OBJECTIVES
1. The pulmonary circulation involves movement of the blood to and from the
A. brain. B. kidneys. C. liver. D. lungs.
The table below shows the blood composition of four individuals. Use the Information contained in the table to answer questions 2 & 3
| Individual | Blood Composition | |||
| Plasma | Red Blood Cells | White Blood Cells | Platelets | |
| I | Normal | Normal | High | Normal |
| II | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| III | Normal | Normal | Low | Normal |
| IV | Normal | Normal | Normal | Low |
2. Which of the individuals is likely to be suffering from haemophilia?
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
3. Which of the individuals is likely to have HIV?
A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV.
4. Carbon dioxide is carried in the plasma
A. in combination with hemoglobin. B. in combination with antibodies. C. by capillary action. D. as bicarbonate ion
5. Blood pressure is higher in the arteries as a result of
A. stress. B. contraction and relaxation. C. blockage in the arteries. D. presence of valves.
6. Which of the following statements is true about the ABO blood group system?
A. Antigens are located on. the surface of white blood cells. B. Antibodies are located in the blood plasma. C. Antibodies are located on the surface of red blood cells. D. Antigens are located in the blood plasma.
7. Which of the following statements is not correct about the mammalian heart?
A. Oxygenated blood enters the left auricle from the pulmonary vein. B. The walls of the ventricle are thicker than those of the auricle. C. Blood passes from the right ventricle to the left auricle through the aorta. D. The tricuspid valve prevents the back flow of blood into the right auricle.
8. Red blood cells were found to have burst open after being placed in distilled water for an hour. This phenomenon is known as
A. plasmolysis. B. diffusion. C. haemolysis. D. wilting.
9. The reason why the flow of blood through the capillaries is very slow is
A. because the walls of capillaries are very thin. B. to avoid high blood pressure. C. to ensure that the individual does not get dizzy. D. to allow adequate time for exchange of materials.
10. Which of these statements about white blood cells is true? They
A. aid clotting of blood. B. carry oxygen round the body. C. are the most numerous blood cells. D. are large nucleated cells.
11. Which of the following blood vessels have valves?
A. Capillary. B. Artery. C. Vein. D. Arteriole.
12. A pulse is best described as
A. contraction of arteries to let out blood. B. contraction of veins to allow blood into them. C. dilation of arteries to accommodate blood rushing through. D. pumping action of the heart to move blood round the body.
13. The organ that receives reduced flow of blood during vigorous exercise is the
A. brain. B. heart. C. lung. D. limb.
14. Which of the following statements best describes hemoglobin?
A. yellowish in colour. B. a red blood cell. C. an oxygen carrying pigment. D. needed for blood clothing.
15. Older parts of plant roots do not normally absorb water because
A. they lack xylem. B. they have small surface area. C. the phloem is dead. D. they lack root hairs.
16. Conduction of water and mineral salts through the xylem vessels is enhanced because the xylem cells are
A. thickened with lignin. B. long, narrow tubes placed end to end. C. close to the endodermis. D. centrally placed in the roots.
17. Which of the following factors is likely to increase the rate of transpiration in plants? A.
A reduction in the number of stomata per unit surface area. B. Increase in humidity around the leaves of plants. C. An increase in leaf surface area to volume ratio. D. Removal of leaves front plant.
18. Which of the following treatments would increase the rate of transpiration in a potted plant?
A. Placing it in a cold room. B. Placing it under a fan in a room. C. Putting it in a cupboard. D. Smearing grease on the lower surface of the leaves.
19. Which of the following statements is true about transpiration? It is the
A. loss of water in the form of vapour from the surface of the leaf. B. loss of water in the form of vapour from the surface of the root. C. absorption of water in the form of vapour from the body of the plant. D. movement of water through the body of the plant.
20. Transportation of water in the xylem tissue involves the following except
A. root pressure. B. capillary action. C. transpiration pull. D. translocation.
21. The following processes are involved in water movement in the endodermis except
A. Osmosis. B. vacuolar pathway. C. diffusion. D. active transport.
22. The ascent of water in tall trees is mainly due to
A. adhesive forces. B. transpiration pull. C. root pressure. D. cohesive forces.
23. Which of the following features is not characteristic of arteries? Arteries
A. possess valves at intervals throughout their length. B. have thick, muscular and elastic walls. C. carry blood away from the heart. D. transport oxygenated blood with the exception of the pulmonary artery.
24. A seedling was made to stand in a solution of red ink for three hours and a transverse section of the stem as examined under the microscope. The process being investigated was
A. the importance of micro elements to plants. B. ascent of water through the xylem. C. diffusion of coloured substances. D. distribution of food in plants.
25. Which of the following is the medium of transportation of nutrients within unicellular organisms?
A. Blood. B. Serum. C. Protoplasm. D. Plasma.
26. Which of the following blood vessels carries oxygenated blood into the heart?
A. Pulmonary vein. B. Anterior vena cava. C. Pulmonary artery. D. Aorta.
27. In unicellular organisms, essential nutrients can be transported directly to all parts of their body by the process of diffusion only because unicellular organisms have
A. a large surface area to volume ratio. B. a large volume to surface area ratio. C. permeable cell membrane. D. outer membrane made of cellulose.
28. Which of the following is more concentrated in the blood within the renal artery than the blood within the renal vein?
A. Urea. B. Red blood cells. C. Glucose. D. Protein.
29. Which of the following statements about the lymphatic system is not correct?
A. The lymph vessels are always larger in size than the arteries. B. The flow of lymph is assisted by general muscular movement. C. Lymph flows only in one direction due to the presence of valves. D. Lymph is emptied into the blood circulatory system through a vein.
In an experiment to study the rate of water loss in plants, leaves of a potted plant were treated as follows: 1. Upper surface covered with vaseline II. Lower surface covered with vaseline III. Both surfaces covered with vaseline IV. None of the leaf surfaces covered,
30. Indicate in a descending order, the rate of water loss from the leaves
A. I, II, III and IV. B. II, I, III and IV. C. III, Il , I and IV. D. IV, I, II and III.
31. The increase in width of blood vessels in the mammalian skin at high temperatures is known as
A. vasolidation. B. sweating. C. vasoconstriction. D. shivering.
32. The function of the red blood cells is to
A. engulf invading bacteria. B. aid in protein formation. C. transport oxygen to the cells. D. control blood glucose level.
33. The bicuspid valve is located between the
A. left auricle and left ventricle. B. aorta and the left ventricle. C. superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. D. right auricle and the superior vena cava.
34. In which of the following processes in mammals is liquid passed from blood capillaries to Bowman’s capsule?
A. Filtration. B. Diffusion. C. Osmosis. D. Reabsorption.
35. The pulmonary artery carries
A. deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. B. oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. C. oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the right auricle. D. deoxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the right auricle.
36. Which of the following blood components has the greatest affinity for oxygen and carbon dioxide?
A. Blood plasma. B. Leucocytes. C. Thrombocytes. D. Erythrocytes.
37. Thrombocytes are blood cells responsible for initiating
A. phagocytosis of bacteria. B. synthesis of ribosomes. C. clotting of the blood. D. immunity to certain infectious diseases.
38. The bicuspid valve is located between
A. left auricle and left ventricle. B. right auricle and right ventricle. C. left and right ventricles. D. left and right auricles.
39. Which of the following adapts the aorta to the high pressure of the blood from the heart?
A. Thin walls. B. Fragile membrane. C. Thick elastic walls. D. Stiff walls.
40. Filtered blood from the kidney is carried back to the circulatory system through the
A. hepatic portal vein. B. renal artery. C. renal vein. D. pulmonary vein.
41. The two important physical processes involved in the absorption and transport of materials in plants are
A. diffusion and plasmolysis. B. cohesion and diffusion. C. flaccidity and turgidity. D. osmosis and diffusion.
42. Which of the following explains the need for transport system in large mammals?
A. The area to volume ratio in large animals is high. B. The area to volume ratio diminishes with large size. C. Diffusion as an adequate means of transport is lacking. D. Large animal have internal fluid which contains different types of cells.
43. Oxygenated blood from the lungs is carried to the left auricle of the heart through the
A. pulmonary vein. B. pulmonary artery. C. hepatic portal vein. D. renal portal vein.
44. Which of the following is not correct about blood platelets? They
A. are also known as thrombocytes. B. have no nucleus. C. are formed in the red bone marrow. D. neutralize the toxins in the blood.
45. The medium in which dissolved nutrients are transported in the body of vertebrates is called
A. latex. B. urine. C. cell sap. D. blood.
46. The hepatic portal vein is often heavily loaded with food-nutrients because it carries blood
A. directly from the heart. B. from the liver to the heart. C. from the small intestine to the liver. D. from the liver to join the posterior vena cava.
47. The physical process which occurs when a red blood cell is placed in distilled water causing it to burst and break down is known as
A. crenation. B. plasmolysis. C. turgidity. D. haemolysis.
48. A major reason why the red blood cells can survive in the blood is that the
A. blood plasma and the red blood cells are isotonic. B. red blood cells are hypotonic to the plasma. C. the red blood cells are hypertonic to the blood plasma. D. the red blood cells received digested nutrients.
49. Which of the following heart structures is best adapted to cope with double circulation
A. One auricle and one ventricle. B. Two auricles and one ventricle. C. Two auricles and partially divided ventricle. D. Two auricles and two ventricles.
50. Which of these factors does not contribute towards the ascent of water in plants
A. Root pressure. B. Capillarity. C. Transpiration pull. D. Turgor pressure
51. The ventricles of the mammalian heart have thicker muscular walls than the auricles because the
A. ventricles are larger. B. ventricles receive more blood. C. ventricles pump blood to longer distances. D. auricles have smaller capacity.
52. A red blood cell haemolyses when placed in a hypotonic solution because
A. it contains haemoglobin. B. the cytoplasm is less dense. C. the cell lacks a wall. D. its pigment has a high affinity for water.
53. Which of the following is not a function of the blood?
A. Maintenance of body temperature. B. Formation of clot. C. Distribution of bile. D. Transportation of excretory materials.
54. Which of the following statements about the circulation of blood is not correct?
A. Deoxygenated blood flows in the heart through the vena cava. B. Blood is pumped out of the heart through the aorta. C. Oxygenated blood from the lungs is carried to the left auricle. D. Ventricles contract to pump blood into the aorta.
55. A difference between the auricle and the ventricle of the mammalian heart is that the
A. ventricles carry deoxygenated blood. B. ventricles do not have outlets. C. auricles have no valves. D. Walls of the ventricles are more muscular than that of the auricles.
56. Which of the following is not a constituent of blood plasma?
A. Proteins. B. Mineral salts. C. Water. D. Platelets.
57. The process by which plants convey food material to different parts of the body is called
A. nutrition. B. absorption. C. circulation. D. translocation.
58. The pulmonary vein carries
A. oxygenated blood from right ventricle to the lungs. B. oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left auricle. C. deoxygenated blood from the lungs to the right auricle. D. oxygenated blood from the lungs to the right auricle.
59. Blood in mammals transports oxygen because it contains the pigment called
A. haemoglobin. B. chlorocruorin. C. melanin. D. haemocyanin.
60. In which of the following is cilia not associated with movement or transport of materials?
A. Fallopian tube funnel. B. Ectoplasm of paramecium. C. Lining of the mammalian trachea. D. Mammalian alimentary canal.
61. The function of the human red blood cells is to al
A. make antibodies. B. carry oxygen. C. absorb heat. D. destroy bacteria.
62. In man, adult schistosoma is found in the
A. blood vessels of the bladder. B. red blood corpuscles. C. lymphatic vessel. D. blood vessels of the lung.
63. Which of the following constitutes the cellular body components of the mammalian blood? I. Haemoglobin II. Erythrocytes III. Leucocytes IV. Platelets
A. I, II and Ill only. B. I, II and IV only. C. II, III and IV only. D. I, II, III and IV.
64. Which organ removes the largest-quantity of water from the blood?
A. Lung. B. Intestine. C. Kidney. D. Skin.
65. The mineral needed for the formation of haemoglobin is
A. magnesium, B. tron. C. phosphorus. D. calcium.
66. Higher organisms use a transport system and not diffusion only to distribute nutrients because
A. the ratio of their surface area to volume is small. B. metabolic waste products diffuse to the surface of the organisms. C. the rate at which nutrients and other substances diffuse increases. D. substances to be transported move shorter distances to reach the numerous cells.
67. Hormones are transported around the mammalian body by
A. water. B. nerves. C. blood. D. osmosis.
68. The vessel that carries blood from the heart to the lungs is called an artery because it
A. contains oxygenated blood. B. contains more blood than the other vessels. C. carries blood away from the heart. D. has thick inelastic wall.
69. Which of the following is correct about the transverse section of a vein, when compared with that of an artery?
A. The lumen of a vein is wider than that of an artery. B. The endothelium of the vein is thinner than that of an artery. C. There are more smooth muscles in a vein than in an artery. D. There are valves in veins but not in arteries.
70. Which of the following structures transports water from the roots to the leaves?
A. Phloem. B. Cambium. C. Pericycle. D. Xylem.
71. The translocation of food materials in plants takes place in the
A. xylem. B. cambium. C. phloem. D. parenchyma.
72. Root hairs absorb water from the soil by
A. diffusion. B. osmosis. C. plasmolysis. D. translocation.
73. The heart can beat continuously without being fatigued because it is composed of
A. skeletal muscles. B. smooth muscles. C. cardiac muscles. D. renal muscles.
The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up. Study it and answer questions 74 and 75.
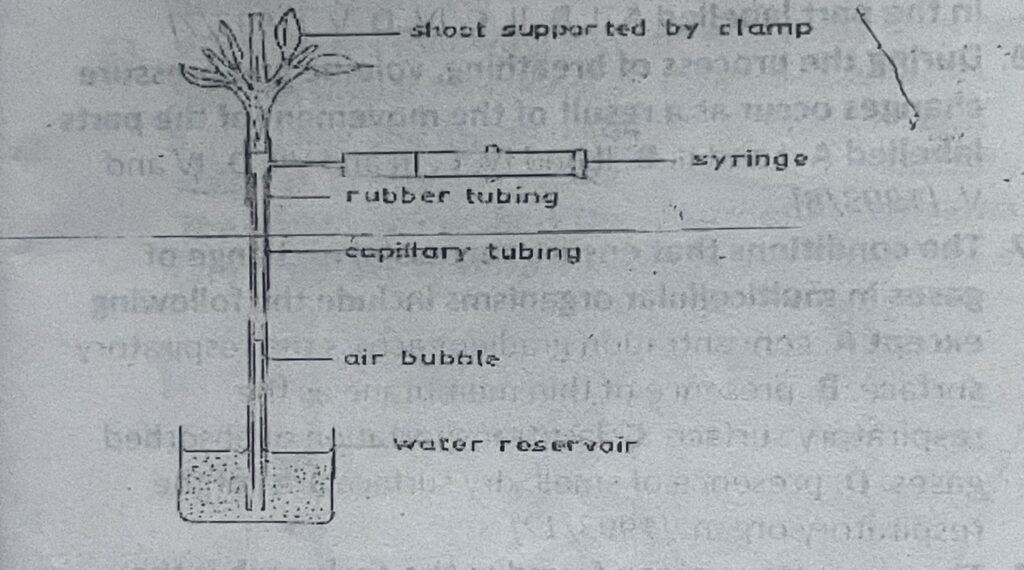
74. The set-up directly measures
A. Transpiration of water from the leaves. B. Evaporation of water from the leaves. C. Absorption of water by the shoot. D. Loss of mineral salts from the leaves.
75. The set-up can measure comparatively the rate of
A. Evaporation from leaves on a single shoot under different experimental conditions. B. Salt uptake by shoots from different plants. C. Transpiration of a single shoot of a plant under different experimental conditions. D. Water uptake by roots of different plants.
76. The blood vessel which carries blood from the alimentary canal to the liver is the
A. hepatic artery. B. hepatic vein. C. hepatic portal D. mesenteric artery.
77. Which of the following blood components has the greatest affinity for oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide?
A. Lymphocyte B. Erythrocyte C. Blood plasma D. Thrombocyte.
78. The tricuspid valve is located between the
A. left auricle and left ventricle: B. right auricle and the superior vena cava. C. aorta and the left ventricle. D. right auricle and right ventricle.
THEORY
1. (a) State the function of each of the following structures: (i) Arteries (ii) Capillaries (iii) Veins (iv) Xylem (v) Phloem. (b) List the cellular components of blood (c) Describe the changes that take place in the composition of human blood as it passes through the (i) Lungs (ii) Liver (iii) Kidneys (iv) small intestine.
2. (a) Explain briefly four factors that affect the diffusion of substances (b) Explain the following terms: (i) active transport (ii) transpiration (c) State four ways by which plants can reduce high rate of transpiration. (d) State the features of red blood cells and how these features adapt the cell to perform its functions.
3. (a) What is translocation? (b) State: (i) three differences (ii) three similarities between the transport systems in flowering plants and mammals.
4. Describe an experiment to show that water is conducted in the xylem tissue of flowering plants.
5. (a) What is transpiration? (b) Name two types of transpiration (c) List four factors which affect the rate of transpiration. (d) Describe the mechanisms of opening and closing of the stomata. (e) State two (i) similarities (ii) differences between transpiration and sweating.
6. Describe an experiment to demonstrate the effect of distilled water on mammalian red blood cell.
7. Explain haemorrhage.
8. (a) Draw and label the mammalian heart. (b) Explain briefly pulmonary circulation in mammals.
9. (a) List the main constituent of mammalian blood (b) State two functions of each constituent (c) Tabulate six differences between arteries and veins (d) Name the main artery which transports blood to the: (i) Lung (ii) Kidney.
10. (a) Write a short note on the importance of the presence of an effective transport system in mammals (b) State eight functions of blood in mammals (c) List four materials transported in the bodies of flowering plants.
11. Describe an experiment to show that the xylem tissue conducts water from the root to the shoot.
12. A sample of human blood was put in a test tube and allowed to spin in a centrifuge. The components of the blood sample were clearly separated. (a) List the four main components of blood that would be in the test tube. (b) Name the component of the blood that: (i) would form the top layer in the test tube; (ii) destroys pathogens; (iii) is biconcave in shape; (iv) would be relatively low in a haemophilic condition; (v) is produced in the bone marrow; (vi) is a thrombocyte; (vii) is nucleated. Mention three chemical substances transported by the blood component named in b (i). (d) List four diseases associated with blood. (e) Explain briefly why a disease of the blood could be dangerous.
13. Explain briefly the following terms: (i) blood transfusion; (ii) antigen.



