
(b) List four sense organs found in mammals.
Explain how bitter taste is detected in humans.
(a) State three ways of caring for the mammalian skin.
(b) List three stimuli to which the mammalian skin is sensitive.
(a) Explain briefly: the process of perceiving smell in humans.
(b) State five differences between the skin of a mammal and the epidermis of a leaf.
(a) Make a labelled diagram to show the internal structure of the mammalian ear
(b) Describe the mechanism of hearing in mammals
(c) State two ways of caring for the ear.
(a) List the principal sense organs in mammals and their functions
(b)(i) Describe the eye defect in which, only distant objects are seen clearly
(ii) How can it be corrected? Illustrate your answer with labelled diagrams
(c) Make a large labelled diagram of the vertical section through the mammalian skin.
(a) What is sensory cell?
(b) State one function each of the following parts of the mammalian eye:
(i) lens
(ii) vitreous humour
(c)(i) List four structures which protect the eye from injury
(ii) Explain briefly how each of these structures performs its function
(d) Explain why a person in a dark room is dazzled for some seconds when he is suddenly
exposed to bright sunlight.
Describe how the mammalian skin can react to regulate the body temperature in a hot room.
(a) What is a sense organ?
(b)(i) State two main functions of the ear
(ii) Explain the mechanism involved in one of the functions stated above
(c) With the aid of a large labelled diagram illustrate the eye defect of short-sight and its
correction.
(a) What is a receptor?
(b) Describe the general features common to all receptors
(c) Make a labelled diagram 8 cm – 10 cm long, to show the outer and middle ear only of human.
(d) List three ways of caring for the ear.
(a) State three effects of lack of sense receptors in the skin to humans
(b) List three layers of the epidermis in the skin to humans.
(a) Explain briefly how the human ear carries out its function of balancing.
(b) (i) Make a drawing, 8 cm – 10 cm long of the structure of the human ear and label fully.
(ii) Describe briefly the structure of the middle ear in humans.
(a) What are sense organs?
(b) Name three sense organs that respond to the stimulus of chemicals.



